Mitra Sadat Mirshafiee
Fetal Gender Identification using Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms on Phonocardiogram Signals
Oct 10, 2021


Abstract:Phonocardiogram (PCG) signal analysis is a critical, widely-studied technology to noninvasively analyze the heart's mechanical activity. Through evaluating heart sounds, this technology has been chiefly leveraged as a preliminary solution to automatically diagnose Cardiovascular diseases among adults; however, prenatal tasks such as fetal gender identification have been relatively less studied using fetal Phonocardiography (FPCG). In this work, we apply common PCG signal processing techniques on the gender-tagged Shiraz University Fetal Heart Sounds Database and study the applicability of previously proposed features in classifying fetal gender using both Machine Learning and Deep Learning models. Even though PCG data acquisition's cost-effectiveness and feasibility make it a convenient method of Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) monitoring, the contaminated nature of PCG signals with the noise of various types makes it a challenging modality. To address this problem, we experimented with both static and adaptive noise reduction techniques such as Low-pass filtering, Denoising Autoencoders, and Source Separators. We apply a wide range of previously proposed classifiers to our dataset and propose a novel ensemble method of Fetal Gender Identification (FGI). Our method substantially outperformed the baseline and reached up to 91% accuracy in classifying fetal gender of unseen subjects.
Prose2Poem: The Blessing of Transformers in Translating Prose to Persian Poetry
Oct 01, 2021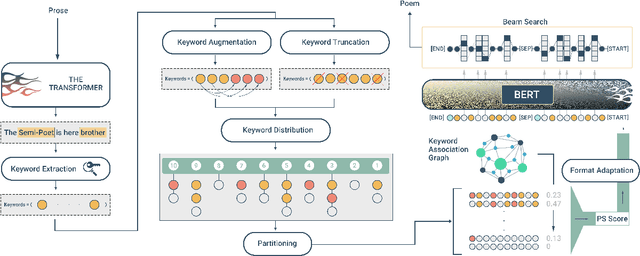
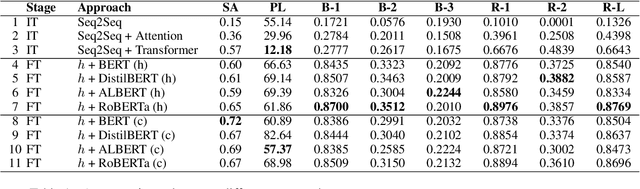

Abstract:Persian Poetry has consistently expressed its philosophy, wisdom, speech, and rationale on the basis of its couplets, making it an enigmatic language on its own to both native and non-native speakers. Nevertheless, the notice able gap between Persian prose and poem has left the two pieces of literature medium-less. Having curated a parallel corpus of prose and their equivalent poems, we introduce a novel Neural Machine Translation (NMT) approach to translate prose to ancient Persian poetry using transformer-based Language Models in an extremely low-resource setting. More specifically, we trained a Transformer model from scratch to obtain initial translations and pretrained different variations of BERT to obtain final translations. To address the challenge of using masked language modelling under poeticness criteria, we heuristically joined the two models and generated valid poems in terms of automatic and human assessments. Final results demonstrate the eligibility and creativity of our novel heuristically aided approach among Literature professionals and non-professionals in generating novel Persian poems.
COPER: a Query-adaptable Semantics-based Search Engine for Persian COVID-19 Articles
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:With the surge of pretrained language models, a new pathway has been opened to incorporate Persian text contextual information. Meanwhile, as many other countries, including Iran, are fighting against COVID-19, a plethora of COVID-19 related articles has been published in Iranian Healthcare magazines to better inform the public of the situation. However, finding answers in this sheer volume of information is an extremely difficult task. In this paper, we collected a large dataset of these articles, leveraged different BERT variations as well as other keyword models such as BM25 and TF-IDF, and created a search engine to sift through these documents and rank them, given a user's query. Our final search engine consists of a ranker and a re-ranker, which adapts itself to the query. We fine-tune our models using Semantic Textual Similarity and evaluate them with standard task metrics. Our final method outperforms the rest by a considerable margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge