Mingtang Deng
Experimental quantum natural gradient optimization in photonics
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Variational quantum algorithms (VQAs) combining the advantages of parameterized quantum circuits and classical optimizers, promise practical quantum applications in the Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum era. The performance of VQAs heavily depends on the optimization method. Compared with gradient-free and ordinary gradient descent methods, the quantum natural gradient (QNG), which mirrors the geometric structure of the parameter space, can achieve faster convergence and avoid local minima more easily, thereby reducing the cost of circuit executions. We utilized a fully programmable photonic chip to experimentally estimate the QNG in photonics for the first time. We obtained the dissociation curve of the He-H$^+$ cation and achieved chemical accuracy, verifying the outperformance of QNG optimization on a photonic device. Our work opens up a vista of utilizing QNG in photonics to implement practical near-term quantum applications.
Quantum generative adversarial learning in photonics
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks (QGANs), an intersection of quantum computing and machine learning, have attracted widespread attention due to their potential advantages over classical analogs. However, in the current era of Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) computing, it is essential to investigate whether QGANs can perform learning tasks on near-term quantum devices usually affected by noise and even defects. In this Letter, using a programmable silicon quantum photonic chip, we experimentally demonstrate the QGAN model in photonics for the first time, and investigate the effects of noise and defects on its performance. Our results show that QGANs can generate high-quality quantum data with a fidelity higher than 90\%, even under conditions where up to half of the generator's phase shifters are damaged, or all of the generator and discriminator's phase shifters are subjected to phase noise up to 0.04$\pi$. Our work sheds light on the feasibility of implementing QGANs on NISQ-era quantum hardware.
Variational Quantum Circuits for Quantum State Tomography
Dec 16, 2019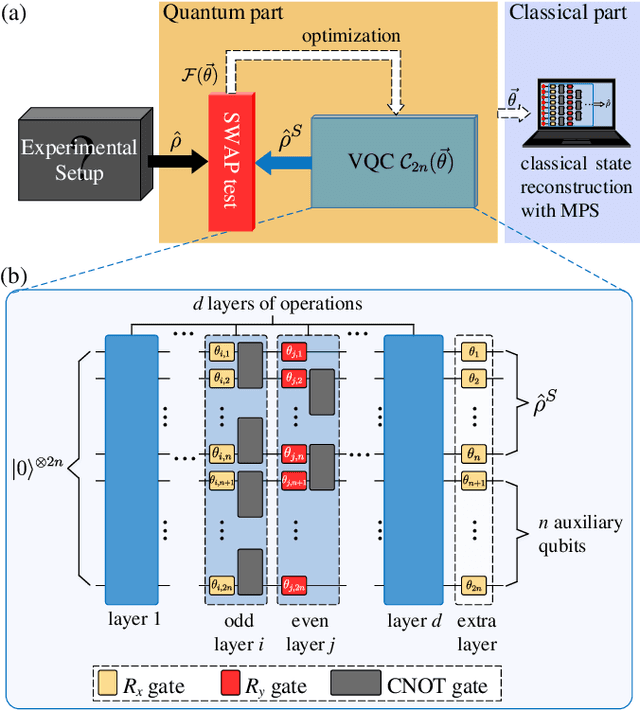
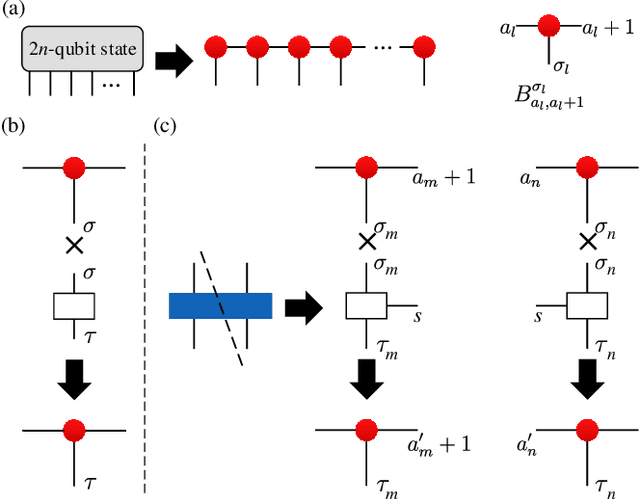
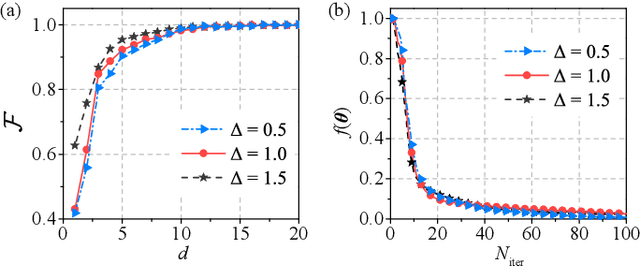
Abstract:We propose a hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for quantum state tomography. Given an unknown quantum state, a quantum machine learning algorithm is used to maximize the fidelity between the output of a variational quantum circuit and this state. The number of parameters of the variational quantum circuit grows linearly with the number of qubits and the circuit depth. After that, a subsequent classical algorithm is used to reconstruct the unknown quantum state. We demonstrate our method by performing numerical simulations to reconstruct the ground state of a one-dimensional quantum spin chain, using a variational quantum circuit simulator. Our method is suitable for near-term quantum computing platforms, and could be used for relatively large-scale quantum state tomography for experimentally relevant quantum states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge