Michael S. Lew
Integrating Information Theory and Adversarial Learning for Cross-modal Retrieval
Apr 11, 2021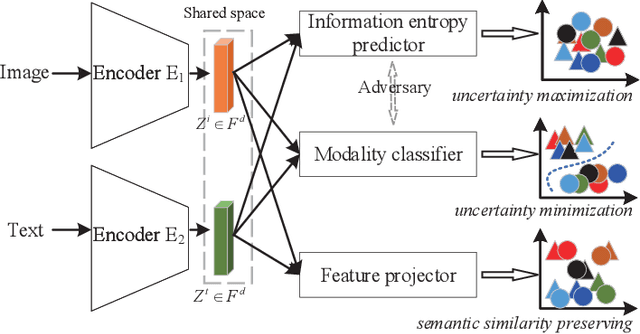
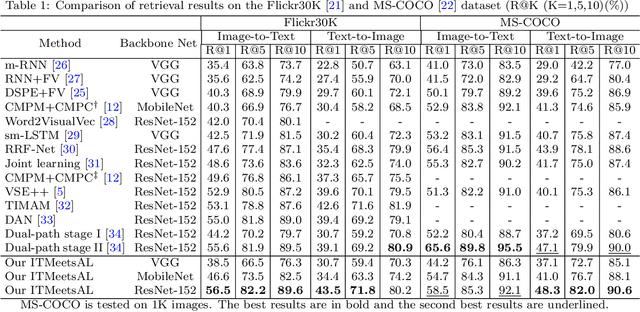
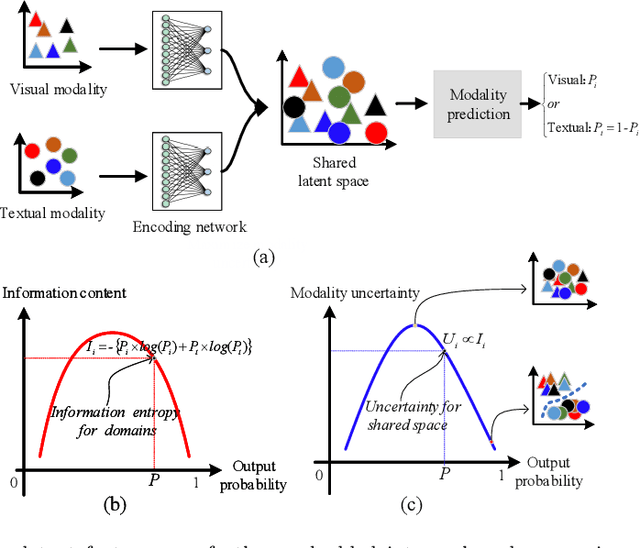
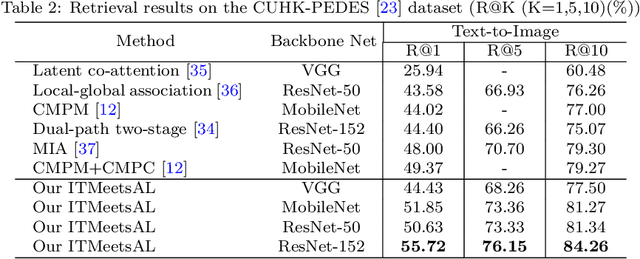
Abstract:Accurately matching visual and textual data in cross-modal retrieval has been widely studied in the multimedia community. To address these challenges posited by the heterogeneity gap and the semantic gap, we propose integrating Shannon information theory and adversarial learning. In terms of the heterogeneity gap, we integrate modality classification and information entropy maximization adversarially. For this purpose, a modality classifier (as a discriminator) is built to distinguish the text and image modalities according to their different statistical properties. This discriminator uses its output probabilities to compute Shannon information entropy, which measures the uncertainty of the modality classification it performs. Moreover, feature encoders (as a generator) project uni-modal features into a commonly shared space and attempt to fool the discriminator by maximizing its output information entropy. Thus, maximizing information entropy gradually reduces the distribution discrepancy of cross-modal features, thereby achieving a domain confusion state where the discriminator cannot classify two modalities confidently. To reduce the semantic gap, Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence and bi-directional triplet loss are used to associate the intra- and inter-modality similarity between features in the shared space. Furthermore, a regularization term based on KL-divergence with temperature scaling is used to calibrate the biased label classifier caused by the data imbalance issue. Extensive experiments with four deep models on four benchmarks are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Lifelong Person Re-Identification via Adaptive Knowledge Accumulation
Mar 23, 2021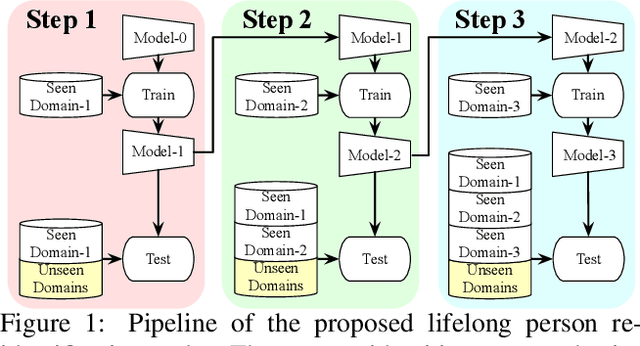
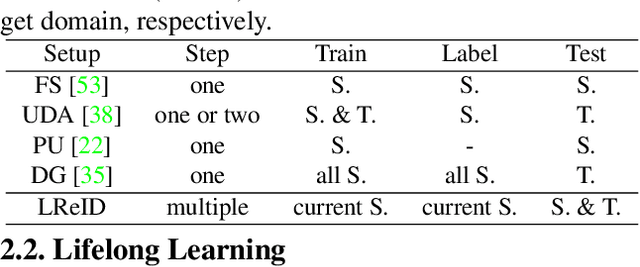
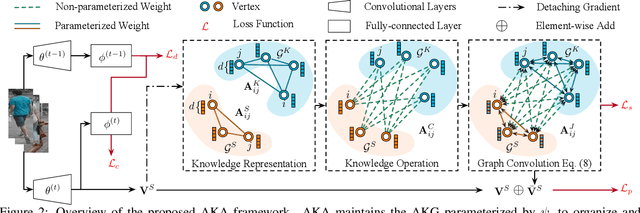
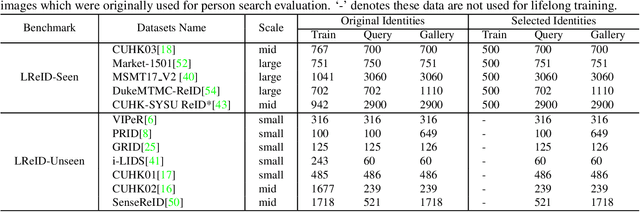
Abstract:Person ReID methods always learn through a stationary domain that is fixed by the choice of a given dataset. In many contexts (e.g., lifelong learning), those methods are ineffective because the domain is continually changing in which case incremental learning over multiple domains is required potentially. In this work we explore a new and challenging ReID task, namely lifelong person re-identification (LReID), which enables to learn continuously across multiple domains and even generalise on new and unseen domains. Following the cognitive processes in the human brain, we design an Adaptive Knowledge Accumulation (AKA) framework that is endowed with two crucial abilities: knowledge representation and knowledge operation. Our method alleviates catastrophic forgetting on seen domains and demonstrates the ability to generalize to unseen domains. Correspondingly, we also provide a new and large-scale benchmark for LReID. Extensive experiments demonstrate our method outperforms other competitors by a margin of 5.8% mAP in generalising evaluation.
Deep Image Retrieval: A Survey
Feb 03, 2021



Abstract:In recent years a vast amount of visual content has been generated and shared from various fields, such as social media platforms, medical images, and robotics. This abundance of content creation and sharing has introduced new challenges. In particular, searching databases for similar content, i.e.content based image retrieval (CBIR), is a long-established research area, and more efficient and accurate methods are needed for real time retrieval. Artificial intelligence has made progress in CBIR and has significantly facilitated the process of intelligent search. In this survey we organize and review recent CBIR works that are developed based on deep learning algorithms and techniques, including insights and techniques from recent papers. We identify and present the commonly-used benchmarks and evaluation methods used in the field. We collect common challenges and propose promising future directions. More specifically, we focus on image retrieval with deep learning and organize the state of the art methods according to the types of deep network structure, deep features, feature enhancement methods, and network fine-tuning strategies. Our survey considers a wide variety of recent methods, aiming to promote a global view of the field of instance-based CBIR.
New Ideas and Trends in Deep Multimodal Content Understanding: A Review
Oct 16, 2020



Abstract:The focus of this survey is on the analysis of two modalities of multimodal deep learning: image and text. Unlike classic reviews of deep learning where monomodal image classifiers such as VGG, ResNet and Inception module are central topics, this paper will examine recent multimodal deep models and structures, including auto-encoders, generative adversarial nets and their variants. These models go beyond the simple image classifiers in which they can do uni-directional (e.g. image captioning, image generation) and bi-directional (e.g. cross-modal retrieval, visual question answering) multimodal tasks. Besides, we analyze two aspects of the challenge in terms of better content understanding in deep multimodal applications. We then introduce current ideas and trends in deep multimodal feature learning, such as feature embedding approaches and objective function design, which are crucial in overcoming the aforementioned challenges. Finally, we include several promising directions for future research.
Dual Gaussian-based Variational Subspace Disentanglement for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Aug 06, 2020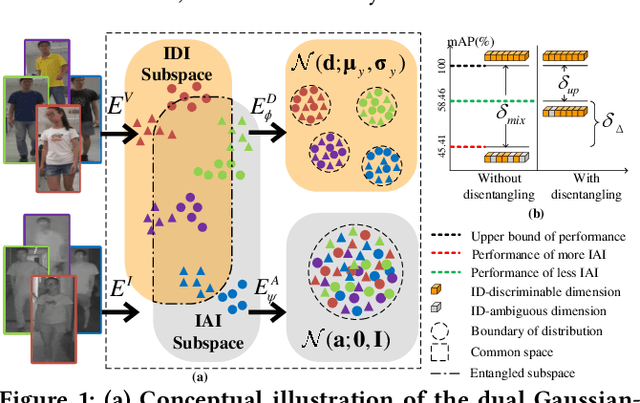
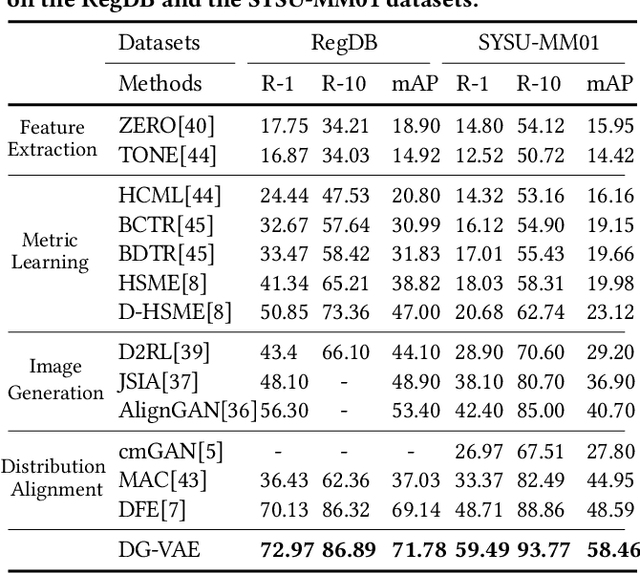
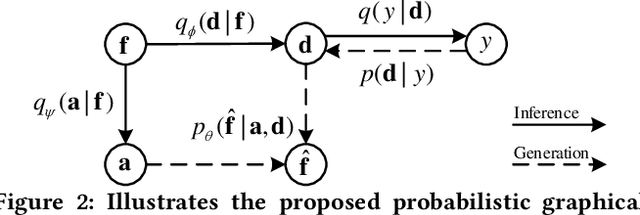
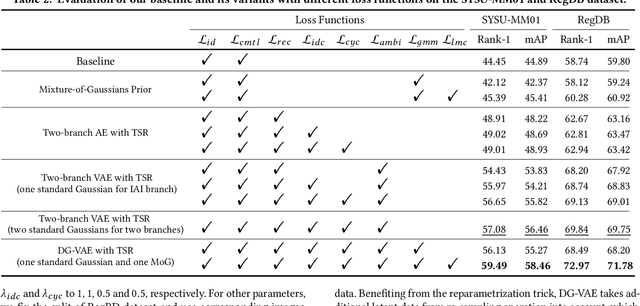
Abstract:Visible-infrared person re-identification (VI-ReID) is a challenging and essential task in night-time intelligent surveillance systems. Except for the intra-modality variance that RGB-RGB person re-identification mainly overcomes, VI-ReID suffers from additional inter-modality variance caused by the inherent heterogeneous gap. To solve the problem, we present a carefully designed dual Gaussian-based variational auto-encoder (DG-VAE), which disentangles an identity-discriminable and an identity-ambiguous cross-modality feature subspace, following a mixture-of-Gaussians (MoG) prior and a standard Gaussian distribution prior, respectively. Disentangling cross-modality identity-discriminable features leads to more robust retrieval for VI-ReID. To achieve efficient optimization like conventional VAE, we theoretically derive two variational inference terms for the MoG prior under the supervised setting, which not only restricts the identity-discriminable subspace so that the model explicitly handles the cross-modality intra-identity variance, but also enables the MoG distribution to avoid posterior collapse. Furthermore, we propose a triplet swap reconstruction (TSR) strategy to promote the above disentangling process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on two VI-ReID datasets.
On the Exploration of Convolutional Fusion Networks for Visual Recognition
Nov 16, 2016



Abstract:Despite recent advances in multi-scale deep representations, their limitations are attributed to expensive parameters and weak fusion modules. Hence, we propose an efficient approach to fuse multi-scale deep representations, called convolutional fusion networks (CFN). Owing to using 1$\times$1 convolution and global average pooling, CFN can efficiently generate the side branches while adding few parameters. In addition, we present a locally-connected fusion module, which can learn adaptive weights for the side branches and form a discriminatively fused feature. CFN models trained on the CIFAR and ImageNet datasets demonstrate remarkable improvements over the plain CNNs. Furthermore, we generalize CFN to three new tasks, including scene recognition, fine-grained recognition and image retrieval. Our experiments show that it can obtain consistent improvements towards the transferring tasks.
Binary and nonbinary description of hypointensity in human brain MR images
Dec 31, 2010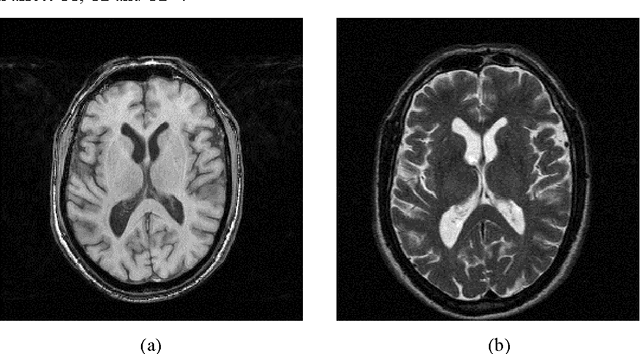
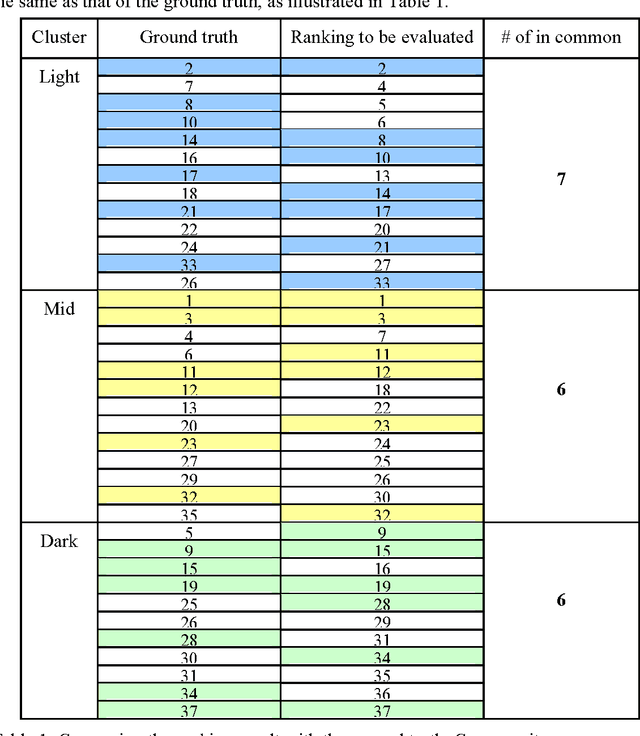
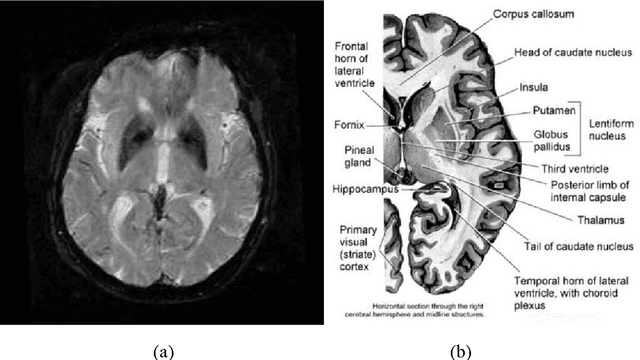
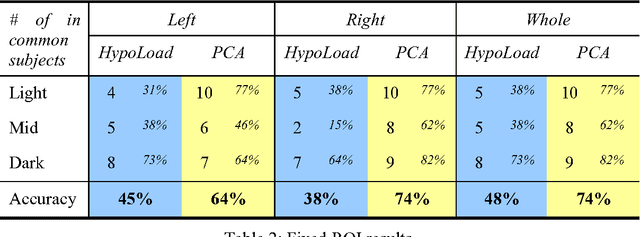
Abstract:Accumulating evidence has shown that iron is involved in the mechanism underlying many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease. Abnormal (higher) iron accumulation has been detected in the brains of most neurodegenerative patients, especially in the basal ganglia region. Presence of iron leads to changes in MR signal in both magnitude and phase. Accordingly, tissues with high iron concentration appear hypo-intense (darker than usual) in MR contrasts. In this report, we proposed an improved binary hypointensity description and a novel nonbinary hypointensity description based on principle components analysis. Moreover, Kendall's rank correlation coefficient was used to compare the complementary and redundant information provided by the two methods in order to better understand the individual descriptions of iron accumulation in the brain.
A Framework for Real-Time Face and Facial Feature Tracking using Optical Flow Pre-estimation and Template Tracking
Dec 31, 2010



Abstract:This work presents a framework for tracking head movements and capturing the movements of the mouth and both the eyebrows in real-time. We present a head tracker which is a combination of a optical flow and a template based tracker. The estimation of the optical flow head tracker is used as starting point for the template tracker which fine-tunes the head estimation. This approach together with re-updating the optical flow points prevents the head tracker from drifting. This combination together with our switching scheme, makes our tracker very robust against fast movement and motion-blur. We also propose a way to reduce the influence of partial occlusion of the head. In both the optical flow and the template based tracker we identify and exclude occluded points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge