Michael Pürrer
Real-time gravitational-wave inference for binary neutron stars using machine learning
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Mergers of binary neutron stars (BNSs) emit signals in both the gravitational-wave (GW) and electromagnetic (EM) spectra. Famously, the 2017 multi-messenger observation of GW170817 led to scientific discoveries across cosmology, nuclear physics, and gravity. Central to these results were the sky localization and distance obtained from GW data, which, in the case of GW170817, helped to identify the associated EM transient, AT 2017gfo, 11 hours after the GW signal. Fast analysis of GW data is critical for directing time-sensitive EM observations; however, due to challenges arising from the length and complexity of signals, it is often necessary to make approximations that sacrifice accuracy. Here, we develop a machine learning approach that performs complete BNS inference in just one second without making any such approximations. This is enabled by a new method for explicit integration of physical domain knowledge into neural networks. Our approach enhances multi-messenger observations by providing (i) accurate localization even before the merger; (ii) improved localization precision by $\sim30\%$ compared to approximate low-latency methods; and (iii) detailed information on luminosity distance, inclination, and masses, which can be used to prioritize expensive telescope time. Additionally, the flexibility and reduced cost of our method open new opportunities for equation-of-state and waveform systematics studies. Finally, we demonstrate that our method scales to extremely long signals, up to an hour in length, thus serving as a blueprint for data analysis for next-generation ground- and space-based detectors.
Adapting to noise distribution shifts in flow-based gravitational-wave inference
Nov 16, 2022



Abstract:Deep learning techniques for gravitational-wave parameter estimation have emerged as a fast alternative to standard samplers $\unicode{x2013}$ producing results of comparable accuracy. These approaches (e.g., DINGO) enable amortized inference by training a normalizing flow to represent the Bayesian posterior conditional on observed data. By conditioning also on the noise power spectral density (PSD) they can even account for changing detector characteristics. However, training such networks requires knowing in advance the distribution of PSDs expected to be observed, and therefore can only take place once all data to be analyzed have been gathered. Here, we develop a probabilistic model to forecast future PSDs, greatly increasing the temporal scope of DINGO networks. Using PSDs from the second LIGO-Virgo observing run (O2) $\unicode{x2013}$ plus just a single PSD from the beginning of the third (O3) $\unicode{x2013}$ we show that we can train a DINGO network to perform accurate inference throughout O3 (on 37 real events). We therefore expect this approach to be a key component to enable the use of deep learning techniques for low-latency analyses of gravitational waves.
Neural Importance Sampling for Rapid and Reliable Gravitational-Wave Inference
Oct 11, 2022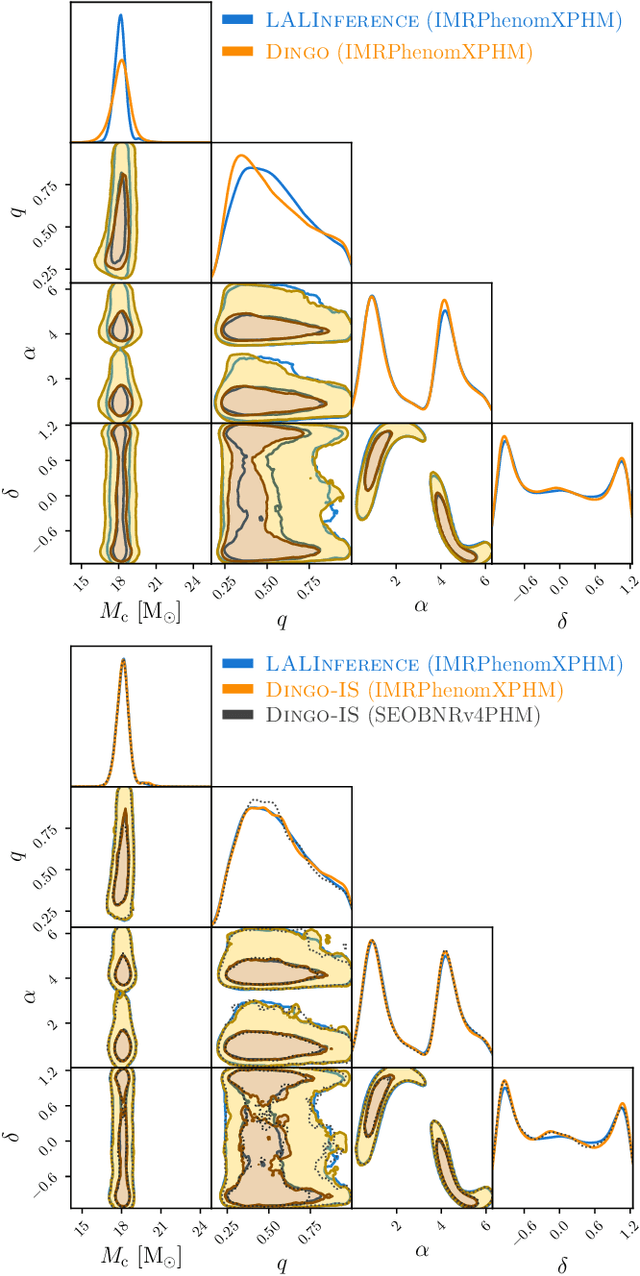
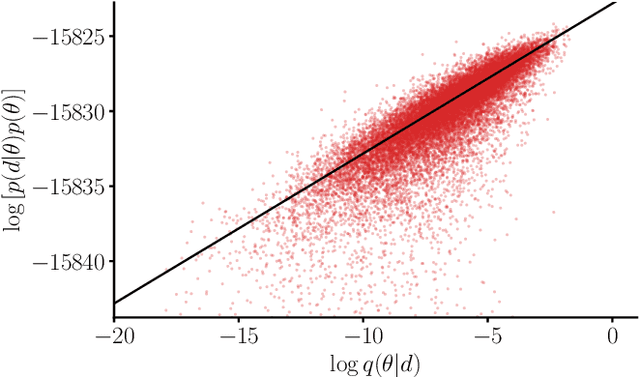
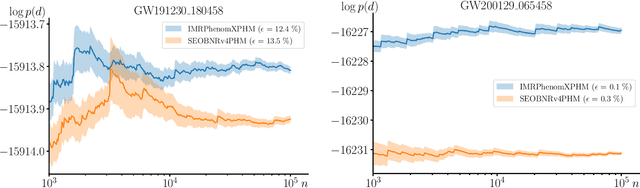
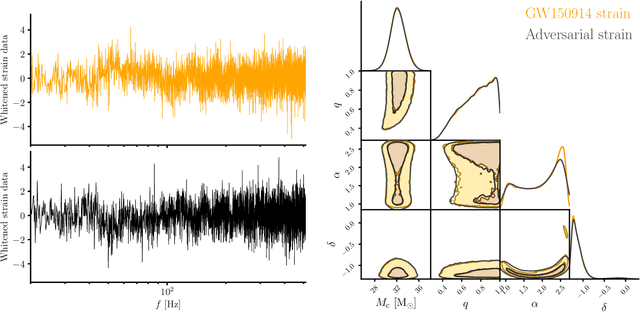
Abstract:We combine amortized neural posterior estimation with importance sampling for fast and accurate gravitational-wave inference. We first generate a rapid proposal for the Bayesian posterior using neural networks, and then attach importance weights based on the underlying likelihood and prior. This provides (1) a corrected posterior free from network inaccuracies, (2) a performance diagnostic (the sample efficiency) for assessing the proposal and identifying failure cases, and (3) an unbiased estimate of the Bayesian evidence. By establishing this independent verification and correction mechanism we address some of the most frequent criticisms against deep learning for scientific inference. We carry out a large study analyzing 42 binary black hole mergers observed by LIGO and Virgo with the SEOBNRv4PHM and IMRPhenomXPHM waveform models. This shows a median sample efficiency of $\approx 10\%$ (two orders-of-magnitude better than standard samplers) as well as a ten-fold reduction in the statistical uncertainty in the log evidence. Given these advantages, we expect a significant impact on gravitational-wave inference, and for this approach to serve as a paradigm for harnessing deep learning methods in scientific applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge