Mingjun Yin
Context-Aware Transfer Attacks for Object Detection
Dec 06, 2021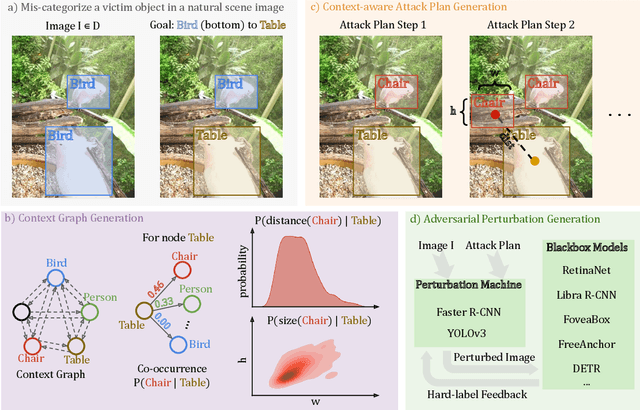
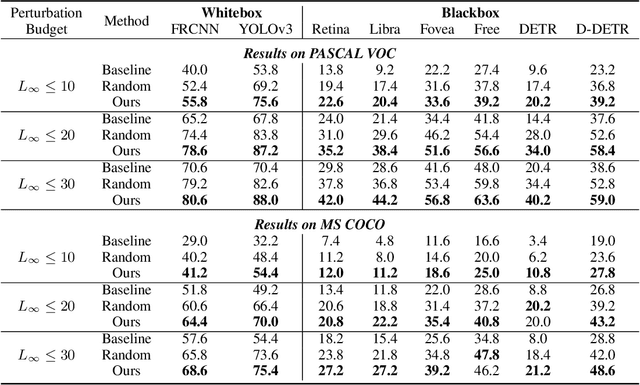

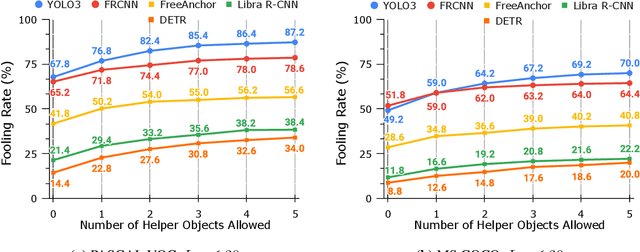
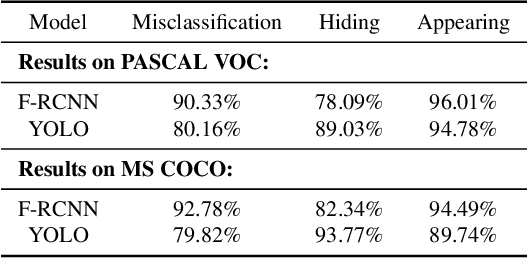
Abstract:Blackbox transfer attacks for image classifiers have been extensively studied in recent years. In contrast, little progress has been made on transfer attacks for object detectors. Object detectors take a holistic view of the image and the detection of one object (or lack thereof) often depends on other objects in the scene. This makes such detectors inherently context-aware and adversarial attacks in this space are more challenging than those targeting image classifiers. In this paper, we present a new approach to generate context-aware attacks for object detectors. We show that by using co-occurrence of objects and their relative locations and sizes as context information, we can successfully generate targeted mis-categorization attacks that achieve higher transfer success rates on blackbox object detectors than the state-of-the-art. We test our approach on a variety of object detectors with images from PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets and demonstrate up to $20$ percentage points improvement in performance compared to the other state-of-the-art methods.
ADC: Adversarial attacks against object Detection that evade Context consistency checks
Oct 24, 2021
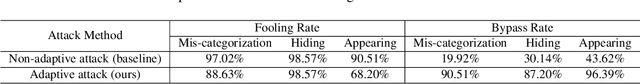
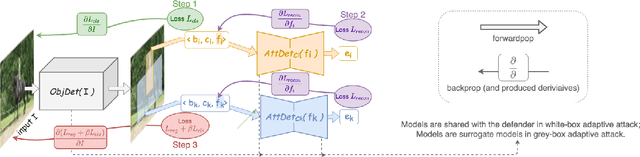
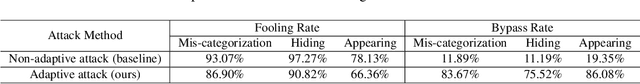
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have been shown to be vulnerable to adversarial examples, which are slightly perturbed input images which lead DNNs to make wrong predictions. To protect from such examples, various defense strategies have been proposed. A very recent defense strategy for detecting adversarial examples, that has been shown to be robust to current attacks, is to check for intrinsic context consistencies in the input data, where context refers to various relationships (e.g., object-to-object co-occurrence relationships) in images. In this paper, we show that even context consistency checks can be brittle to properly crafted adversarial examples and to the best of our knowledge, we are the first to do so. Specifically, we propose an adaptive framework to generate examples that subvert such defenses, namely, Adversarial attacks against object Detection that evade Context consistency checks (ADC). In ADC, we formulate a joint optimization problem which has two attack goals, viz., (i) fooling the object detector and (ii) evading the context consistency check system, at the same time. Experiments on both PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets show that examples generated with ADC fool the object detector with a success rate of over 85% in most cases, and at the same time evade the recently proposed context consistency checks, with a bypassing rate of over 80% in most cases. Our results suggest that how to robustly model context and check its consistency, is still an open problem.
Exploiting Multi-Object Relationships for Detecting Adversarial Attacks in Complex Scenes
Aug 19, 2021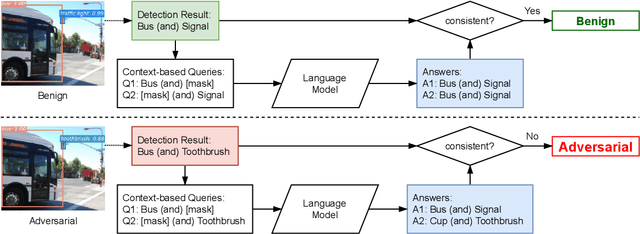
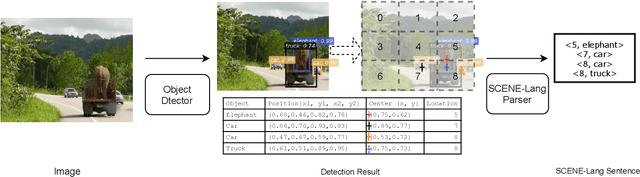

Abstract:Vision systems that deploy Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples. Recent research has shown that checking the intrinsic consistencies in the input data is a promising way to detect adversarial attacks (e.g., by checking the object co-occurrence relationships in complex scenes). However, existing approaches are tied to specific models and do not offer generalizability. Motivated by the observation that language descriptions of natural scene images have already captured the object co-occurrence relationships that can be learned by a language model, we develop a novel approach to perform context consistency checks using such language models. The distinguishing aspect of our approach is that it is independent of the deployed object detector and yet offers very high accuracy in terms of detecting adversarial examples in practical scenes with multiple objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge