Mehdi Allahyari
COPER: a Query-adaptable Semantics-based Search Engine for Persian COVID-19 Articles
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:With the surge of pretrained language models, a new pathway has been opened to incorporate Persian text contextual information. Meanwhile, as many other countries, including Iran, are fighting against COVID-19, a plethora of COVID-19 related articles has been published in Iranian Healthcare magazines to better inform the public of the situation. However, finding answers in this sheer volume of information is an extremely difficult task. In this paper, we collected a large dataset of these articles, leveraged different BERT variations as well as other keyword models such as BM25 and TF-IDF, and created a search engine to sift through these documents and rank them, given a user's query. Our final search engine consists of a ranker and a re-ranker, which adapts itself to the query. We fine-tune our models using Semantic Textual Similarity and evaluate them with standard task metrics. Our final method outperforms the rest by a considerable margin.
A Comprehensive Survey of Ontology Summarization: Measures and Methods
Jan 05, 2018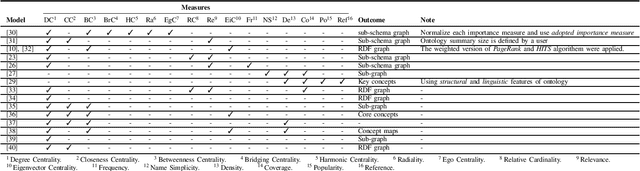
Abstract:The Semantic Web is becoming a large scale framework that enables data to be published, shared, and reused in the form of ontologies. The ontology which is considered as basic building block of semantic web consists of two layers including data and schema layer. With the current exponential development of ontologies in both data size and complexity of schemas, ontology understanding which is playing an important role in different tasks such as ontology engineering, ontology learning, etc., is becoming more difficult. Ontology summarization as a way to distill knowledge from an ontology and generate an abridge version to facilitate a better understanding is getting more attention recently. There are various approaches available for ontology summarization which are focusing on different measures in order to produce a proper summary for a given ontology. In this paper, we mainly focus on the common metrics which are using for ontology summarization and meet the state-of-the-art in ontology summarization.
Text Summarization Techniques: A Brief Survey
Jul 28, 2017Abstract:In recent years, there has been a explosion in the amount of text data from a variety of sources. This volume of text is an invaluable source of information and knowledge which needs to be effectively summarized to be useful. In this review, the main approaches to automatic text summarization are described. We review the different processes for summarization and describe the effectiveness and shortcomings of the different methods.
A Brief Survey of Text Mining: Classification, Clustering and Extraction Techniques
Jul 28, 2017
Abstract:The amount of text that is generated every day is increasing dramatically. This tremendous volume of mostly unstructured text cannot be simply processed and perceived by computers. Therefore, efficient and effective techniques and algorithms are required to discover useful patterns. Text mining is the task of extracting meaningful information from text, which has gained significant attentions in recent years. In this paper, we describe several of the most fundamental text mining tasks and techniques including text pre-processing, classification and clustering. Additionally, we briefly explain text mining in biomedical and health care domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge