Minhwan Ko
Curriculum Fine-tuning of Vision Foundation Model for Medical Image Classification Under Label Noise
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated remarkable performance in various vision tasks, but their success heavily depends on the quality of the training data. Noisy labels are a critical issue in medical datasets and can significantly degrade model performance. Previous clean sample selection methods have not utilized the well pre-trained features of vision foundation models (VFMs) and assumed that training begins from scratch. In this paper, we propose CUFIT, a curriculum fine-tuning paradigm of VFMs for medical image classification under label noise. Our method is motivated by the fact that linear probing of VFMs is relatively unaffected by noisy samples, as it does not update the feature extractor of the VFM, thus robustly classifying the training samples. Subsequently, curriculum fine-tuning of two adapters is conducted, starting with clean sample selection from the linear probing phase. Our experimental results demonstrate that CUFIT outperforms previous methods across various medical image benchmarks. Specifically, our method surpasses previous baselines by 5.0%, 2.1%, 4.6%, and 5.8% at a 40% noise rate on the HAM10000, APTOS-2019, BloodMnist, and OrgancMnist datasets, respectively. Furthermore, we provide extensive analyses to demonstrate the impact of our method on noisy label detection. For instance, our method shows higher label precision and recall compared to previous approaches. Our work highlights the potential of leveraging VFMs in medical image classification under challenging conditions of noisy labels.
Domain-Specific Block Selection and Paired-View Pseudo-Labeling for Online Test-Time Adaptation
Apr 17, 2024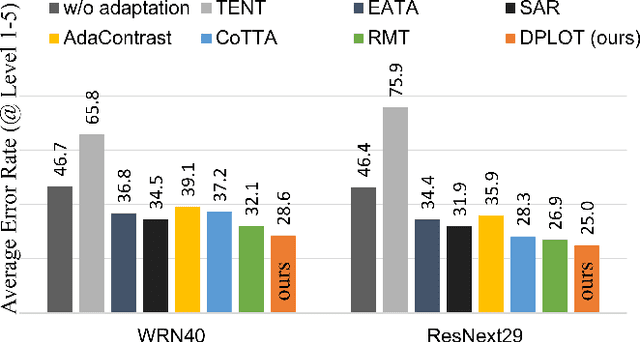
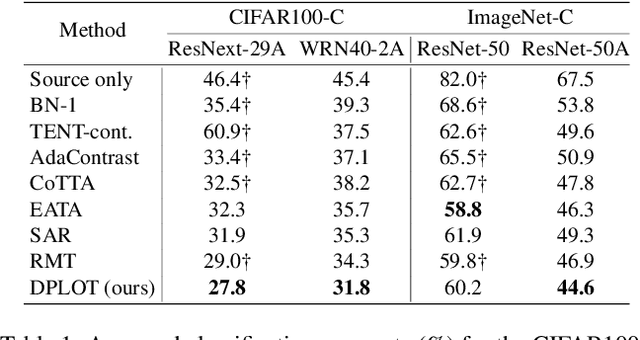
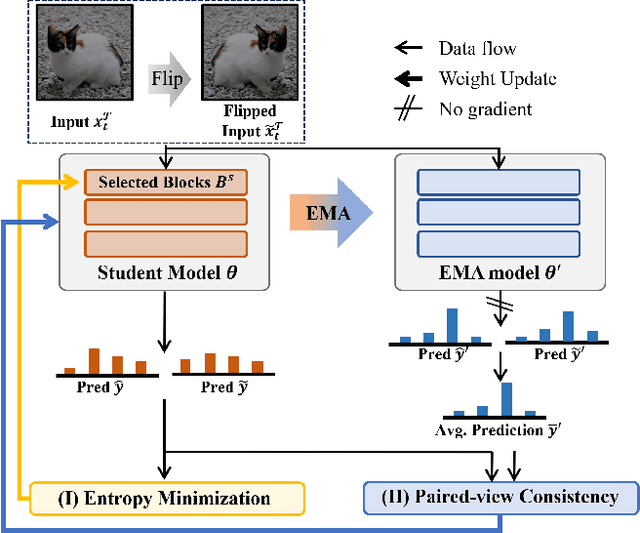
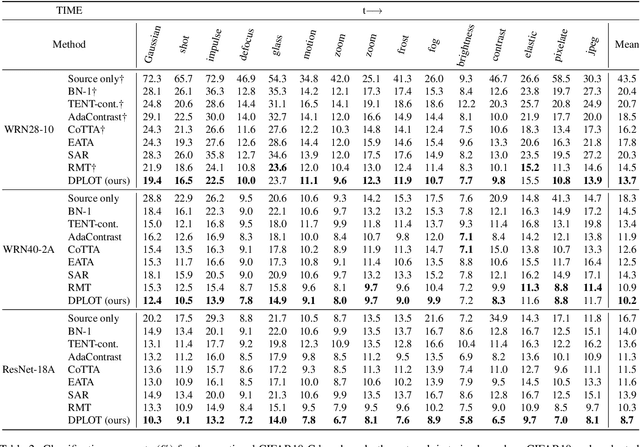
Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) aims to adapt a pre-trained model to a new test domain without access to source data after deployment. Existing approaches typically rely on self-training with pseudo-labels since ground-truth cannot be obtained from test data. Although the quality of pseudo labels is important for stable and accurate long-term adaptation, it has not been previously addressed. In this work, we propose DPLOT, a simple yet effective TTA framework that consists of two components: (1) domain-specific block selection and (2) pseudo-label generation using paired-view images. Specifically, we select blocks that involve domain-specific feature extraction and train these blocks by entropy minimization. After blocks are adjusted for current test domain, we generate pseudo-labels by averaging given test images and corresponding flipped counterparts. By simply using flip augmentation, we prevent a decrease in the quality of the pseudo-labels, which can be caused by the domain gap resulting from strong augmentation. Our experimental results demonstrate that DPLOT outperforms previous TTA methods in CIFAR10-C, CIFAR100-C, and ImageNet-C benchmarks, reducing error by up to 5.4%, 9.1%, and 2.9%, respectively. Also, we provide an extensive analysis to demonstrate effectiveness of our framework. Code is available at https://github.com/gist-ailab/domain-specific-block-selection-and-paired-view-pseudo-labeling-for-online-TTA.
PolyFit: A Peg-in-hole Assembly Framework for Unseen Polygon Shapes via Sim-to-real Adaptation
Dec 05, 2023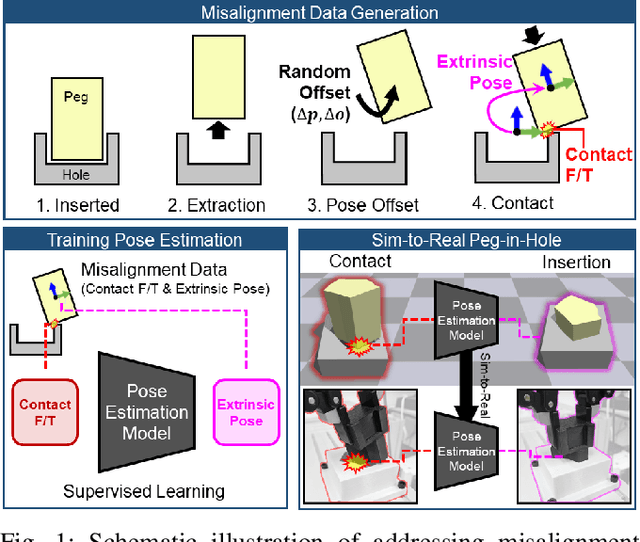
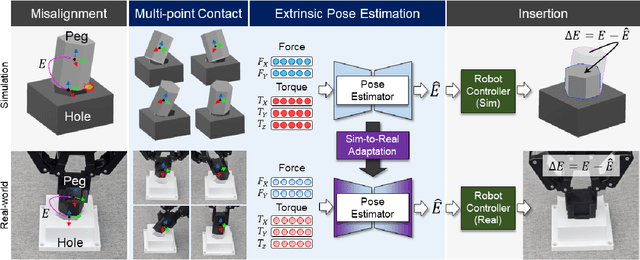
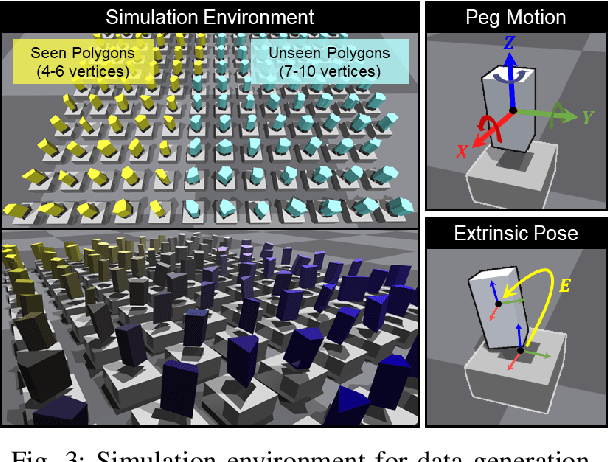
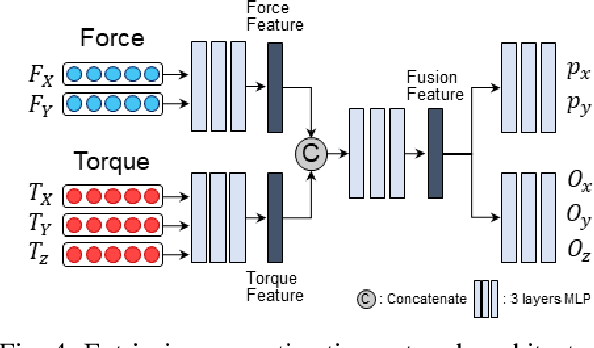
Abstract:The study addresses the foundational and challenging task of peg-in-hole assembly in robotics, where misalignments caused by sensor inaccuracies and mechanical errors often result in insertion failures or jamming. This research introduces PolyFit, representing a paradigm shift by transitioning from a reinforcement learning approach to a supervised learning methodology. PolyFit is a Force/Torque (F/T)-based supervised learning framework designed for 5-DoF peg-in-hole assembly. It utilizes F/T data for accurate extrinsic pose estimation and adjusts the peg pose to rectify misalignments. Extensive training in a simulated environment involves a dataset encompassing a diverse range of peg-hole shapes, extrinsic poses, and their corresponding contact F/T readings. To enhance extrinsic pose estimation, a multi-point contact strategy is integrated into the model input, recognizing that identical F/T readings can indicate different poses. The study proposes a sim-to-real adaptation method for real-world application, using a sim-real paired dataset to enable effective generalization to complex and unseen polygon shapes. PolyFit achieves impressive peg-in-hole success rates of 97.3% and 96.3% for seen and unseen shapes in simulations, respectively. Real-world evaluations further demonstrate substantial success rates of 86.7% and 85.0%, highlighting the robustness and adaptability of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge