Michele Catellani
Semi-supervised GAN for Bladder Tissue Classification in Multi-Domain Endoscopic Images
Dec 21, 2022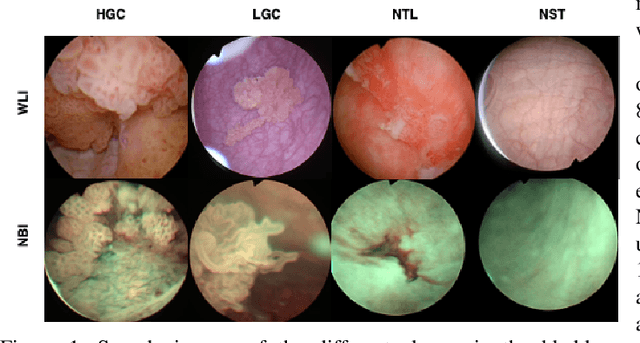
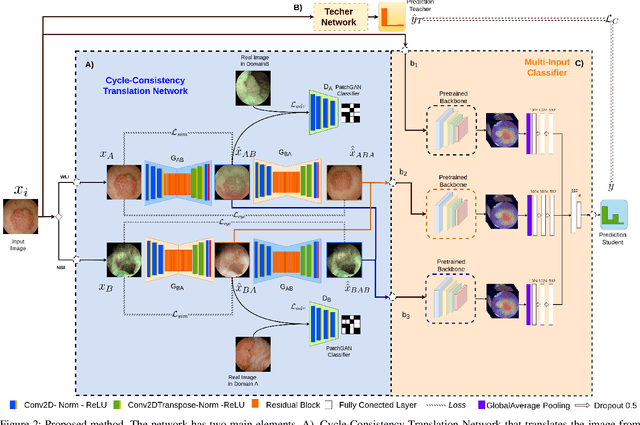
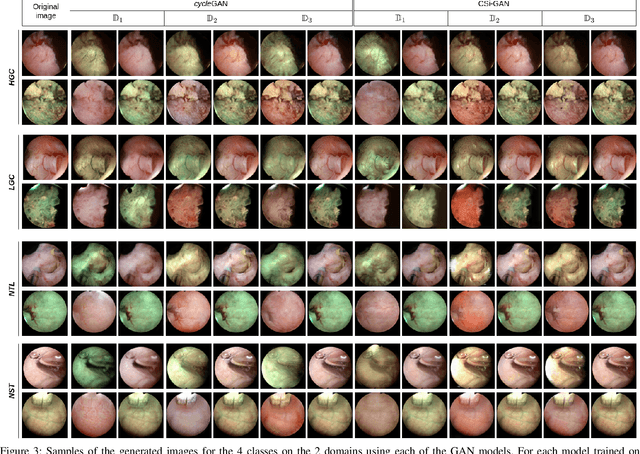
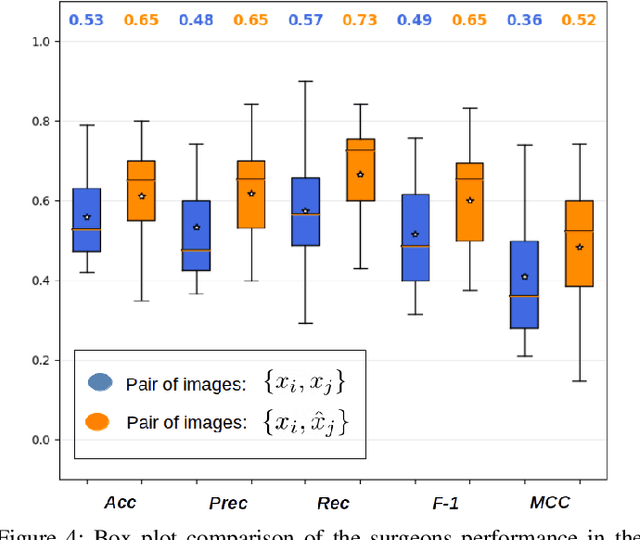
Abstract:Objective: Accurate visual classification of bladder tissue during Trans-Urethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) procedures is essential to improve early cancer diagnosis and treatment. During TURBT interventions, White Light Imaging (WLI) and Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) techniques are used for lesion detection. Each imaging technique provides diverse visual information that allows clinicians to identify and classify cancerous lesions. Computer vision methods that use both imaging techniques could improve endoscopic diagnosis. We address the challenge of tissue classification when annotations are available only in one domain, in our case WLI, and the endoscopic images correspond to an unpaired dataset, i.e. there is no exact equivalent for every image in both NBI and WLI domains. Method: We propose a semi-surprised Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based method composed of three main components: a teacher network trained on the labeled WLI data; a cycle-consistency GAN to perform unpaired image-to-image translation, and a multi-input student network. To ensure the quality of the synthetic images generated by the proposed GAN we perform a detailed quantitative, and qualitative analysis with the help of specialists. Conclusion: The overall average classification accuracy, precision, and recall obtained with the proposed method for tissue classification are 0.90, 0.88, and 0.89 respectively, while the same metrics obtained in the unlabeled domain (NBI) are 0.92, 0.64, and 0.94 respectively. The quality of the generated images is reliable enough to deceive specialists. Significance: This study shows the potential of using semi-supervised GAN-based classification to improve bladder tissue classification when annotations are limited in multi-domain data.
Autonomous Intraluminal Navigation of a Soft Robot using Deep-Learning-based Visual Servoing
Jul 01, 2022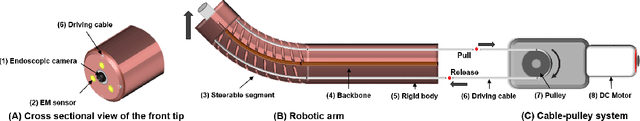
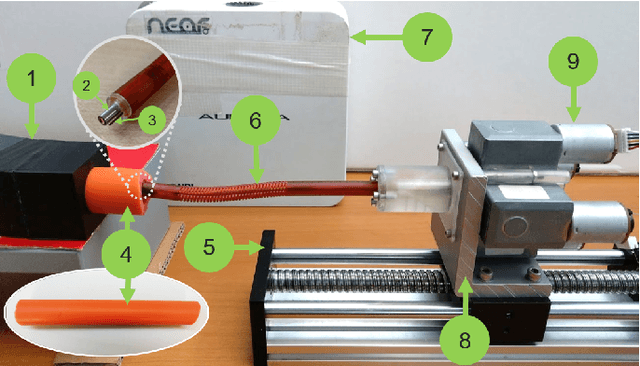
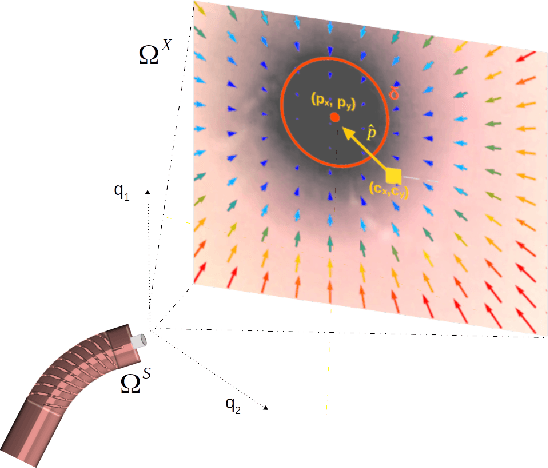
Abstract:Navigation inside luminal organs is an arduous task that requires non-intuitive coordination between the movement of the operator's hand and the information obtained from the endoscopic video. The development of tools to automate certain tasks could alleviate the physical and mental load of doctors during interventions, allowing them to focus on diagnosis and decision-making tasks. In this paper, we present a synergic solution for intraluminal navigation consisting of a 3D printed endoscopic soft robot that can move safely inside luminal structures. Visual servoing, based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) is used to achieve the autonomous navigation task. The CNN is trained with phantoms and in-vivo data to segment the lumen, and a model-less approach is presented to control the movement in constrained environments. The proposed robot is validated in anatomical phantoms in different path configurations. We analyze the movement of the robot using different metrics such as task completion time, smoothness, error in the steady-state, and mean and maximum error. We show that our method is suitable to navigate safely in hollow environments and conditions which are different than the ones the network was originally trained on.
A transfer-learning approach for lesion detection in endoscopic images from the urinary tract
Apr 08, 2021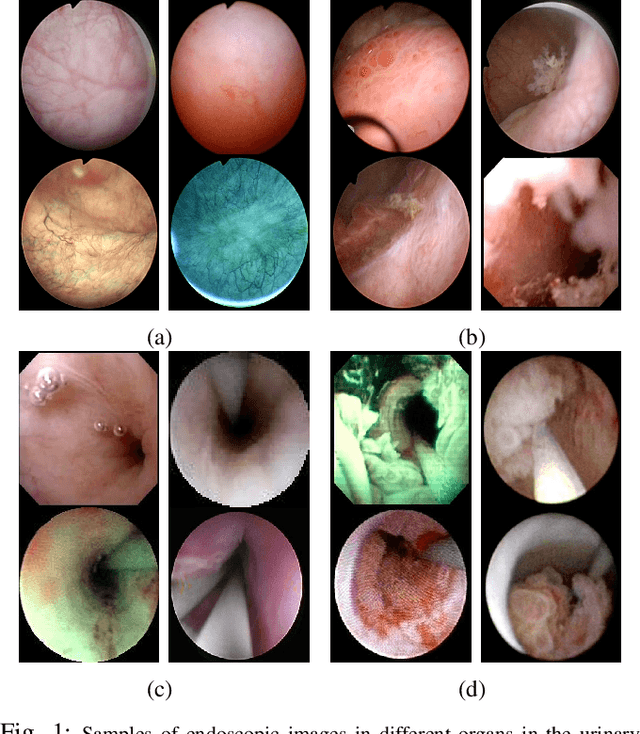
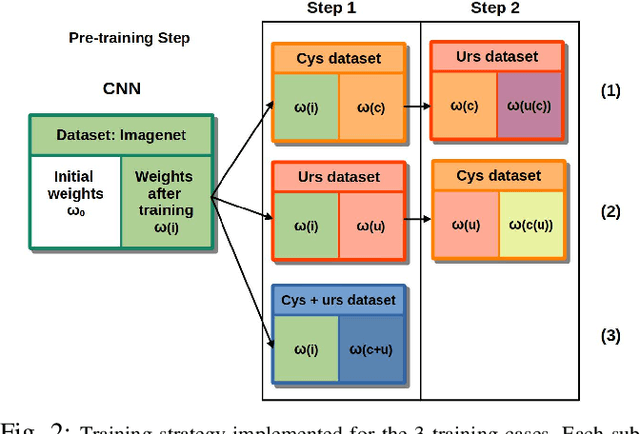
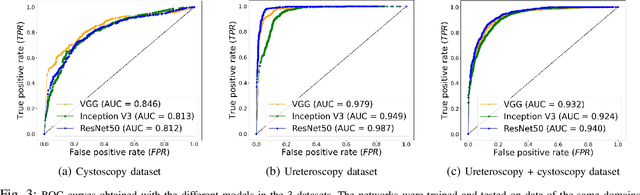
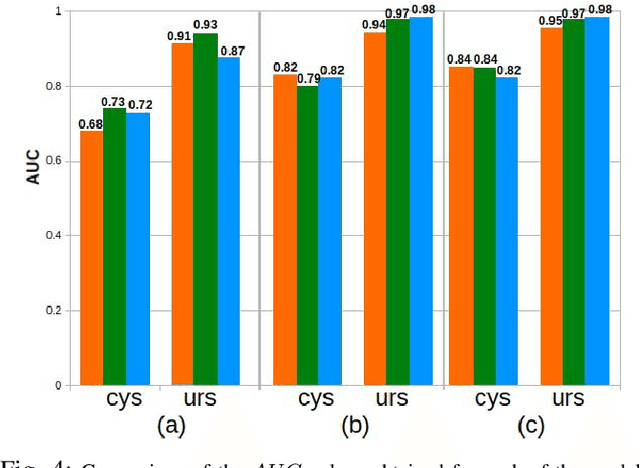
Abstract:Ureteroscopy and cystoscopy are the gold standard methods to identify and treat tumors along the urinary tract. It has been reported that during a normal procedure a rate of 10-20 % of the lesions could be missed. In this work we study the implementation of 3 different Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), using a 2-steps training strategy, to classify images from the urinary tract with and without lesions. A total of 6,101 images from ureteroscopy and cystoscopy procedures were collected. The CNNs were trained and tested using transfer learning in a two-steps fashion on 3 datasets. The datasets used were: 1) only ureteroscopy images, 2) only cystoscopy images and 3) the combination of both of them. For cystoscopy data, VGG performed better obtaining an Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) value of 0.846. In the cases of ureteroscopy and the combination of both datasets, ResNet50 achieved the best results with AUC values of 0.987 and 0.940. The use of a training dataset that comprehends both domains results in general better performances, but performing a second stage of transfer learning achieves comparable ones. There is no single model which performs better in all scenarios, but ResNet50 is the network that achieves the best performances in most of them. The obtained results open the opportunity for further investigation with a view for improving lesion detection in endoscopic images of the urinary system.
Using spatial-temporal ensembles of convolutional neural networks for lumen segmentation in ureteroscopy
Apr 05, 2021



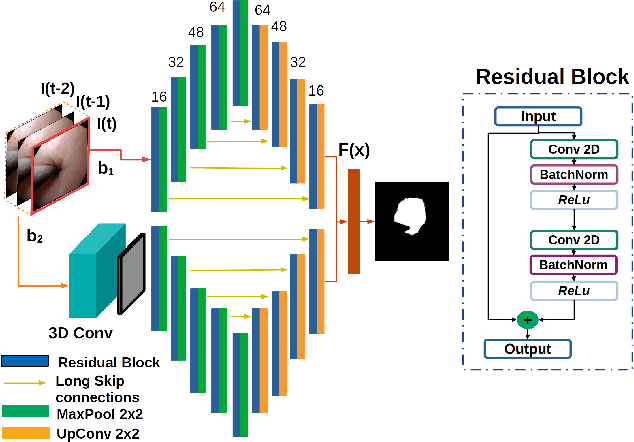
Abstract:Purpose: Ureteroscopy is an efficient endoscopic minimally invasive technique for the diagnosis and treatment of upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). During ureteroscopy, the automatic segmentation of the hollow lumen is of primary importance, since it indicates the path that the endoscope should follow. In order to obtain an accurate segmentation of the hollow lumen, this paper presents an automatic method based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Methods: The proposed method is based on an ensemble of 4 parallel CNNs to simultaneously process single and multi-frame information. Of these, two architectures are taken as core-models, namely U-Net based in residual blocks($m_1$) and Mask-RCNN($m_2$), which are fed with single still-frames $I(t)$. The other two models ($M_1$, $M_2$) are modifications of the former ones consisting on the addition of a stage which makes use of 3D Convolutions to process temporal information. $M_1$, $M_2$ are fed with triplets of frames ($I(t-1)$, $I(t)$, $I(t+1)$) to produce the segmentation for $I(t)$. Results: The proposed method was evaluated using a custom dataset of 11 videos (2,673 frames) which were collected and manually annotated from 6 patients. We obtain a Dice similarity coefficient of 0.80, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods. Conclusion: The obtained results show that spatial-temporal information can be effectively exploited by the ensemble model to improve hollow lumen segmentation in ureteroscopic images. The method is effective also in presence of poor visibility, occasional bleeding, or specular reflections.
A Lumen Segmentation Method in Ureteroscopy Images based on a Deep Residual U-Net architecture
Jan 13, 2021



Abstract:Ureteroscopy is becoming the first surgical treatment option for the majority of urinary affections. This procedure is performed using an endoscope which provides the surgeon with the visual information necessary to navigate inside the urinary tract. Having in mind the development of surgical assistance systems, that could enhance the performance of surgeon, the task of lumen segmentation is a fundamental part since this is the visual reference which marks the path that the endoscope should follow. This is something that has not been analyzed in ureteroscopy data before. However, this task presents several challenges given the image quality and the conditions itself of ureteroscopy procedures. In this paper, we study the implementation of a Deep Neural Network which exploits the advantage of residual units in an architecture based on U-Net. For the training of these networks, we analyze the use of two different color spaces: gray-scale and RGB data images. We found that training on gray-scale images gives the best results obtaining mean values of Dice Score, Precision, and Recall of 0.73, 0.58, and 0.92 respectively. The results obtained shows that the use of residual U-Net could be a suitable model for further development for a computer-aided system for navigation and guidance through the urinary system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge