Matthias Kohler
A data acquisition setup for data driven acoustic design
Sep 24, 2021
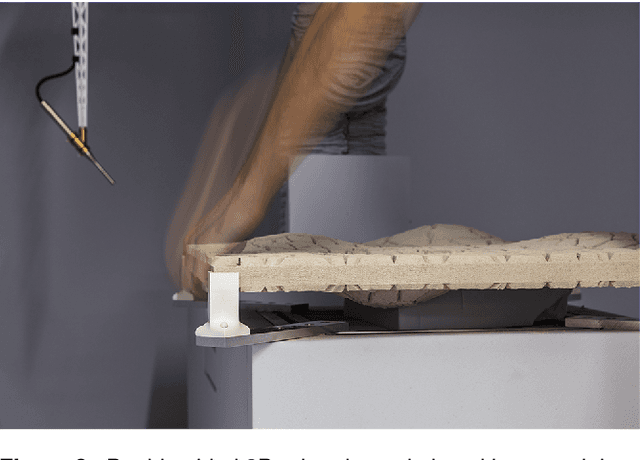

Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel interdisciplinary approach to study the relationship between diffusive surface structures and their acoustic performance. Using computational design, surface structures are iteratively generated and 3D printed at 1:10 model scale. They originate from different fabrication typologies and are designed to have acoustic diffusion and absorption effects. An automated robotic process measures the impulse responses of these surfaces by positioning a microphone and a speaker at multiple locations. The collected data serves two purposes: first, as an exploratory catalogue of different spatio-temporal-acoustic scenarios and second, as data set for predicting the acoustic response of digitally designed surface geometries using machine learning. In this paper, we present the automated data acquisition setup, the data processing and the computational generation of diffusive surface structures. We describe first results of comparative studies of measured surface panels and conclude with steps of future research.
Mobile Robotic Fabrication at 1:1 scale: the In situ Fabricator
Jan 13, 2017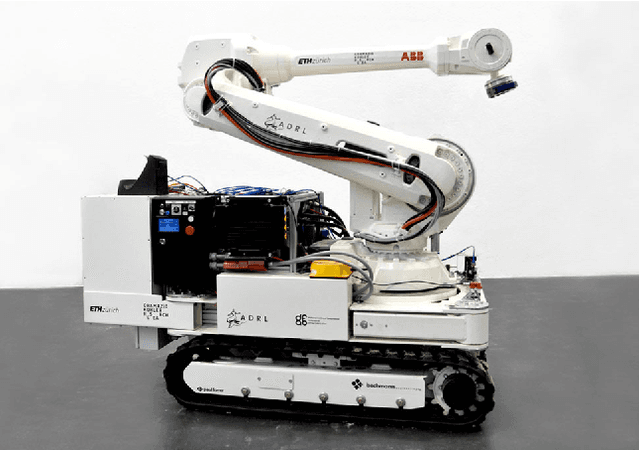
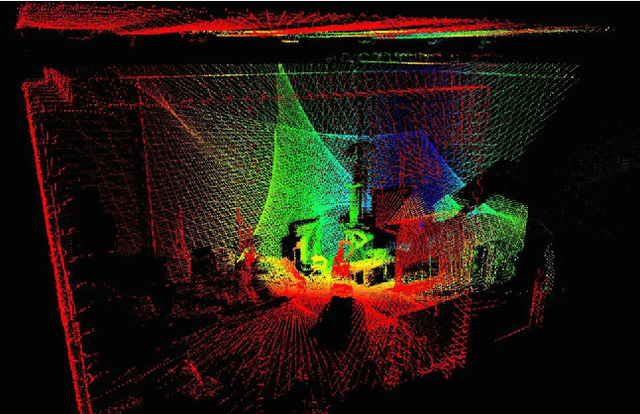

Abstract:This paper presents the concept of an In situ Fabricator, a mobile robot intended for on-site manufacturing, assembly and digital fabrication. We present an overview of a prototype system, its capabilities, and highlight the importance of high-performance control, estimation and planning algorithms for achieving desired construction goals. Next, we detail on two architectural application scenarios: first, building a full-size undulating brick wall, which required a number of repositioning and autonomous localisation manoeuvres. Second, the Mesh Mould concrete process, which shows that an In situ Fabricator in combination with an innovative digital fabrication tool can be used to enable completely novel building technologies. Subsequently, important limitations and disadvantages of our approach are discussed. Based on that, we identify the need for a new type of robotic actuator, which facilitates the design of novel full-scale construction robots. We provide brief insight into the development of this actuator and conclude the paper with an outlook on the next-generation In situ Fabricator, which is currently under development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge