Mahesh Ketkar
Automatic Microprocessor Performance Bug Detection
Nov 19, 2020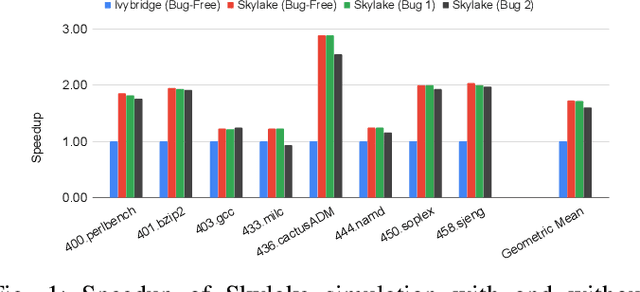
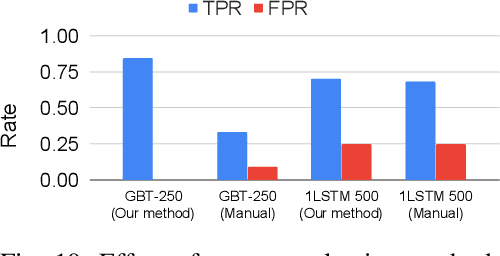
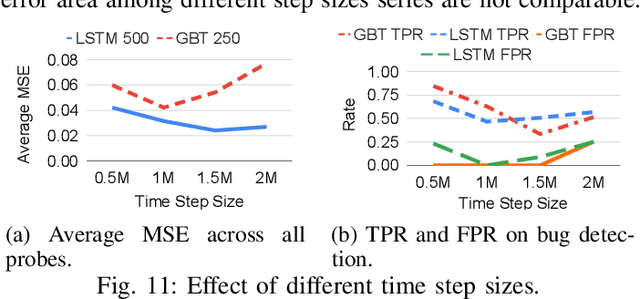
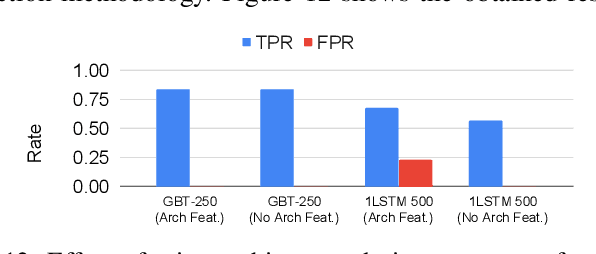
Abstract:Processor design validation and debug is a difficult and complex task, which consumes the lion's share of the design process. Design bugs that affect processor performance rather than its functionality are especially difficult to catch, particularly in new microarchitectures. This is because, unlike functional bugs, the correct processor performance of new microarchitectures on complex, long-running benchmarks is typically not deterministically known. Thus, when performance benchmarking new microarchitectures, performance teams may assume that the design is correct when the performance of the new microarchitecture exceeds that of the previous generation, despite significant performance regressions existing in the design. In this work, we present a two-stage, machine learning-based methodology that is able to detect the existence of performance bugs in microprocessors. Our results show that our best technique detects 91.5% of microprocessor core performance bugs whose average IPC impact across the studied applications is greater than 1% versus a bug-free design with zero false positives. When evaluated on memory system bugs, our technique achieves 100% detection with zero false positives. Moreover, the detection is automatic, requiring very little performance engineer time.
Mining Message Flows using Recurrent Neural Networks for System-on-Chip Designs
Apr 29, 2020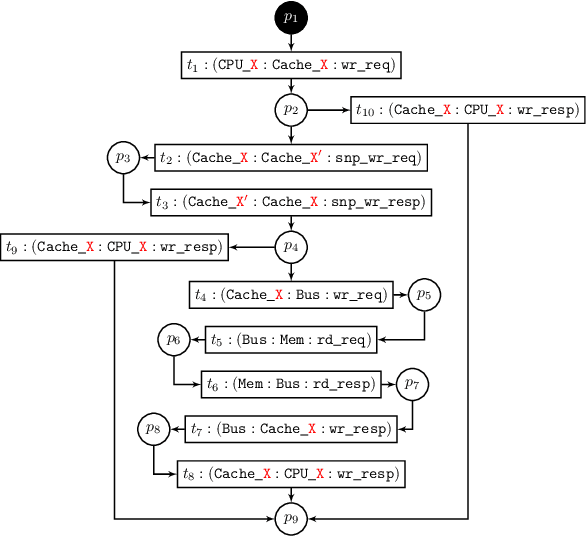
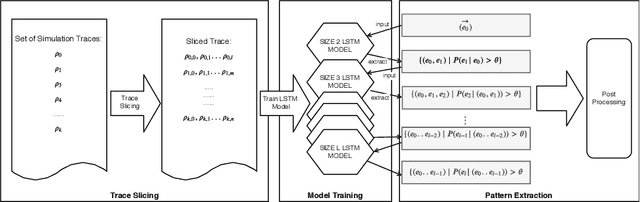
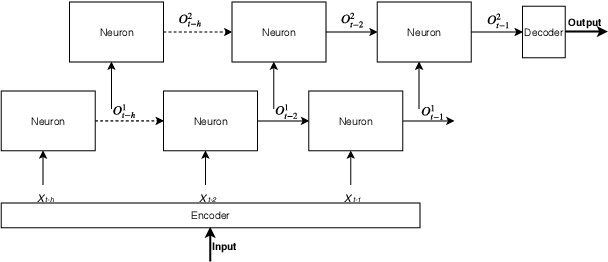
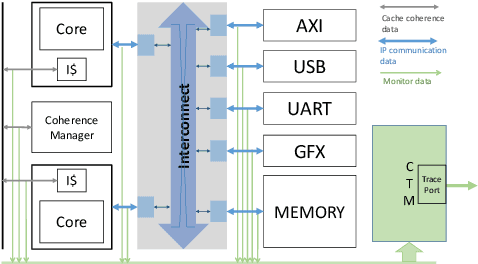
Abstract:Comprehensive specifications are essential for various activities across the entire validation continuum for system-on-chip (SoC) designs. However, specifications are often ambiguous, incomplete, or even contain inconsistencies or errors. This paper addresses this problem by developing a specification mining approach that automatically extracts sequential patterns from SoC transaction-level traces such that the mined patterns collectively characterize system-level specifications for SoC designs. This approach exploits long short-term memory (LSTM) networks trained with the collected SoC execution traces to capture sequential dependencies among various communication events. Then, a novel algorithm is developed to efficiently extract sequential patterns on system-level communications from the trained LSTM models. Several trace processing techniques are also proposed to enhance the mining performance. We evaluate the proposed approach on simulation traces of a non-trivial multi-core SoC prototype. Initial results show that the proposed approach is capable of extracting various patterns on system-level specifications from the highly concurrent SoC execution traces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge