Miguel Graça
LumberChunker: Long-Form Narrative Document Segmentation
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Modern NLP tasks increasingly rely on dense retrieval methods to access up-to-date and relevant contextual information. We are motivated by the premise that retrieval benefits from segments that can vary in size such that a content's semantic independence is better captured. We propose LumberChunker, a method leveraging an LLM to dynamically segment documents, which iteratively prompts the LLM to identify the point within a group of sequential passages where the content begins to shift. To evaluate our method, we introduce GutenQA, a benchmark with 3000 "needle in a haystack" type of question-answer pairs derived from 100 public domain narrative books available on Project Gutenberg. Our experiments show that LumberChunker not only outperforms the most competitive baseline by 7.37% in retrieval performance (DCG@20) but also that, when integrated into a RAG pipeline, LumberChunker proves to be more effective than other chunking methods and competitive baselines, such as the Gemini 1.5M Pro. Our Code and Data are available at https://github.com/joaodsmarques/LumberChunker
When and Why is Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation Useless?
Apr 22, 2020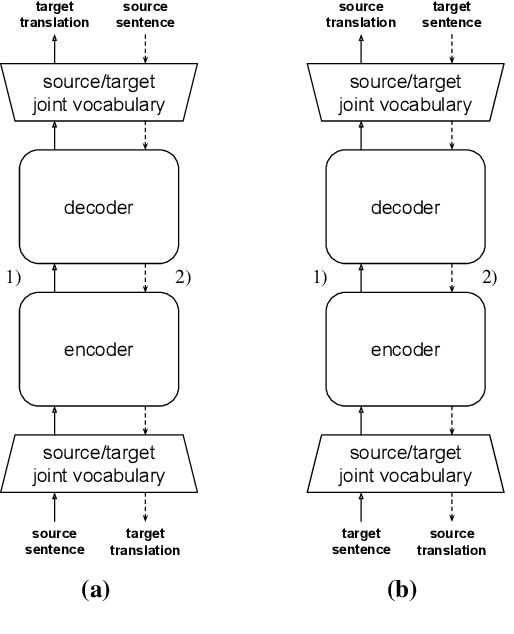
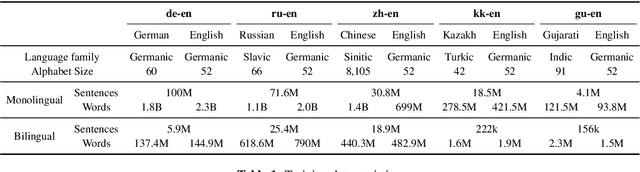
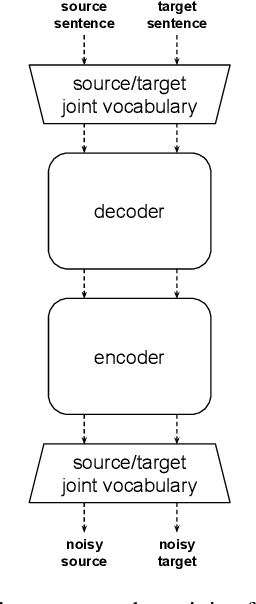
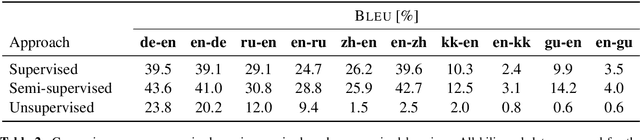
Abstract:This paper studies the practicality of the current state-of-the-art unsupervised methods in neural machine translation (NMT). In ten translation tasks with various data settings, we analyze the conditions under which the unsupervised methods fail to produce reasonable translations. We show that their performance is severely affected by linguistic dissimilarity and domain mismatch between source and target monolingual data. Such conditions are common for low-resource language pairs, where unsupervised learning works poorly. In all of our experiments, supervised and semi-supervised baselines with 50k-sentence bilingual data outperform the best unsupervised results. Our analyses pinpoint the limits of the current unsupervised NMT and also suggest immediate research directions.
Generalizing Back-Translation in Neural Machine Translation
Jun 17, 2019
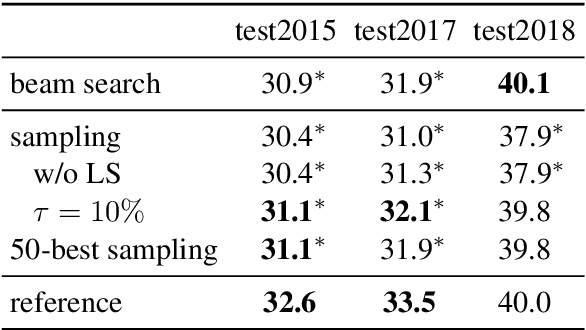
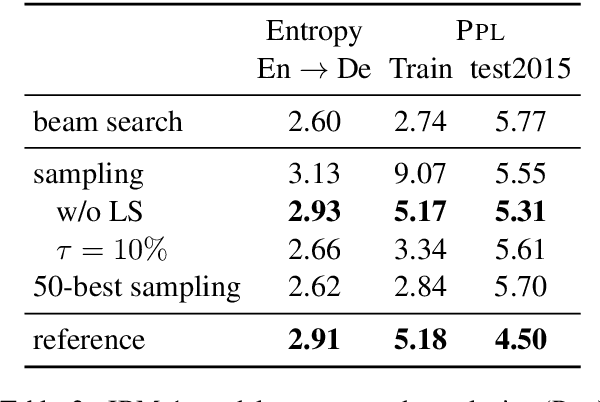
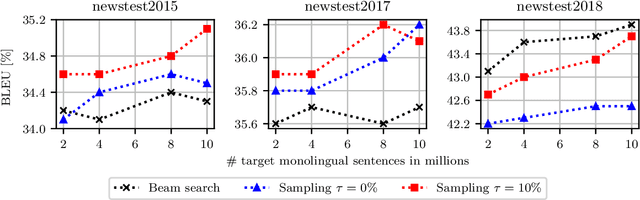
Abstract:Back-translation - data augmentation by translating target monolingual data - is a crucial component in modern neural machine translation (NMT). In this work, we reformulate back-translation in the scope of cross-entropy optimization of an NMT model, clarifying its underlying mathematical assumptions and approximations beyond its heuristic usage. Our formulation covers broader synthetic data generation schemes, including sampling from a target-to-source NMT model. With this formulation, we point out fundamental problems of the sampling-based approaches and propose to remedy them by (i) disabling label smoothing for the target-to-source model and (ii) sampling from a restricted search space. Our statements are investigated on the WMT 2018 German - English news translation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge