Matan Ostrovsky
Towards Foundation Models on Graphs: An Analysis on Cross-Dataset Transfer of Pretrained GNNs
Dec 23, 2024
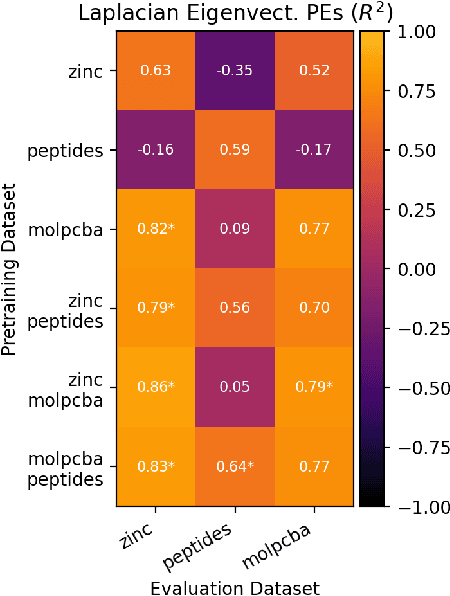
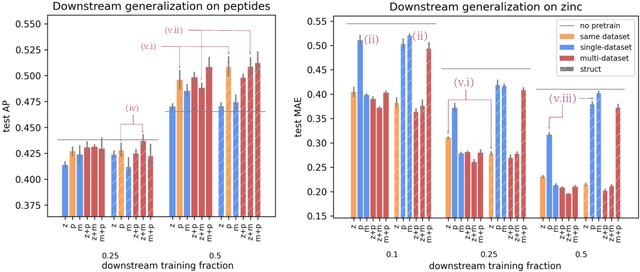
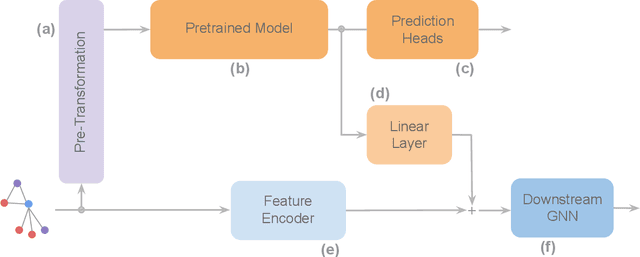
Abstract:To develop a preliminary understanding towards Graph Foundation Models, we study the extent to which pretrained Graph Neural Networks can be applied across datasets, an effort requiring to be agnostic to dataset-specific features and their encodings. We build upon a purely structural pretraining approach and propose an extension to capture feature information while still being feature-agnostic. We evaluate pretrained models on downstream tasks for varying amounts of training samples and choices of pretraining datasets. Our preliminary results indicate that embeddings from pretrained models improve generalization only with enough downstream data points and in a degree which depends on the quantity and properties of pretraining data. Feature information can lead to improvements, but currently requires some similarities between pretraining and downstream feature spaces.
An Abstraction-Refinement Approach to Verifying Convolutional Neural Networks
Jan 06, 2022



Abstract:Convolutional neural networks have gained vast popularity due to their excellent performance in the fields of computer vision, image processing, and others. Unfortunately, it is now well known that convolutional networks often produce erroneous results - for example, minor perturbations of the inputs of these networks can result in severe classification errors. Numerous verification approaches have been proposed in recent years to prove the absence of such errors, but these are typically geared for fully connected networks and suffer from exacerbated scalability issues when applied to convolutional networks. To address this gap, we present here the Cnn-Abs framework, which is particularly aimed at the verification of convolutional networks. The core of Cnn-Abs is an abstraction-refinement technique, which simplifies the verification problem through the removal of convolutional connections in a way that soundly creates an over-approximation of the original problem; and which restores these connections if the resulting problem becomes too abstract. Cnn-Abs is designed to use existing verification engines as a backend, and our evaluation demonstrates that it can significantly boost the performance of a state-of-the-art DNN verification engine, reducing runtime by 15.7% on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge