Matteo Merler
ViPlan: A Benchmark for Visual Planning with Symbolic Predicates and Vision-Language Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Integrating Large Language Models with symbolic planners is a promising direction for obtaining verifiable and grounded plans compared to planning in natural language, with recent works extending this idea to visual domains using Vision-Language Models (VLMs). However, rigorous comparison between VLM-grounded symbolic approaches and methods that plan directly with a VLM has been hindered by a lack of common environments, evaluation protocols and model coverage. We introduce ViPlan, the first open-source benchmark for Visual Planning with symbolic predicates and VLMs. ViPlan features a series of increasingly challenging tasks in two domains: a visual variant of the classic Blocksworld planning problem and a simulated household robotics environment. We benchmark nine open-source VLM families across multiple sizes, along with selected closed models, evaluating both VLM-grounded symbolic planning and using the models directly to propose actions. We find symbolic planning to outperform direct VLM planning in Blocksworld, where accurate image grounding is crucial, whereas the opposite is true in the household robotics tasks, where commonsense knowledge and the ability to recover from errors are beneficial. Finally, we show that across most models and methods, there is no significant benefit to using Chain-of-Thought prompting, suggesting that current VLMs still struggle with visual reasoning.
Generating Code World Models with Large Language Models Guided by Monte Carlo Tree Search
May 24, 2024Abstract:In this work we consider Code World Models, world models generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) in the form of Python code for model-based Reinforcement Learning (RL). Calling code instead of LLMs for planning has the advantages of being precise, reliable, interpretable, and extremely efficient. However, writing appropriate Code World Models requires the ability to understand complex instructions, to generate exact code with non-trivial logic and to self-debug a long program with feedback from unit tests and environment trajectories. To address these challenges, we propose Generate, Improve and Fix with Monte Carlo Tree Search (GIF-MCTS), a new code generation strategy for LLMs. To test our approach, we introduce the Code World Models Benchmark (CWMB), a suite of program synthesis and planning tasks comprised of 18 diverse RL environments paired with corresponding textual descriptions and curated trajectories. GIF-MCTS surpasses all baselines on the CWMB and two other benchmarks, and we show that the Code World Models synthesized with it can be successfully used for planning, resulting in model-based RL agents with greatly improved sample efficiency and inference speed.
In-Context Symbolic Regression: Leveraging Language Models for Function Discovery
Apr 29, 2024


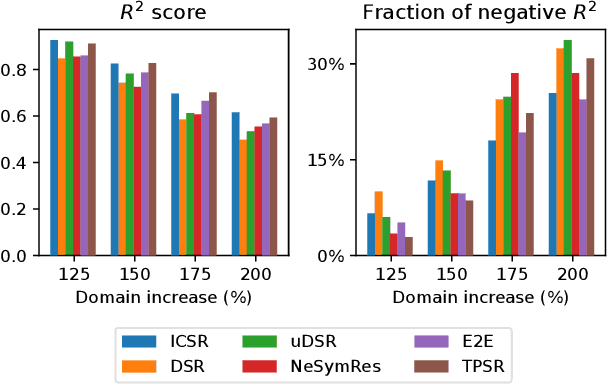
Abstract:Symbolic Regression (SR) is a task which aims to extract the mathematical expression underlying a set of empirical observations. Transformer-based methods trained on SR datasets detain the current state-of-the-art in this task, while the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) to SR remains unexplored. This work investigates the integration of pre-trained LLMs into the SR pipeline, utilizing an approach that iteratively refines a functional form based on the prediction error it achieves on the observation set, until it reaches convergence. Our method leverages LLMs to propose an initial set of possible functions based on the observations, exploiting their strong pre-training prior. These functions are then iteratively refined by the model itself and by an external optimizer for their coefficients. The process is repeated until the results are satisfactory. We then analyze Vision-Language Models in this context, exploring the inclusion of plots as visual inputs to aid the optimization process. Our findings reveal that LLMs are able to successfully recover good symbolic equations that fit the given data, outperforming SR baselines based on Genetic Programming, with the addition of images in the input showing promising results for the most complex benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge