Michael Toss
SlideGraph+: Whole Slide Image Level Graphs to Predict HER2Status in Breast Cancer
Oct 12, 2021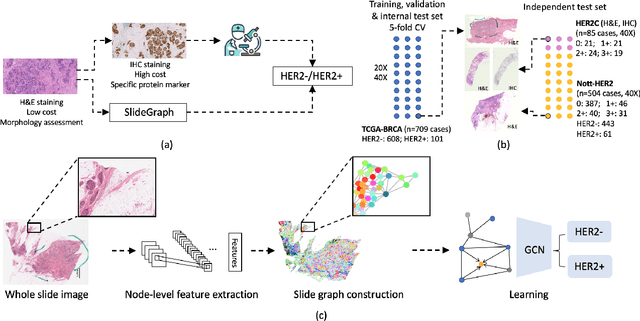
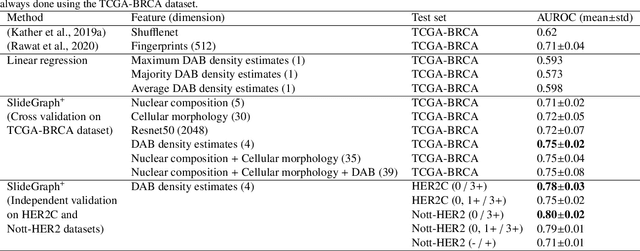
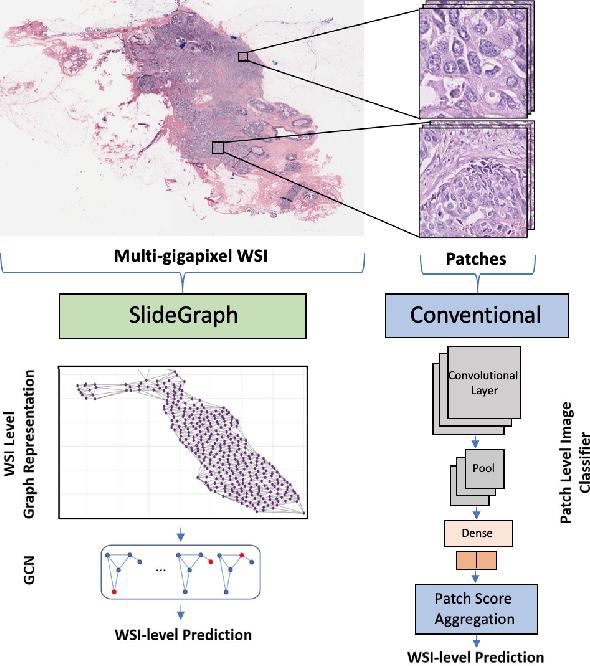

Abstract:Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is an important prognostic and predictive factor which is overexpressed in 15-20% of breast cancer (BCa). The determination of its status is a key clinical decision making step for selection of treatment regimen and prognostication. HER2 status is evaluated using transcroptomics or immunohistochemistry (IHC) through situ hybridisation (ISH) which require additional costs and tissue burden in addition to analytical variabilities in terms of manual observational biases in scoring. In this study, we propose a novel graph neural network (GNN) based model (termed SlideGraph+) to predict HER2 status directly from whole-slide images of routine Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) slides. The network was trained and tested on slides from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) in addition to two independent test datasets. We demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods with area under the ROC curve (AUC) values > 0.75 on TCGA and 0.8 on independent test sets. Our experiments show that the proposed approach can be utilised for case triaging as well as pre-ordering diagnostic tests in a diagnostic setting. It can also be used for other weakly supervised prediction problems in computational pathology. The SlideGraph+ code is available at https://github.com/wenqi006/SlideGraph.
Semantic annotation for computational pathology: Multidisciplinary experience and best practice recommendations
Jun 25, 2021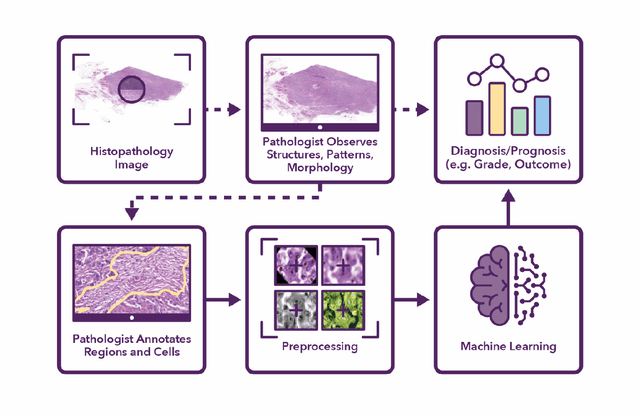

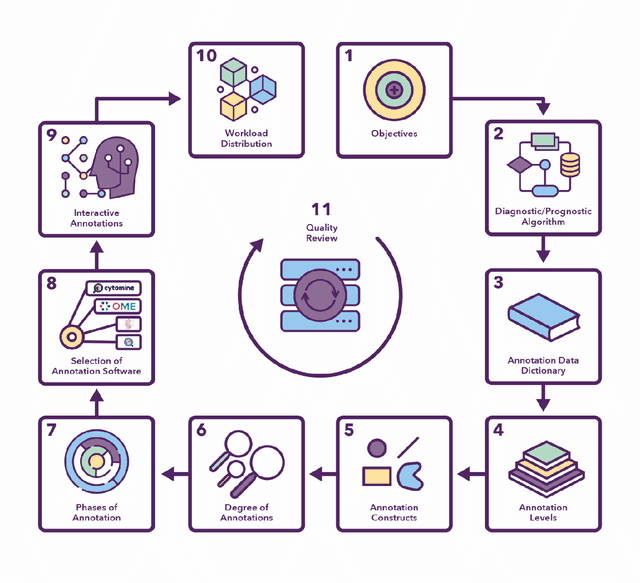
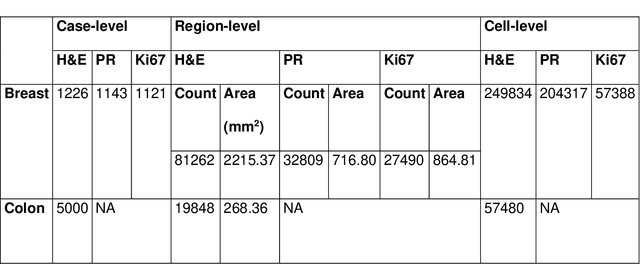
Abstract:Recent advances in whole slide imaging (WSI) technology have led to the development of a myriad of computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) based diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive algorithms. Computational Pathology (CPath) offers an integrated solution to utilize information embedded in pathology WSIs beyond what we obtain through visual assessment. For automated analysis of WSIs and validation of machine learning (ML) models, annotations at the slide, tissue and cellular levels are required. The annotation of important visual constructs in pathology images is an important component of CPath projects. Improper annotations can result in algorithms which are hard to interpret and can potentially produce inaccurate and inconsistent results. Despite the crucial role of annotations in CPath projects, there are no well-defined guidelines or best practices on how annotations should be carried out. In this paper, we address this shortcoming by presenting the experience and best practices acquired during the execution of a large-scale annotation exercise involving a multidisciplinary team of pathologists, ML experts and researchers as part of the Pathology image data Lake for Analytics, Knowledge and Education (PathLAKE) consortium. We present a real-world case study along with examples of different types of annotations, diagnostic algorithm, annotation data dictionary and annotation constructs. The analyses reported in this work highlight best practice recommendations that can be used as annotation guidelines over the lifecycle of a CPath project.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge