MohammadAmin Fazli
RealDrag: The First Dragging Benchmark with Real Target Image
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:The evaluation of drag based image editing models is unreliable due to a lack of standardized benchmarks and metrics. This ambiguity stems from inconsistent evaluation protocols and, critically, the absence of datasets containing ground truth target images, making objective comparisons between competing methods difficult. To address this, we introduce \textbf{RealDrag}, the first comprehensive benchmark for point based image editing that includes paired ground truth target images. Our dataset contains over 400 human annotated samples from diverse video sources, providing source/target images, handle/target points, editable region masks, and descriptive captions for both the image and the editing action. We also propose four novel, task specific metrics: Semantical Distance (SeD), Outer Mask Preserving Score (OMPS), Inner Patch Preserving Score (IPPS), and Directional Similarity (DiS). These metrics are designed to quantify pixel level matching fidelity, check preservation of non edited (out of mask) regions, and measure semantic alignment with the desired task. Using this benchmark, we conduct the first large scale systematic analysis of the field, evaluating 17 SOTA models. Our results reveal clear trade offs among current approaches and establish a robust, reproducible baseline to guide future research. Our dataset and evaluation toolkit will be made publicly available.
Cold Start Active Preference Learning in Socio-Economic Domains
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Active preference learning is a powerful paradigm for efficiently modeling preferences, yet it suffers from the cold-start problem: a significant drop in performance when no initial labeled data is available. This challenge is particularly acute in computational social systems and economic analysis, where labeled data is often scarce, expensive, and subject to expert noise. To address this gap, we propose a novel framework for cold-start active preference learning. Our method initiates the learning process through a self-supervised pre-training phase, utilizing Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to derive initial pseudo-labels from the data's inherent structure, thereby creating a cold-start model without any initial oracle interaction. Subsequently, the model is refined through an active learning loop that strategically queries a simulated noisy oracle for labels. We conduct extensive experiments on diverse datasets from different domains, including financial credibility, career success rate, and socio-economic status. The results demonstrate that our cold-start approach outperforms standard active learning strategies that begin from a blank slate, achieving higher accuracy with substantially fewer labeled pairs. Our framework offers a practical and effective solution to mitigate the cold-start problem, enhancing the sample efficiency and applicability of preference learning in data-constrained environments. We release our code at https://github.com/Dan-A2/cold-start-preference-learning
A Comprehensive Survey of Convolutions in Deep Learning: Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:In today's digital age, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a subset of Deep Learning (DL), are widely used for various computer vision tasks such as image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. There are numerous types of CNNs designed to meet specific needs and requirements, including 1D, 2D, and 3D CNNs, as well as dilated, grouped, attention, depthwise convolutions, and NAS, among others. Each type of CNN has its unique structure and characteristics, making it suitable for specific tasks. It's crucial to gain a thorough understanding and perform a comparative analysis of these different CNN types to understand their strengths and weaknesses. Furthermore, studying the performance, limitations, and practical applications of each type of CNN can aid in the development of new and improved architectures in the future. We also dive into the platforms and frameworks that researchers utilize for their research or development from various perspectives. Additionally, we explore the main research fields of CNN like 6D vision, generative models, and meta-learning. This survey paper provides a comprehensive examination and comparison of various CNN architectures, highlighting their architectural differences and emphasizing their respective advantages, disadvantages, applications, challenges, and future trends.
Effect of Choosing Loss Function when Using T-batching for Representation Learning on Dynamic Networks
Aug 13, 2023Abstract:Representation learning methods have revolutionized machine learning on networks by converting discrete network structures into continuous domains. However, dynamic networks that evolve over time pose new challenges. To address this, dynamic representation learning methods have gained attention, offering benefits like reduced learning time and improved accuracy by utilizing temporal information. T-batching is a valuable technique for training dynamic network models that reduces training time while preserving vital conditions for accurate modeling. However, we have identified a limitation in the training loss function used with t-batching. Through mathematical analysis, we propose two alternative loss functions that overcome these issues, resulting in enhanced training performance. We extensively evaluate the proposed loss functions on synthetic and real-world dynamic networks. The results consistently demonstrate superior performance compared to the original loss function. Notably, in a real-world network characterized by diverse user interaction histories, the proposed loss functions achieved more than 26.9% enhancement in Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) and more than 11.8% improvement in Recall@10. These findings underscore the efficacy of the proposed loss functions in dynamic network modeling.
A Novel Experts Advice Aggregation Framework Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Portfolio Management
Dec 29, 2022

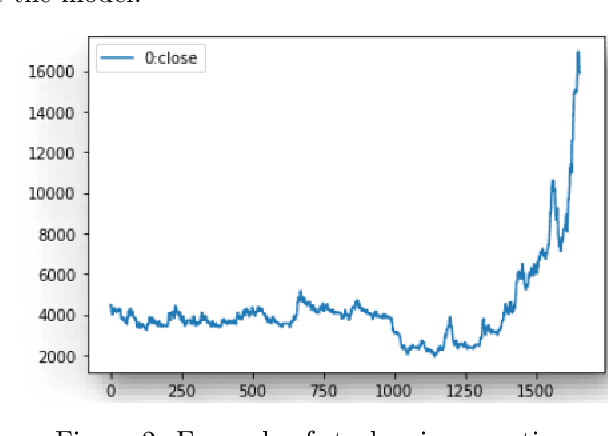

Abstract:Solving portfolio management problems using deep reinforcement learning has been getting much attention in finance for a few years. We have proposed a new method using experts signals and historical price data to feed into our reinforcement learning framework. Although experts signals have been used in previous works in the field of finance, as far as we know, it is the first time this method, in tandem with deep RL, is used to solve the financial portfolio management problem. Our proposed framework consists of a convolutional network for aggregating signals, another convolutional network for historical price data, and a vanilla network. We used the Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm as the agent to process the reward and take action in the environment. The results suggested that, on average, our framework could gain 90 percent of the profit earned by the best expert.
Under the Skin of Foundation NFT Auctions
Sep 25, 2021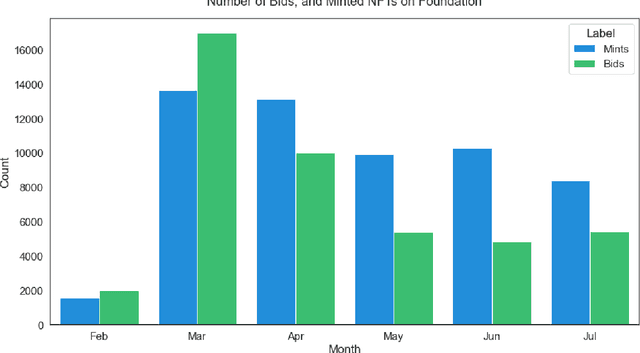
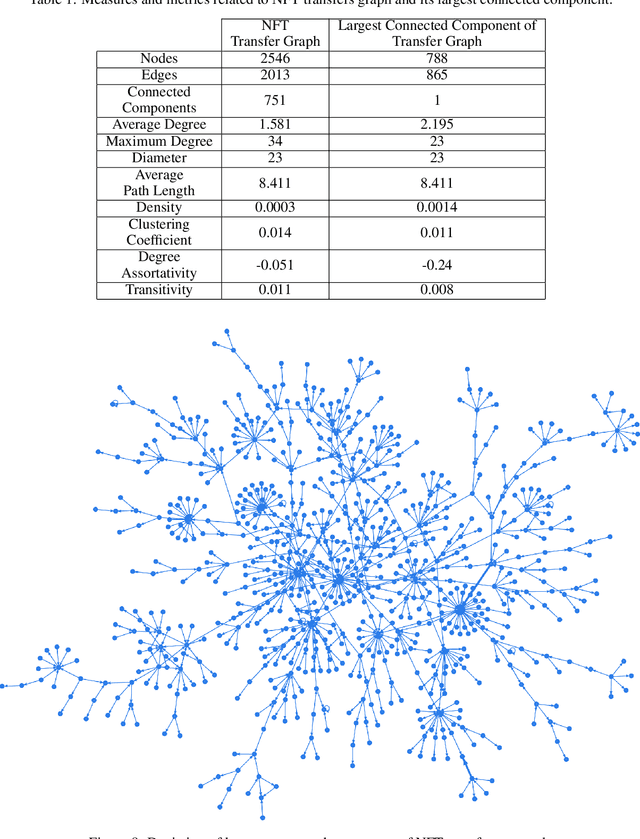
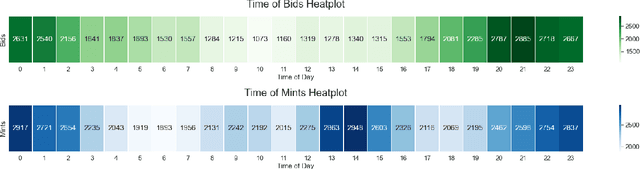
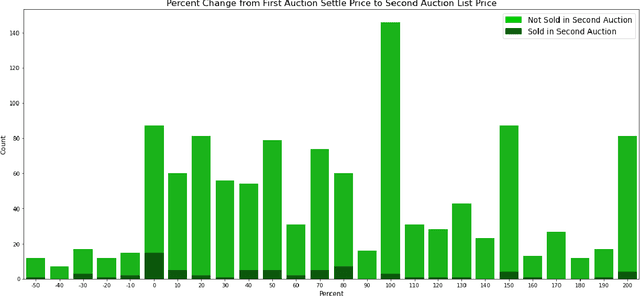
Abstract:Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have gained a solid foothold within the crypto community, and substantial amounts of money have been allocated to their trades. In this paper, we studied one of the most prominent marketplaces dedicated to NFT auctions and trades, Foundation. We analyzed the activities on Foundation and identified several intriguing underlying dynamics that occur on this platform. Moreover, We performed social network analysis on a graph that we had created based on transferred NFTs on Foundation, and then described the characteristics of this graph. Lastly, We built a neural network-based similarity model for retrieving and clustering similar NFTs. We also showed that for most NFTs, their performances in auctions were comparable with the auction performance of other NFTs in their cluster.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge