Ming Ying Yang
Evaluating the Impact of Social Determinants on Health Prediction
May 22, 2023
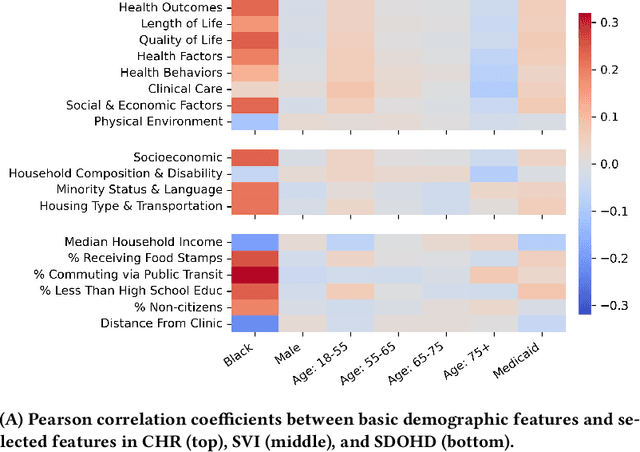


Abstract:Social determinants of health (SDOH) -- the conditions in which people live, grow, and age -- play a crucial role in a person's health and well-being. There is a large, compelling body of evidence in population health studies showing that a wide range of SDOH is strongly correlated with health outcomes. Yet, a majority of the risk prediction models based on electronic health records (EHR) do not incorporate a comprehensive set of SDOH features as they are often noisy or simply unavailable. Our work links a publicly available EHR database, MIMIC-IV, to well-documented SDOH features. We investigate the impact of such features on common EHR prediction tasks across different patient populations. We find that community-level SDOH features do not improve model performance for a general patient population, but can improve data-limited model fairness for specific subpopulations. We also demonstrate that SDOH features are vital for conducting thorough audits of algorithmic biases beyond protective attributes. We hope the new integrated EHR-SDOH database will enable studies on the relationship between community health and individual outcomes and provide new benchmarks to study algorithmic biases beyond race, gender, and age.
Write It Like You See It: Detectable Differences in Clinical Notes By Race Lead To Differential Model Recommendations
May 08, 2022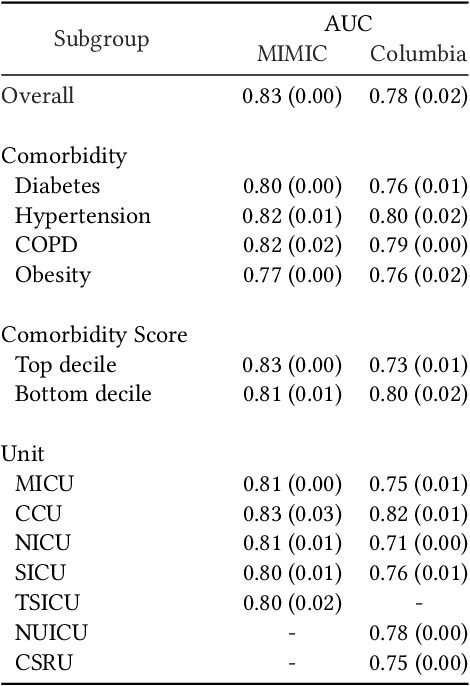
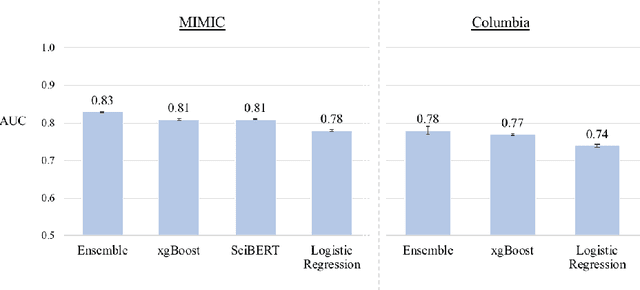

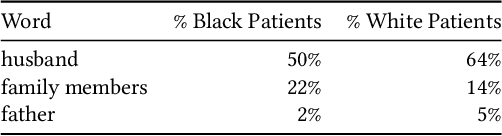
Abstract:Clinical notes are becoming an increasingly important data source for machine learning (ML) applications in healthcare. Prior research has shown that deploying ML models can perpetuate existing biases against racial minorities, as bias can be implicitly embedded in data. In this study, we investigate the level of implicit race information available to ML models and human experts and the implications of model-detectable differences in clinical notes. Our work makes three key contributions. First, we find that models can identify patient self-reported race from clinical notes even when the notes are stripped of explicit indicators of race. Second, we determine that human experts are not able to accurately predict patient race from the same redacted clinical notes. Finally, we demonstrate the potential harm of this implicit information in a simulation study, and show that models trained on these race-redacted clinical notes can still perpetuate existing biases in clinical treatment decisions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge