Md. Rabiul Islam
Surface EMG-Based Inter-Session/Inter-Subject Gesture Recognition by Leveraging Lightweight All-ConvNet and Transfer Learning
May 13, 2023



Abstract:Gesture recognition using low-resolution instantaneous HD-sEMG images opens up new avenues for the development of more fluid and natural muscle-computer interfaces. However, the data variability between inter-session and inter-subject scenarios presents a great challenge. The existing approaches employed very large and complex deep ConvNet or 2SRNN-based domain adaptation methods to approximate the distribution shift caused by these inter-session and inter-subject data variability. Hence, these methods also require learning over millions of training parameters and a large pre-trained and target domain dataset in both the pre-training and adaptation stages. As a result, it makes high-end resource-bounded and computationally very expensive for deployment in real-time applications. To overcome this problem, we propose a lightweight All-ConvNet+TL model that leverages lightweight All-ConvNet and transfer learning (TL) for the enhancement of inter-session and inter-subject gesture recognition performance. The All-ConvNet+TL model consists solely of convolutional layers, a simple yet efficient framework for learning invariant and discriminative representations to address the distribution shifts caused by inter-session and inter-subject data variability. Experiments on four datasets demonstrate that our proposed methods outperform the most complex existing approaches by a large margin and achieve state-of-the-art results on inter-session and inter-subject scenarios and perform on par or competitively on intra-session gesture recognition. These performance gaps increase even more when a tiny amount (e.g., a single trial) of data is available on the target domain for adaptation. These outstanding experimental results provide evidence that the current state-of-the-art models may be overparameterized for sEMG-based inter-session and inter-subject gesture recognition tasks.
Human Gait Analysis using Gait Energy Image
Mar 17, 2022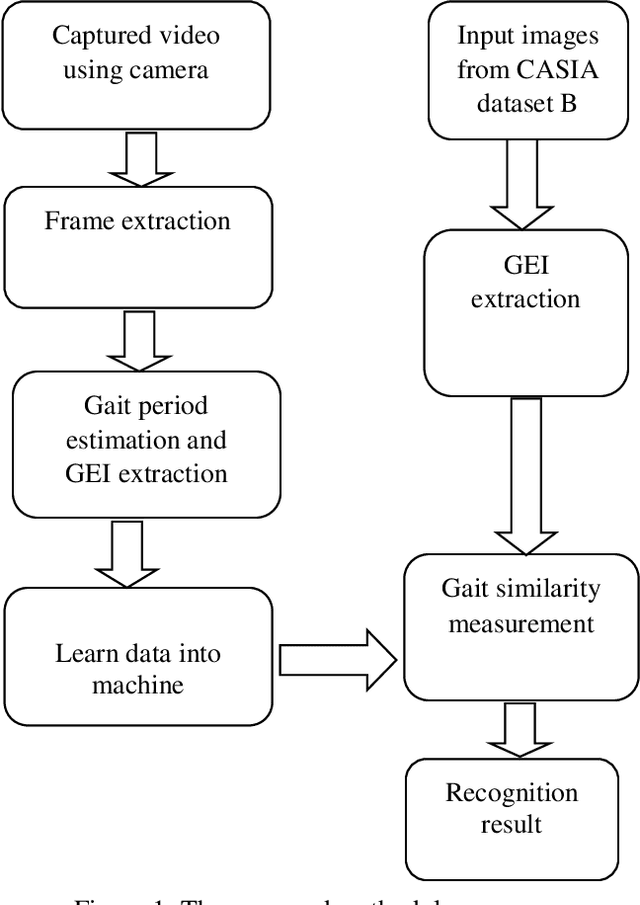
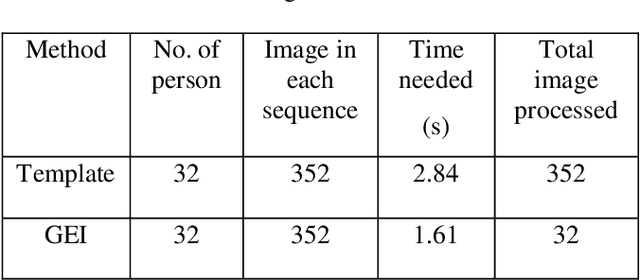

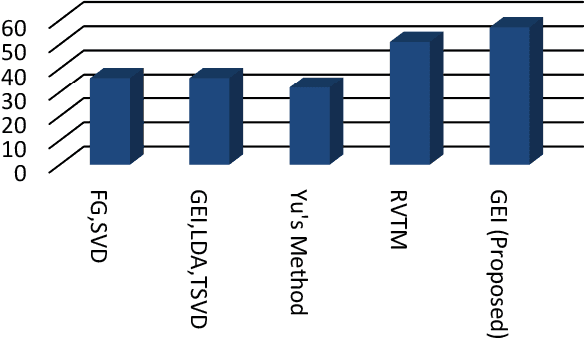
Abstract:Gait recognition is one of the most recent emerging techniques of human biometric which can be used for security based purposes having unobtrusive learning method. In comparison with other bio-metrics gait analysis has some special security features. Most of the biometric technique uses sequential template based component analysis for recognition. Comparing with those methods, we proposed a developed technique for gait identification using the feature Gait Energy Image (GEI). GEI representation of gait contains all information of each image in one gait cycle and requires less storage and low processing speed. As only one image is enough to store the necessary information in GEI feature recognition process is very easier than any other feature for gait recognition. Gait recognition has some limitations in recognition process like viewing angle variation, walking speed, clothes, carrying load etc. Our proposed method in the paper compares the recognition performance with template based feature extraction which needs to process each frame in the cycle. We use GEI which gives relatively all information about all the frames in the cycle and results in better performance than other feature of gait analysis.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Detection from Microscopic Images Using Weighted Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks
May 09, 2021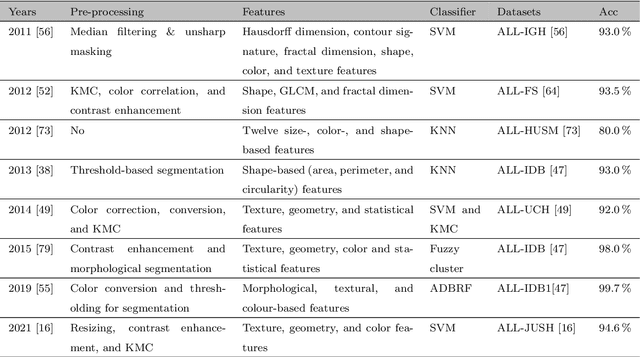
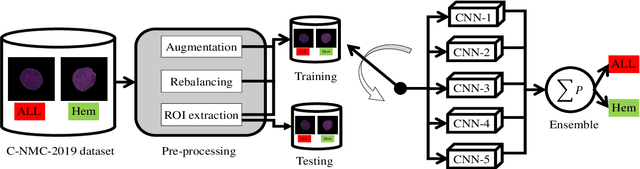
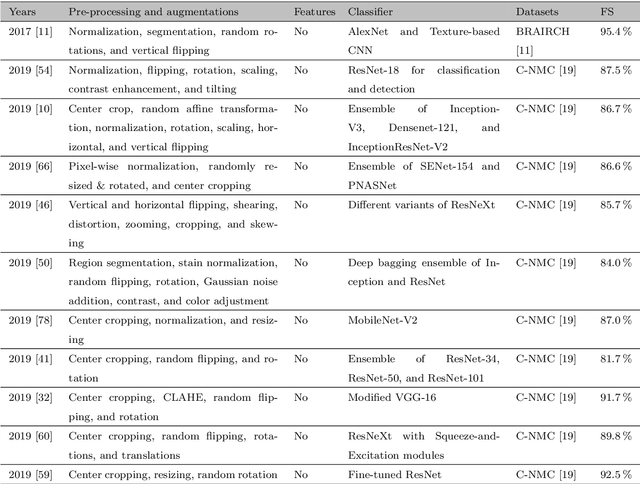
Abstract:Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a blood cell cancer characterized by numerous immature lymphocytes. Even though automation in ALL prognosis is an essential aspect of cancer diagnosis, it is challenging due to the morphological correlation between malignant and normal cells. The traditional ALL classification strategy demands experienced pathologists to carefully read the cell images, which is arduous, time-consuming, and often suffers inter-observer variations. This article has automated the ALL detection task from microscopic cell images, employing deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). We explore the weighted ensemble of different deep CNNs to recommend a better ALL cell classifier. The weights for the ensemble candidate models are estimated from their corresponding metrics, such as accuracy, F1-score, AUC, and kappa values. Various data augmentations and pre-processing are incorporated for achieving a better generalization of the network. We utilize the publicly available C-NMC-2019 ALL dataset to conduct all the comprehensive experiments. Our proposed weighted ensemble model, using the kappa values of the ensemble candidates as their weights, has outputted a weighted F1-score of 88.6 %, a balanced accuracy of 86.2 %, and an AUC of 0.941 in the preliminary test set. The qualitative results displaying the gradient class activation maps confirm that the introduced model has a concentrated learned region. In contrast, the ensemble candidate models, such as Xception, VGG-16, DenseNet-121, MobileNet, and InceptionResNet-V2, separately produce coarse and scatter learned areas for most example cases. Since the proposed kappa value-based weighted ensemble yields a better result for the aimed task in this article, it can experiment in other domains of medical diagnostic applications.
Codebook Design Method for Noise Robust Speaker Identification based on Genetic Algorithm
Sep 03, 2009
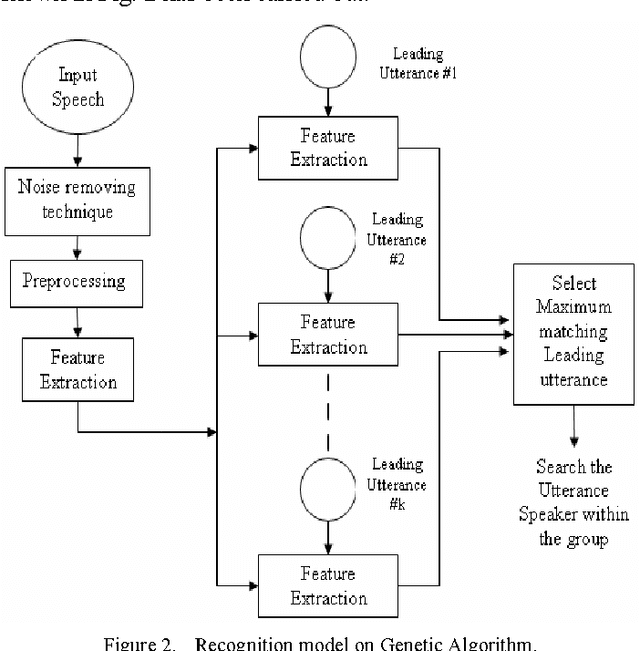
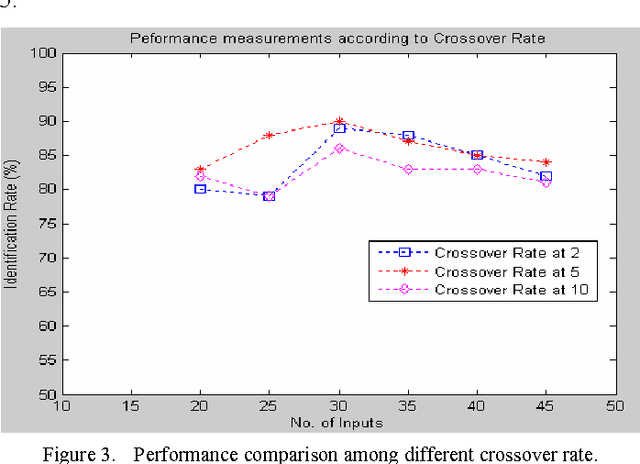
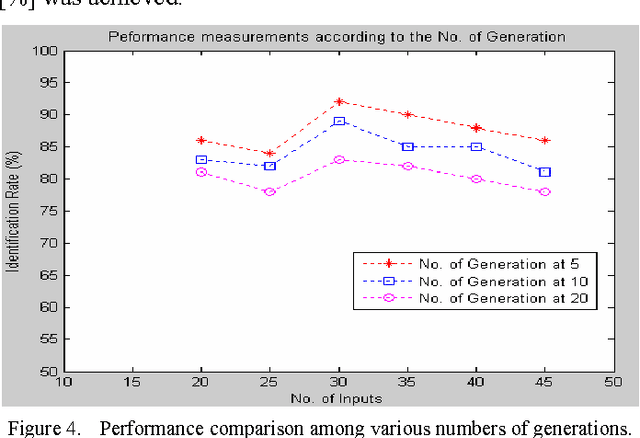
Abstract:In this paper, a novel method of designing a codebook for noise robust speaker identification purpose utilizing Genetic Algorithm has been proposed. Wiener filter has been used to remove the background noises from the source speech utterances. Speech features have been extracted using standard speech parameterization method such as LPC, LPCC, RCC, MFCC, (delta)MFCC and (delta)(delta) MFCC. For each of these techniques, the performance of the proposed system has been compared. In this codebook design method, Genetic Algorithm has the capability of getting global optimal result and hence improves the quality of the codebook. Comparing with the NOIZEOUS speech database, the experimental result shows that 79.62 percent accuracy has been achieved.
* 5 Pages IEEE format, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security, IJCSIS 2009, ISSN 1947 5500, Impact factor 0.423,http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge