Mohsen Malmir
Video Moment Retrieval via Natural Language Queries
Sep 10, 2020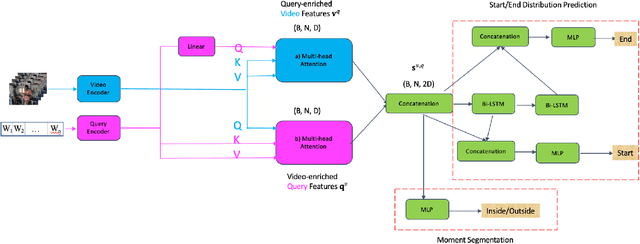
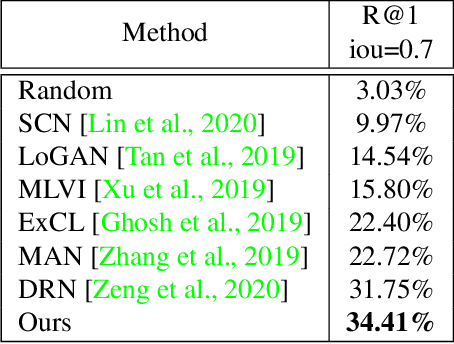
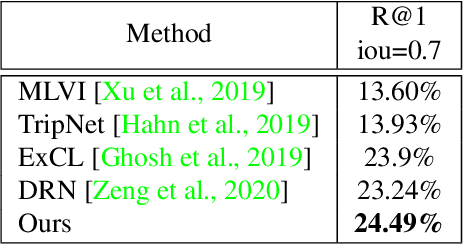
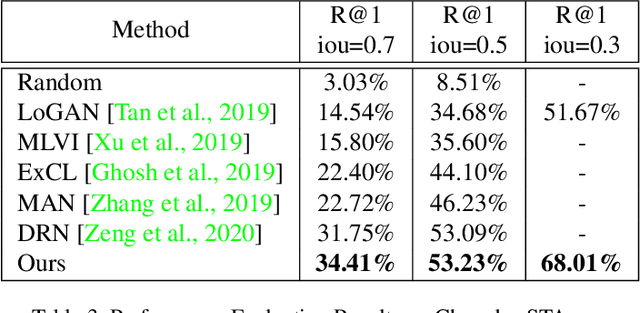
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method for video moment retrieval (VMR) that achieves state of the arts (SOTA) performance on R@1 metrics and surpassing the SOTA on the high IoU metric (R@1, IoU=0.7). First, we propose to use a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and further a cross-attention scheme to capture video/query interaction and long-range query dependencies from video context. The attention-based methods can develop frame-to-query interaction and query-to-frame interaction at arbitrary positions and the multi-head setting ensures the sufficient understanding of complicated dependencies. Our model has a simple architecture, which enables faster training and inference while maintaining . Second, We also propose to use multiple task training objective consists of moment segmentation task, start/end distribution prediction and start/end location regression task. We have verified that start/end prediction are noisy due to annotator disagreement and joint training with moment segmentation task can provide richer information since frames inside the target clip are also utilized as positive training examples. Third, we propose to use an early fusion approach, which achieves better performance at the cost of inference time. However, the inference time will not be a problem for our model since our model has a simple architecture which enables efficient training and inference.
Belief Tree Search for Active Object Recognition
Aug 13, 2017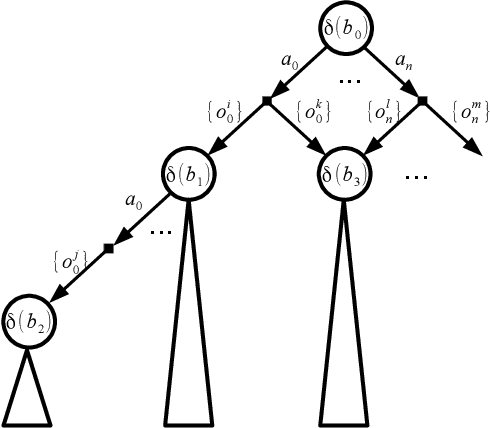
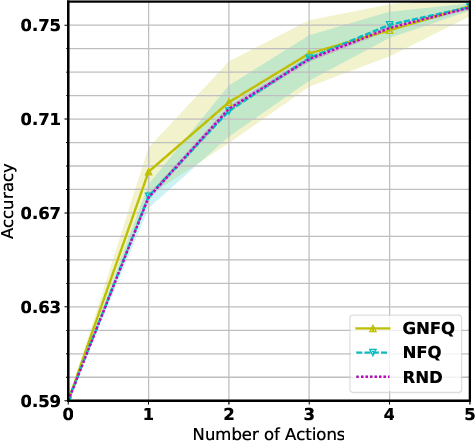
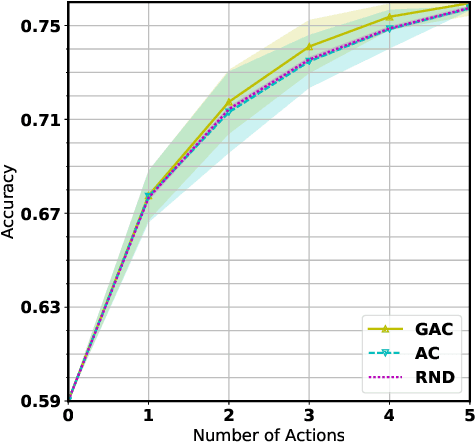
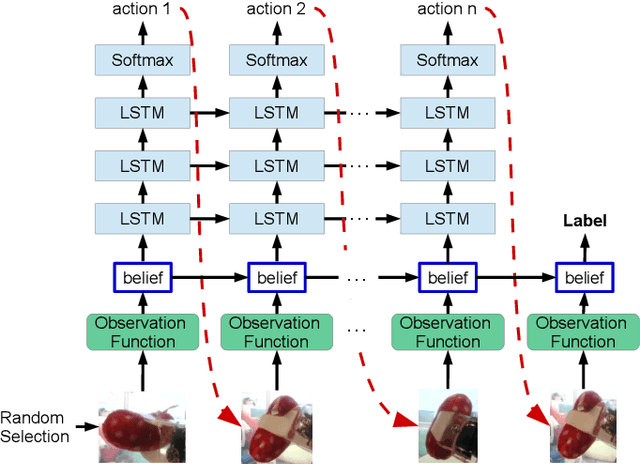
Abstract:Active Object Recognition (AOR) has been approached as an unsupervised learning problem, in which optimal trajectories for object inspection are not known and are to be discovered by reducing label uncertainty measures or training with reinforcement learning. Such approaches have no guarantees of the quality of their solution. In this paper, we treat AOR as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) and find near-optimal policies on training data using Belief Tree Search (BTS) on the corresponding belief Markov Decision Process (MDP). AOR then reduces to the problem of knowledge transfer from near-optimal policies on training set to the test set. We train a Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) network to predict the best next action on the training set rollouts. We sho that the proposed AOR method generalizes well to novel views of familiar objects and also to novel objects. We compare this supervised scheme against guided policy search, and find that the LSTM network reaches higher recognition accuracy compared to the guided policy method. We further look into optimizing the observation function to increase the total collected reward of optimal policy. In AOR, the observation function is known only approximately. We propose a gradient-based method update to this approximate observation function to increase the total reward of any policy. We show that by optimizing the observation function and retraining the supervised LSTM network, the AOR performance on the test set improves significantly.
Deep Active Object Recognition by Joint Label and Action Prediction
Dec 17, 2015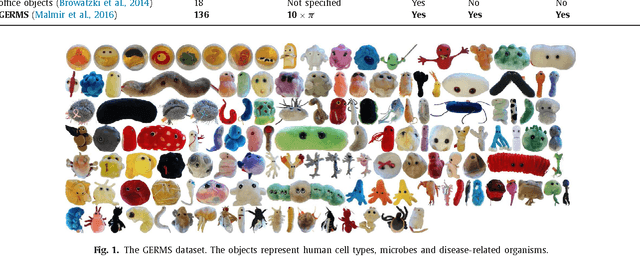
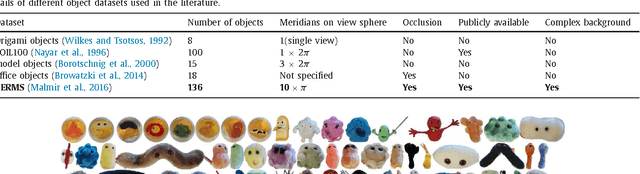
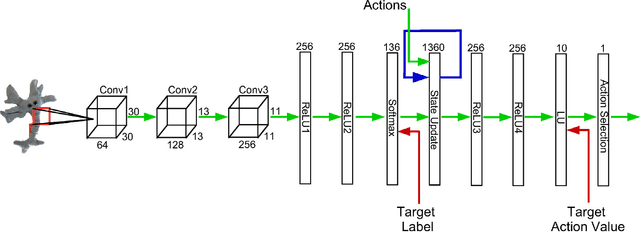
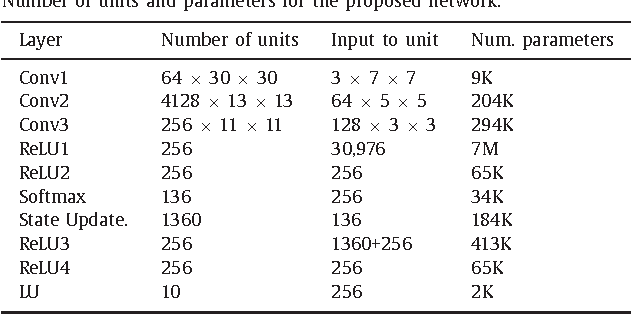
Abstract:An active object recognition system has the advantage of being able to act in the environment to capture images that are more suited for training and that lead to better performance at test time. In this paper, we propose a deep convolutional neural network for active object recognition that simultaneously predicts the object label, and selects the next action to perform on the object with the aim of improving recognition performance. We treat active object recognition as a reinforcement learning problem and derive the cost function to train the network for joint prediction of the object label and the action. A generative model of object similarities based on the Dirichlet distribution is proposed and embedded in the network for encoding the state of the system. The training is carried out by simultaneously minimizing the label and action prediction errors using gradient descent. We empirically show that the proposed network is able to predict both the object label and the actions on GERMS, a dataset for active object recognition. We compare the test label prediction accuracy of the proposed model with Dirichlet and Naive Bayes state encoding. The results of experiments suggest that the proposed model equipped with Dirichlet state encoding is superior in performance, and selects images that lead to better training and higher accuracy of label prediction at test time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge