Mei Qiu
Lane-Wise Highway Anomaly Detection
May 05, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a scalable and interpretable framework for lane-wise highway traffic anomaly detection, leveraging multi-modal time series data extracted from surveillance cameras. Unlike traditional sensor-dependent methods, our approach uses AI-powered vision models to extract lane-specific features, including vehicle count, occupancy, and truck percentage, without relying on costly hardware or complex road modeling. We introduce a novel dataset containing 73,139 lane-wise samples, annotated with four classes of expert-validated anomalies: three traffic-related anomalies (lane blockage and recovery, foreign object intrusion, and sustained congestion) and one sensor-related anomaly (camera angle shift). Our multi-branch detection system integrates deep learning, rule-based logic, and machine learning to improve robustness and precision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in precision, recall, and F1-score, providing a cost-effective and scalable solution for real-world intelligent transportation systems.
Towards Predicting the Success of Transfer-based Attacks by Quantifying Shared Feature Representations
Dec 06, 2024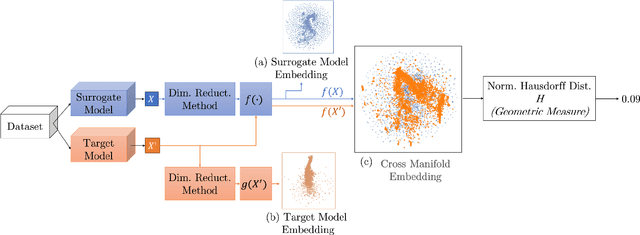
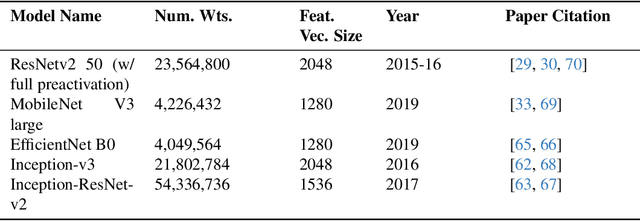
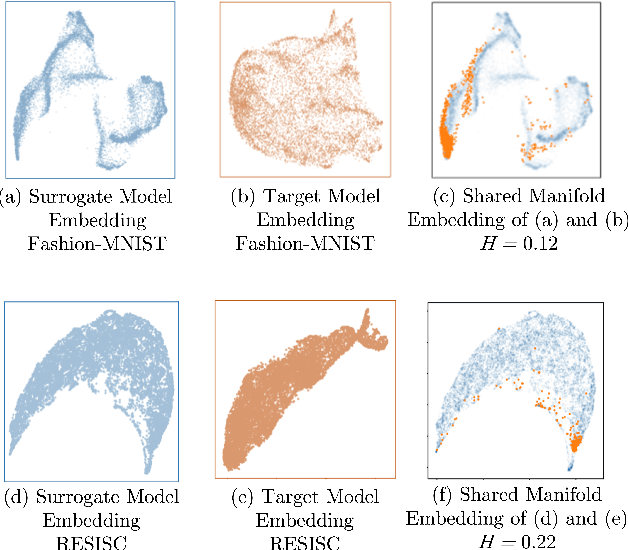
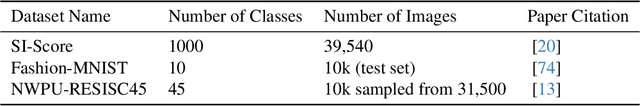
Abstract:Much effort has been made to explain and improve the success of transfer-based attacks (TBA) on black-box computer vision models. This work provides the first attempt at a priori prediction of attack success by identifying the presence of vulnerable features within target models. Recent work by Chen and Liu (2024) proposed the manifold attack model, a unifying framework proposing that successful TBA exist in a common manifold space. Our work experimentally tests the common manifold space hypothesis by a new methodology: first, projecting feature vectors from surrogate and target feature extractors trained on ImageNet onto the same low-dimensional manifold; second, quantifying any observed structure similarities on the manifold; and finally, by relating these observed similarities to the success of the TBA. We find that shared feature representation moderately correlates with increased success of TBA (\r{ho}= 0.56). This method may be used to predict whether an attack will transfer without information of the model weights, training, architecture or details of the attack. The results confirm the presence of shared feature representations between two feature extractors of different sizes and complexities, and demonstrate the utility of datasets from different target domains as test signals for interpreting black-box feature representations.
Adaptive Aspect Ratios with Patch-Mixup-ViT-based Vehicle ReID
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown exceptional performance in vehicle re-identification (ReID) tasks. However, non-square aspect ratios of image or video inputs can negatively impact re-identification accuracy. To address this challenge, we propose a novel, human perception driven, and general ViT-based ReID framework that fuses models trained on various aspect ratios. Our key contributions are threefold: (i) We analyze the impact of aspect ratios on performance using the VeRi-776 and VehicleID datasets, providing guidance for input settings based on the distribution of original image aspect ratios. (ii) We introduce patch-wise mixup strategy during ViT patchification (guided by spatial attention scores) and implement uneven stride for better alignment with object aspect ratios. (iii) We propose a dynamic feature fusion ReID network to enhance model robustness. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art transformer-based approaches on both datasets, with only a minimal increase in inference time per image.
Optimizing ROI Benefits Vehicle ReID in ITS
Jul 13, 2024



Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (ReID) is a computer vision task that matches the same vehicle across different cameras or viewpoints in a surveillance system. This is crucial for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), where the effectiveness is influenced by the regions from which vehicle images are cropped. This study explores whether optimal vehicle detection regions, guided by detection confidence scores, can enhance feature matching and ReID tasks. Using our framework with multiple Regions of Interest (ROIs) and lane-wise vehicle counts, we employed YOLOv8 for detection and DeepSORT for tracking across twelve Indiana Highway videos, including two pairs of videos from non-overlapping cameras. Tracked vehicle images were cropped from inside and outside the ROIs at five-frame intervals. Features were extracted using pre-trained models: ResNet50, ResNeXt50, Vision Transformer, and Swin-Transformer. Feature consistency was assessed through cosine similarity, information entropy, and clustering variance. Results showed that features from images cropped inside ROIs had higher mean cosine similarity values compared to those involving one image inside and one outside the ROIs. The most significant difference was observed during night conditions (0.7842 inside vs. 0.5 outside the ROI with Swin-Transformer) and in cross-camera scenarios (0.75 inside-inside vs. 0.52 inside-outside the ROI with Vision Transformer). Information entropy and clustering variance further supported that features in ROIs are more consistent. These findings suggest that strategically selected ROIs can enhance tracking performance and ReID accuracy in ITS.
Study on Aspect Ratio Variability toward Robustness of Vision Transformer-based Vehicle Re-identification
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have excelled in vehicle re-identification (ReID) tasks. However, non-square aspect ratios of image or video input might significantly affect the re-identification performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel ViT-based ReID framework in this paper, which fuses models trained on a variety of aspect ratios. Our main contributions are threefold: (i) We analyze aspect ratio performance on VeRi-776 and VehicleID datasets, guiding input settings based on aspect ratios of original images. (ii) We introduce patch-wise mixup intra-image during ViT patchification (guided by spatial attention scores) and implement uneven stride for better object aspect ratio matching. (iii) We propose a dynamic feature fusing ReID network, enhancing model robustness. Our ReID method achieves a significantly improved mean Average Precision (mAP) of 91.0\% compared to the the closest state-of-the-art (CAL) result of 80.9\% on VehicleID dataset.
Enhancing Vehicle Re-identification and Matching for Weaving Analysis
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:Vehicle weaving on highways contributes to traffic congestion, raises safety issues, and underscores the need for sophisticated traffic management systems. Current tools are inadequate in offering precise and comprehensive data on lane-specific weaving patterns. This paper introduces an innovative method for collecting non-overlapping video data in weaving zones, enabling the generation of quantitative insights into lane-specific weaving behaviors. Our experimental results confirm the efficacy of this approach, delivering critical data that can assist transportation authorities in enhancing traffic control and roadway infrastructure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge