Matthias Zöhrer
Resource-Efficient Speech Mask Estimation for Multi-Channel Speech Enhancement
Jul 22, 2020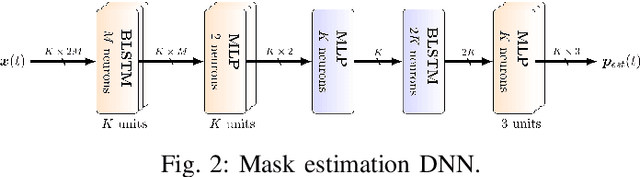
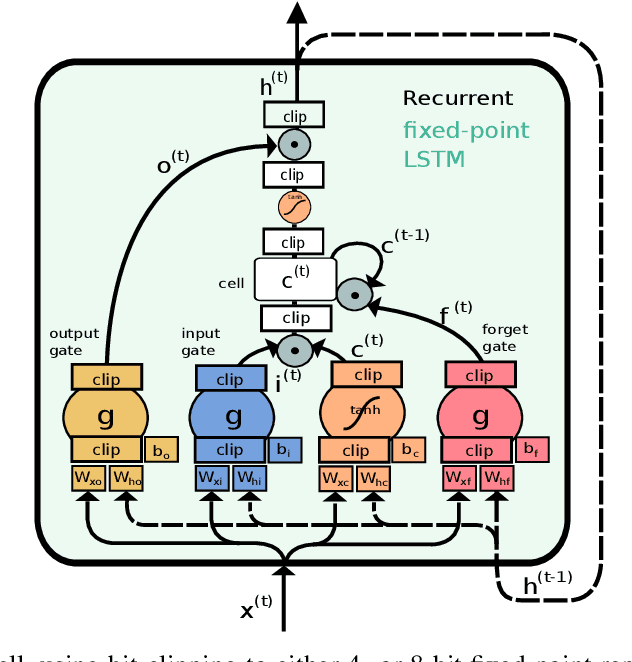
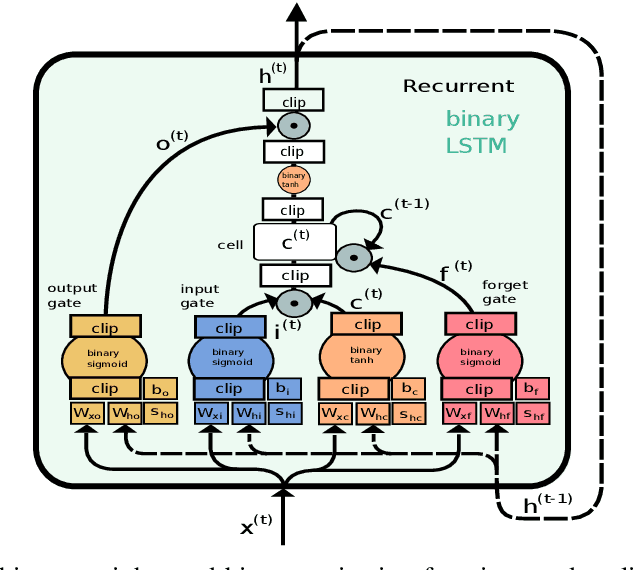
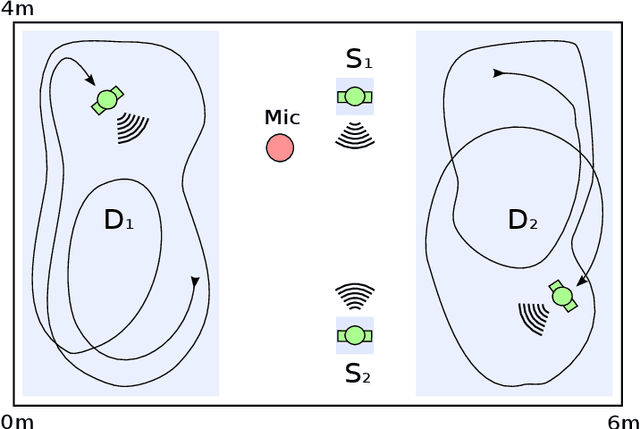
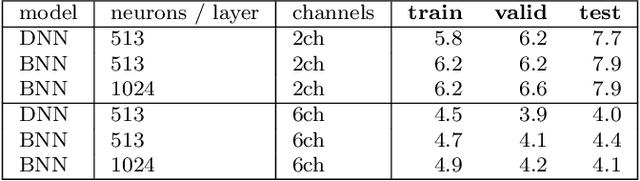
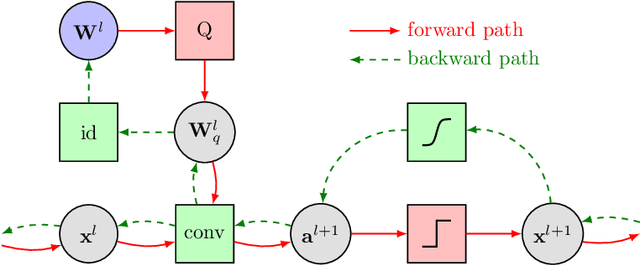
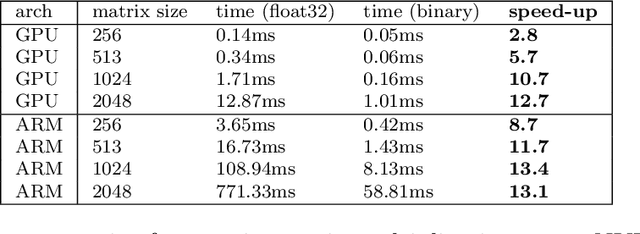
Abstract:While machine learning techniques are traditionally resource intensive, we are currently witnessing an increased interest in hardware and energy efficient approaches. This need for resource-efficient machine learning is primarily driven by the demand for embedded systems and their usage in ubiquitous computing and IoT applications. In this article, we provide a resource-efficient approach for multi-channel speech enhancement based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). In particular, we use reduced-precision DNNs for estimating a speech mask from noisy, multi-channel microphone observations. This speech mask is used to obtain either the Minimum Variance Distortionless Response (MVDR) or Generalized Eigenvalue (GEV) beamformer. In the extreme case of binary weights and reduced precision activations, a significant reduction of execution time and memory footprint is possible while still obtaining an audio quality almost on par to single-precision DNNs and a slightly larger Word Error Rate (WER) for single speaker scenarios using the WSJ0 speech corpus.
Resource-Efficient Neural Networks for Embedded Systems
Jan 07, 2020
Abstract:While machine learning is traditionally a resource intensive task, embedded systems, autonomous navigation, and the vision of the Internet of Things fuel the interest in resource-efficient approaches. These approaches aim for a carefully chosen trade-off between performance and resource consumption in terms of computation and energy. The development of such approaches is among the major challenges in current machine learning research and key to ensure a smooth transition of machine learning technology from a scientific environment with virtually unlimited computing resources into every day's applications. In this article, we provide an overview of the current state of the art of machine learning techniques facilitating these real-world requirements. In particular, we focus on deep neural networks (DNNs), the predominant machine learning models of the past decade. We give a comprehensive overview of the vast literature that can be mainly split into three non-mutually exclusive categories: (i) quantized neural networks, (ii) network pruning, and (iii) structural efficiency. These techniques can be applied during training or as post-processing, and they are widely used to reduce the computational demands in terms of memory footprint, inference speed, and energy efficiency. We substantiate our discussion with experiments on well-known benchmark data sets to showcase the difficulty of finding good trade-offs between resource-efficiency and predictive performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge