Minsung Kang
Neural radiance fields-based holography [Invited]
Mar 02, 2024![Figure 1 for Neural radiance fields-based holography [Invited]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F52e54793884240e12519f7239ad5282b05f074bd%2F2-Figure1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 2 for Neural radiance fields-based holography [Invited]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F52e54793884240e12519f7239ad5282b05f074bd%2F2-Figure2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 3 for Neural radiance fields-based holography [Invited]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F52e54793884240e12519f7239ad5282b05f074bd%2F3-Figure3-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 4 for Neural radiance fields-based holography [Invited]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2F52e54793884240e12519f7239ad5282b05f074bd%2F3-Figure4-1.png&w=640&q=75)
Abstract:This study presents a novel approach for generating holograms based on the neural radiance fields (NeRF) technique. Generating three-dimensional (3D) data is difficult in hologram computation. NeRF is a state-of-the-art technique for 3D light-field reconstruction from 2D images based on volume rendering. The NeRF can rapidly predict new-view images that do not include a training dataset. In this study, we constructed a rendering pipeline directly from a 3D light field generated from 2D images by NeRF for hologram generation using deep neural networks within a reasonable time. The pipeline comprises three main components: the NeRF, a depth predictor, and a hologram generator, all constructed using deep neural networks. The pipeline does not include any physical calculations. The predicted holograms of a 3D scene viewed from any direction were computed using the proposed pipeline. The simulation and experimental results are presented.
HCLAS-X: Hierarchical and Cascaded Lyrics Alignment System Using Multimodal Cross-Correlation
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:In this work, we address the challenge of lyrics alignment, which involves aligning the lyrics and vocal components of songs. This problem requires the alignment of two distinct modalities, namely text and audio. To overcome this challenge, we propose a model that is trained in a supervised manner, utilizing the cross-correlation matrix of latent representations between vocals and lyrics. Our system is designed in a hierarchical and cascaded manner. It predicts synced time first on a sentence-level and subsequently on a word-level. This design enables the system to process long sequences, as the cross-correlation uses quadratic memory with respect to sequence length. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed system achieves a significant improvement in mean average error, showcasing its robustness in comparison to the previous state-of-the-art model. Additionally, we conduct a qualitative analysis of the system after successfully deploying it in several music streaming services.
A Demand-Driven Perspective on Generative Audio AI
Jul 10, 2023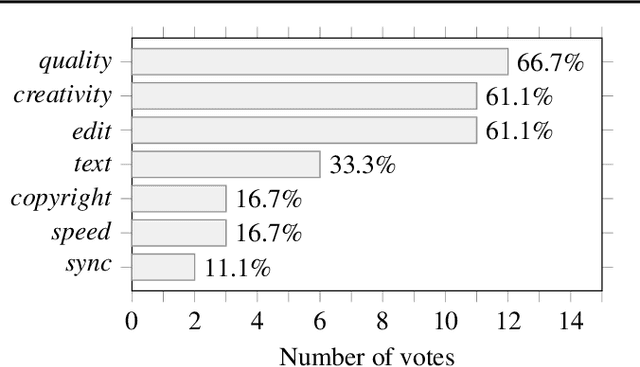
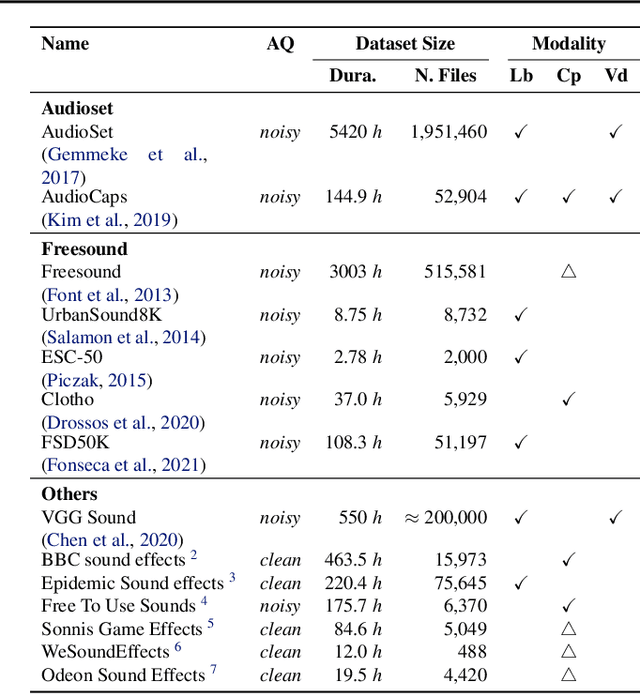
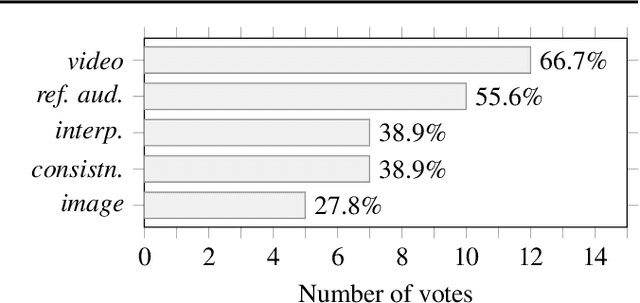

Abstract:To achieve successful deployment of AI research, it is crucial to understand the demands of the industry. In this paper, we present the results of a survey conducted with professional audio engineers, in order to determine research priorities and define various research tasks. We also summarize the current challenges in audio quality and controllability based on the survey. Our analysis emphasizes that the availability of datasets is currently the main bottleneck for achieving high-quality audio generation. Finally, we suggest potential solutions for some revealed issues with empirical evidence.
FALL-E: A Foley Sound Synthesis Model and Strategies
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces FALL-E, a foley synthesis system and its training/inference strategies. The FALL-E model employs a cascaded approach comprising low-resolution spectrogram generation, spectrogram super-resolution, and a vocoder. We trained every sound-related model from scratch using our extensive datasets, and utilized a pre-trained language model. We conditioned the model with dataset-specific texts, enabling it to learn sound quality and recording environment based on text input. Moreover, we leveraged external language models to improve text descriptions of our datasets and performed prompt engineering for quality, coherence, and diversity. FALL-E was evaluated by an objective measure as well as listening tests in the DCASE 2023 challenge Task 7. The submission achieved the second place on average, while achieving the best score for diversity, second place for audio quality, and third place for class fitness.
A Proposal for Foley Sound Synthesis Challenge
Jul 21, 2022Abstract:"Foley" refers to sound effects that are added to multimedia during post-production to enhance its perceived acoustic properties, e.g., by simulating the sounds of footsteps, ambient environmental sounds, or visible objects on the screen. While foley is traditionally produced by foley artists, there is increasing interest in automatic or machine-assisted techniques building upon recent advances in sound synthesis and generative models. To foster more participation in this growing research area, we propose a challenge for automatic foley synthesis. Through case studies on successful previous challenges in audio and machine learning, we set the goals of the proposed challenge: rigorous, unified, and efficient evaluation of different foley synthesis systems, with an overarching goal of drawing active participation from the research community. We outline the details and design considerations of a foley sound synthesis challenge, including task definition, dataset requirements, and evaluation criteria.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge