Cynthia He
Towards Multi-Objective Statistically Fair Federated Learning
Jan 24, 2022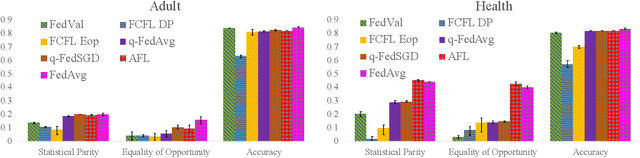
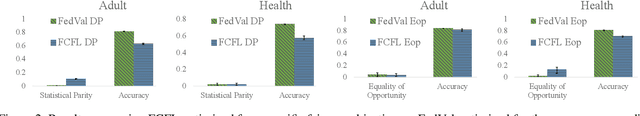
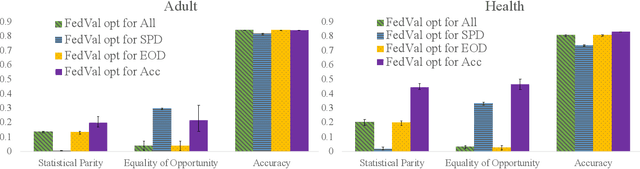
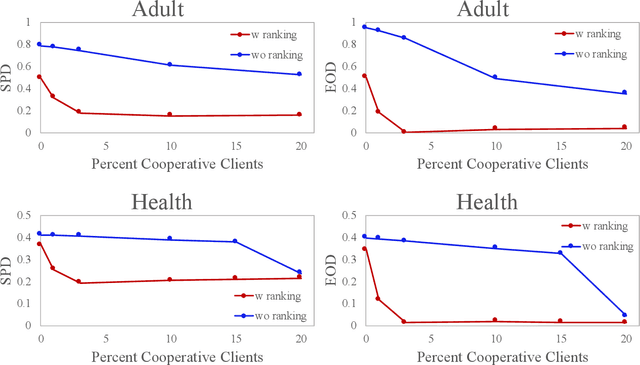
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a result of data ownership and privacy concerns to prevent data from being shared between multiple parties included in a training procedure. Although issues, such as privacy, have gained significant attention in this domain, not much attention has been given to satisfying statistical fairness measures in the FL setting. With this goal in mind, we conduct studies to show that FL is able to satisfy different fairness metrics under different data regimes consisting of different types of clients. More specifically, uncooperative or adversarial clients might contaminate the global FL model by injecting biased or poisoned models due to existing biases in their training datasets. Those biases might be a result of imbalanced training set (Zhang and Zhou 2019), historical biases (Mehrabi et al. 2021a), or poisoned data-points from data poisoning attacks against fairness (Mehrabi et al. 2021b; Solans, Biggio, and Castillo 2020). Thus, we propose a new FL framework that is able to satisfy multiple objectives including various statistical fairness metrics. Through experimentation, we then show the effectiveness of this method comparing it with various baselines, its ability in satisfying different objectives collectively and individually, and its ability in identifying uncooperative or adversarial clients and down-weighing their effect
Video Moment Retrieval via Natural Language Queries
Sep 10, 2020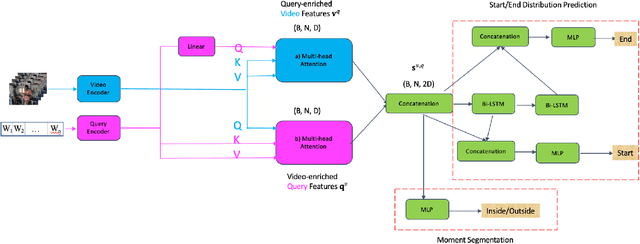
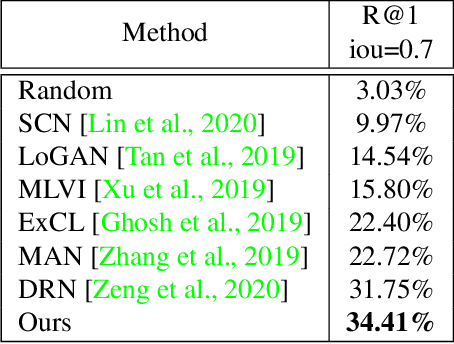
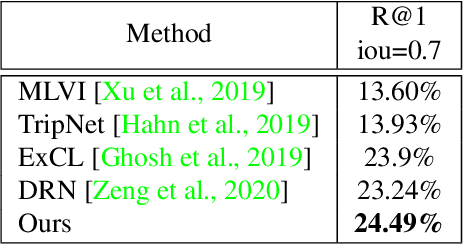
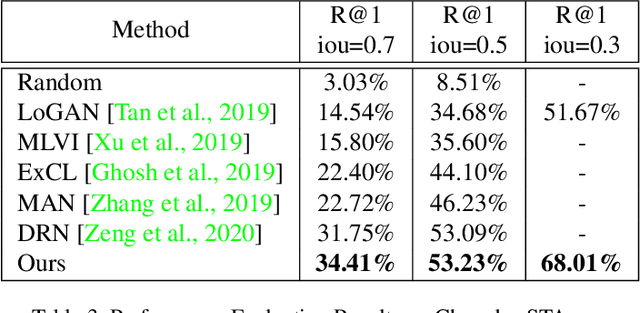
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method for video moment retrieval (VMR) that achieves state of the arts (SOTA) performance on R@1 metrics and surpassing the SOTA on the high IoU metric (R@1, IoU=0.7). First, we propose to use a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and further a cross-attention scheme to capture video/query interaction and long-range query dependencies from video context. The attention-based methods can develop frame-to-query interaction and query-to-frame interaction at arbitrary positions and the multi-head setting ensures the sufficient understanding of complicated dependencies. Our model has a simple architecture, which enables faster training and inference while maintaining . Second, We also propose to use multiple task training objective consists of moment segmentation task, start/end distribution prediction and start/end location regression task. We have verified that start/end prediction are noisy due to annotator disagreement and joint training with moment segmentation task can provide richer information since frames inside the target clip are also utilized as positive training examples. Third, we propose to use an early fusion approach, which achieves better performance at the cost of inference time. However, the inference time will not be a problem for our model since our model has a simple architecture which enables efficient training and inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge