Maximilian Koerner
Are we using appropriate segmentation metrics? Identifying correlates of human expert perception for CNN training beyond rolling the DICE coefficient
Mar 10, 2021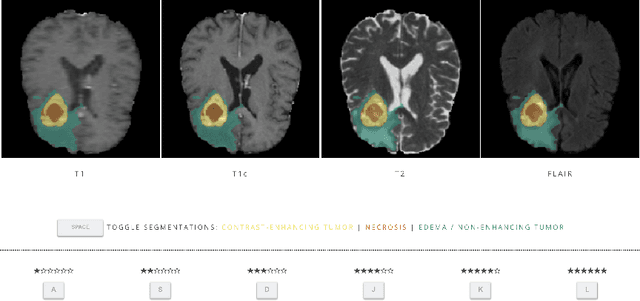

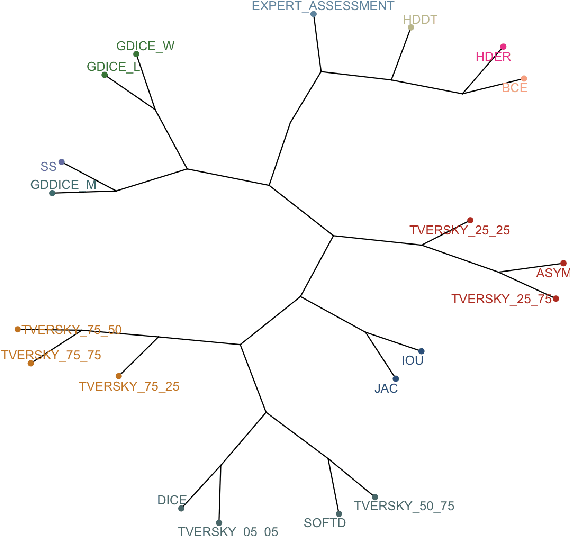
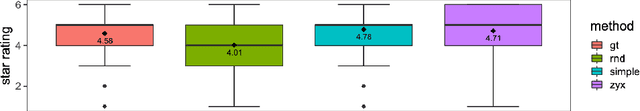
Abstract:In this study, we explore quantitative correlates of qualitative human expert perception. We discover that current quality metrics and loss functions, considered for biomedical image segmentation tasks, correlate moderately with segmentation quality assessment by experts, especially for small yet clinically relevant structures, such as the enhancing tumor in brain glioma. We propose a method employing classical statistics and experimental psychology to create complementary compound loss functions for modern deep learning methods, towards achieving a better fit with human quality assessment. When training a CNN for delineating adult brain tumor in MR images, all four proposed loss candidates outperform the established baselines on the clinically important and hardest to segment enhancing tumor label, while maintaining performance for other label channels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge