Michael Kishinevsky
Automatic Microprocessor Performance Bug Detection
Nov 19, 2020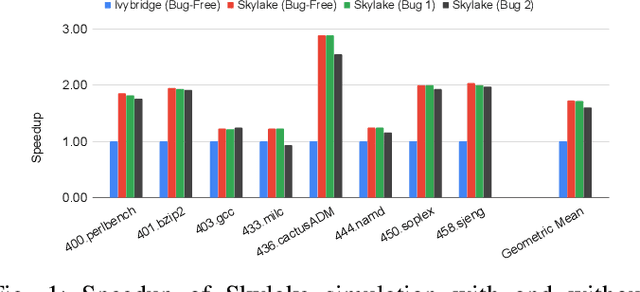
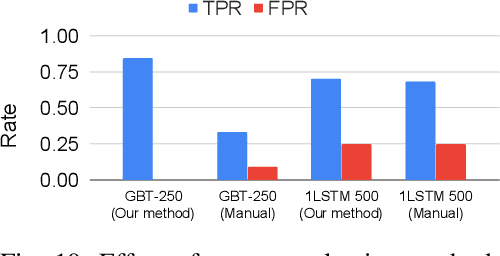
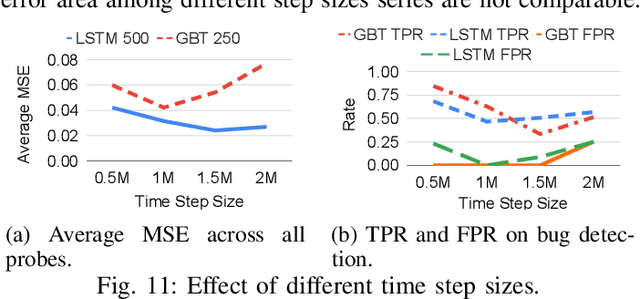
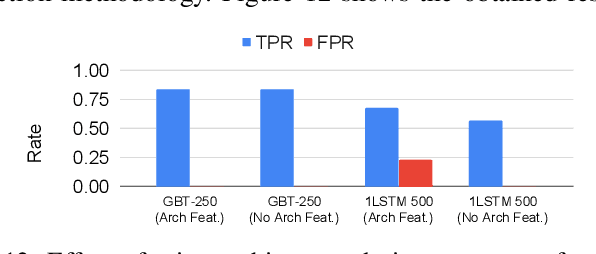
Abstract:Processor design validation and debug is a difficult and complex task, which consumes the lion's share of the design process. Design bugs that affect processor performance rather than its functionality are especially difficult to catch, particularly in new microarchitectures. This is because, unlike functional bugs, the correct processor performance of new microarchitectures on complex, long-running benchmarks is typically not deterministically known. Thus, when performance benchmarking new microarchitectures, performance teams may assume that the design is correct when the performance of the new microarchitecture exceeds that of the previous generation, despite significant performance regressions existing in the design. In this work, we present a two-stage, machine learning-based methodology that is able to detect the existence of performance bugs in microprocessors. Our results show that our best technique detects 91.5% of microprocessor core performance bugs whose average IPC impact across the studied applications is greater than 1% versus a bug-free design with zero false positives. When evaluated on memory system bugs, our technique achieves 100% detection with zero false positives. Moreover, the detection is automatic, requiring very little performance engineer time.
Online Adaptive Learning for Runtime Resource Management of Heterogeneous SoCs
Aug 22, 2020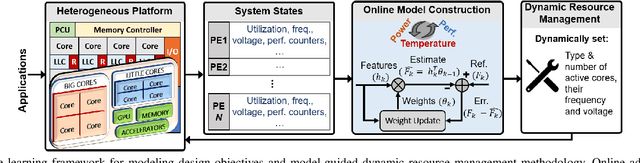
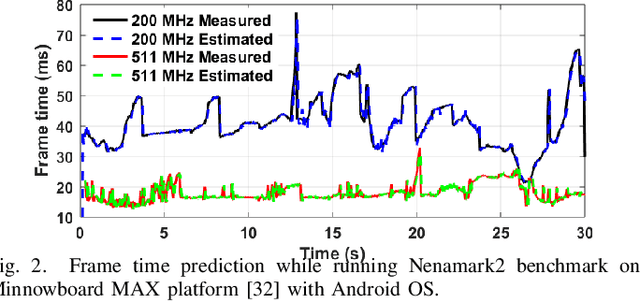
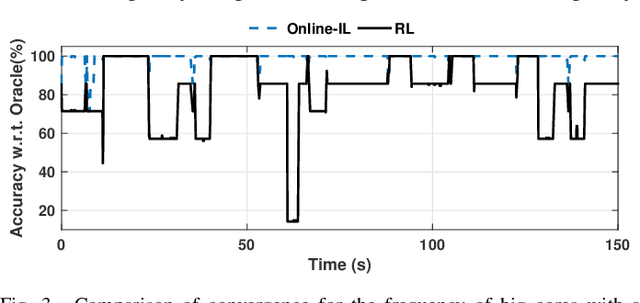
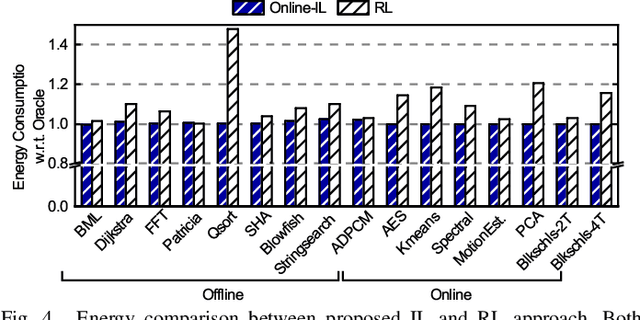
Abstract:Dynamic resource management has become one of the major areas of research in modern computer and communication system design due to lower power consumption and higher performance demands. The number of integrated cores, level of heterogeneity and amount of control knobs increase steadily. As a result, the system complexity is increasing faster than our ability to optimize and dynamically manage the resources. Moreover, offline approaches are sub-optimal due to workload variations and large volume of new applications unknown at design time. This paper first reviews recent online learning techniques for predicting system performance, power, and temperature. Then, we describe the use of predictive models for online control using two modern approaches: imitation learning (IL) and an explicit nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC). Evaluations on a commercial mobile platform with 16 benchmarks show that the IL approach successfully adapts the control policy to unknown applications. The explicit NMPC provides 25% energy savings compared to a state-of-the-art algorithm for multi-variable power management of modern GPU sub-systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge