Meirong Ma
CPNet: Exploiting CLIP-based Attention Condenser and Probability Map Guidance for High-fidelity Talking Face Generation
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Recently, talking face generation has drawn ever-increasing attention from the research community in computer vision due to its arduous challenges and widespread application scenarios, e.g. movie animation and virtual anchor. Although persevering efforts have been undertaken to enhance the fidelity and lip-sync quality of generated talking face videos, there is still large room for further improvements of synthesis quality and efficiency. Actually, these attempts somewhat ignore the explorations of fine-granularity feature extraction/integration and the consistency between probability distributions of landmarks, thereby recurring the issues of local details blurring and degraded fidelity. To mitigate these dilemmas, in this paper, a novel CLIP-based Attention and Probability Map Guided Network (CPNet) is delicately designed for inferring high-fidelity talking face videos. Specifically, considering the demands of fine-grained feature recalibration, a clip-based attention condenser is exploited to transfer knowledge with rich semantic priors from the prevailing CLIP model. Moreover, to guarantee the consistency in probability space and suppress the landmark ambiguity, we creatively propose the density map of facial landmark as auxiliary supervisory signal to guide the landmark distribution learning of generated frame. Extensive experiments on the widely-used benchmark dataset demonstrate the superiority of our CPNet against state of the arts in terms of image and lip-sync quality. In addition, a cohort of studies are also conducted to ablate the impacts of the individual pivotal components.
Prompt-based Connective Prediction Method for Fine-grained Implicit Discourse Relation Recognition
Oct 16, 2022

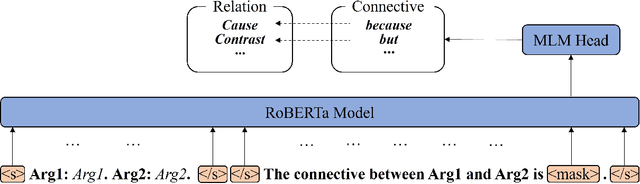
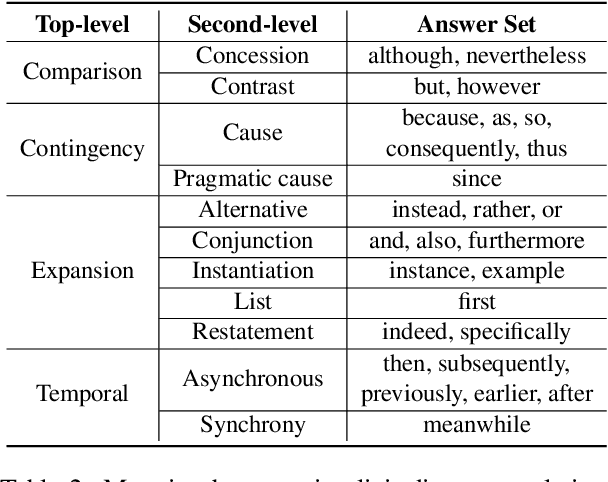
Abstract:Due to the absence of connectives, implicit discourse relation recognition (IDRR) is still a challenging and crucial task in discourse analysis. Most of the current work adopted multi-task learning to aid IDRR through explicit discourse relation recognition (EDRR) or utilized dependencies between discourse relation labels to constrain model predictions. But these methods still performed poorly on fine-grained IDRR and even utterly misidentified on most of the few-shot discourse relation classes. To address these problems, we propose a novel Prompt-based Connective Prediction (PCP) method for IDRR. Our method instructs large-scale pre-trained models to use knowledge relevant to discourse relation and utilizes the strong correlation between connectives and discourse relation to help the model recognize implicit discourse relations. Experimental results show that our method surpasses the current state-of-the-art model and achieves significant improvements on those fine-grained few-shot discourse relation. Moreover, our approach is able to be transferred to EDRR and obtain acceptable results. Our code is released in https://github.com/zh-i9/PCP-for-IDRR.
A Simple Temporal Information Matching Mechanism for Entity Alignment Between Temporal Knowledge Graphs
Sep 20, 2022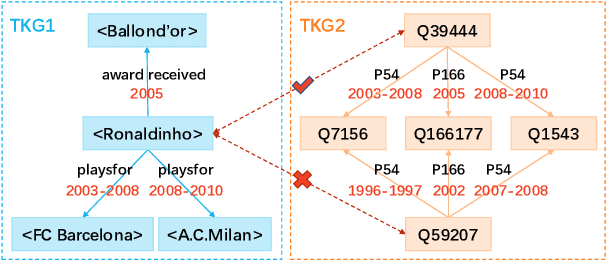
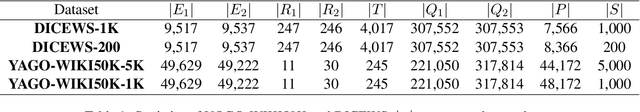
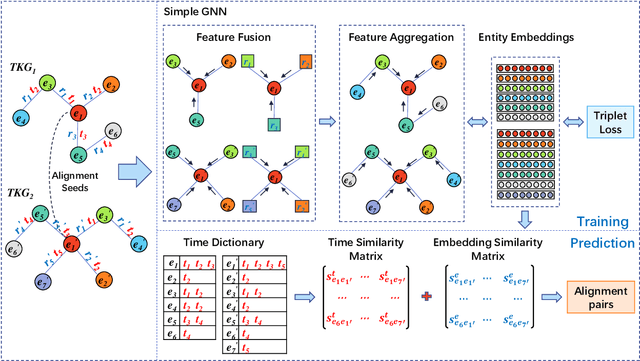
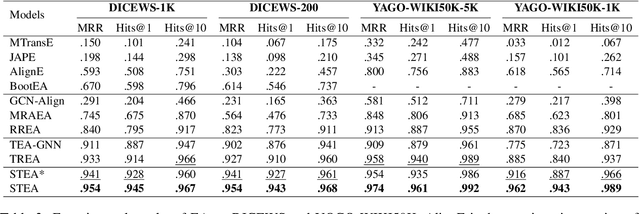
Abstract:Entity alignment (EA) aims to find entities in different knowledge graphs (KGs) that refer to the same object in the real world. Recent studies incorporate temporal information to augment the representations of KGs. The existing methods for EA between temporal KGs (TKGs) utilize a time-aware attention mechanism to incorporate relational and temporal information into entity embeddings. The approaches outperform the previous methods by using temporal information. However, we believe that it is not necessary to learn the embeddings of temporal information in KGs since most TKGs have uniform temporal representations. Therefore, we propose a simple graph neural network (GNN) model combined with a temporal information matching mechanism, which achieves better performance with less time and fewer parameters. Furthermore, since alignment seeds are difficult to label in real-world applications, we also propose a method to generate unsupervised alignment seeds via the temporal information of TKG. Extensive experiments on public datasets indicate that our supervised method significantly outperforms the previous methods and the unsupervised one has competitive performance.
A Dual-Attention Neural Network for Pun Location and Using Pun-Gloss Pairs for Interpretation
Oct 14, 2021

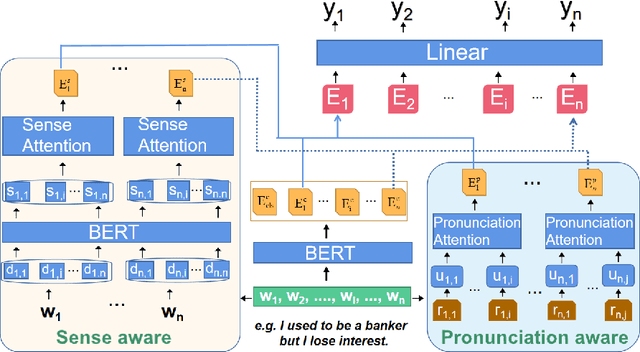
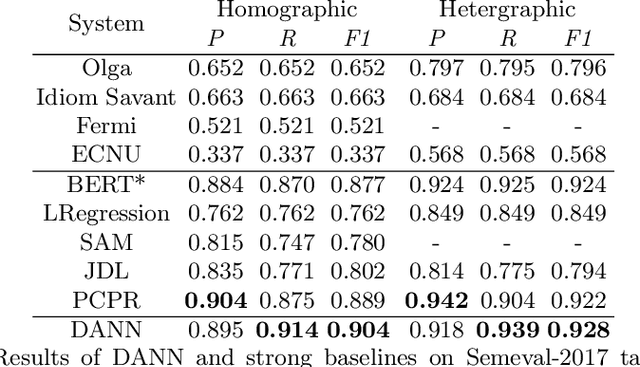
Abstract:Pun location is to identify the punning word (usually a word or a phrase that makes the text ambiguous) in a given short text, and pun interpretation is to find out two different meanings of the punning word. Most previous studies adopt limited word senses obtained by WSD(Word Sense Disambiguation) technique or pronunciation information in isolation to address pun location. For the task of pun interpretation, related work pays attention to various WSD algorithms. In this paper, a model called DANN (Dual-Attentive Neural Network) is proposed for pun location, effectively integrates word senses and pronunciation with context information to address two kinds of pun at the same time. Furthermore, we treat pun interpretation as a classification task and construct pungloss pairs as processing data to solve this task. Experiments on the two benchmark datasets show that our proposed methods achieve new state-of-the-art results. Our source code is available in the public code repository.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge