Masoud S. Nosrati
Multi-lane Cruising Using Hierarchical Planning and Reinforcement Learning
Oct 01, 2021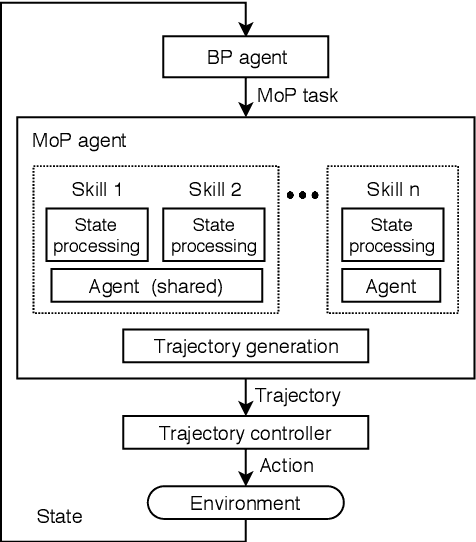
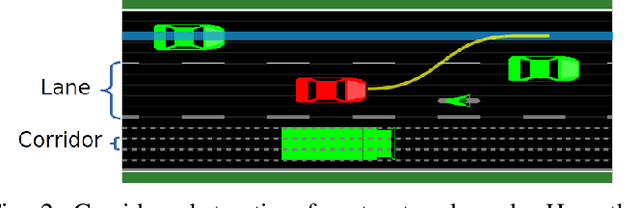
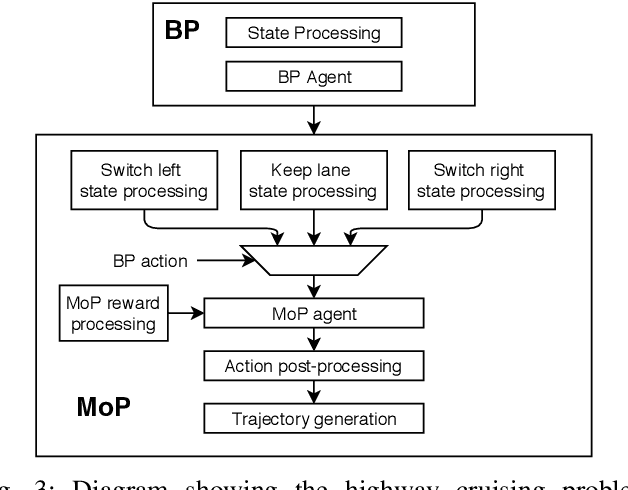
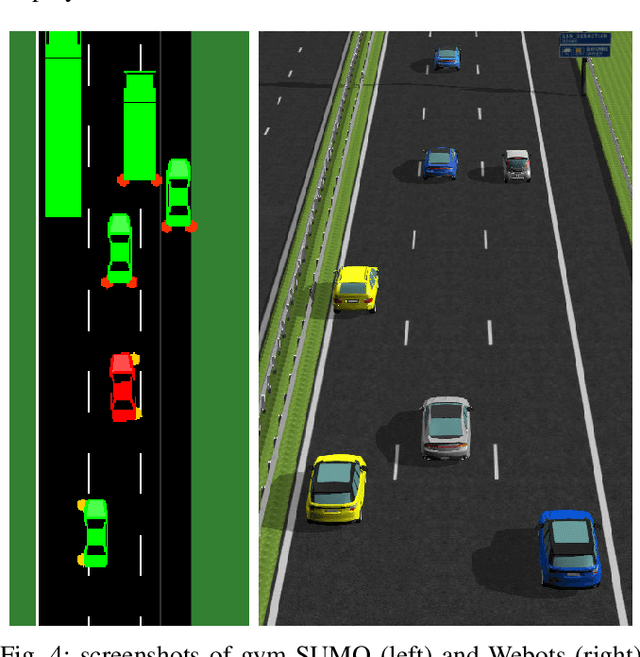
Abstract:Competent multi-lane cruising requires using lane changes and within-lane maneuvers to achieve good speed and maintain safety. This paper proposes a design for autonomous multi-lane cruising by combining a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework with a novel state-action space abstraction. While the proposed solution follows the classical hierarchy of behavior decision, motion planning and control, it introduces a key intermediate abstraction within the motion planner to discretize the state-action space according to high level behavioral decisions. We argue that this design allows principled modular extension of motion planning, in contrast to using either monolithic behavior cloning or a large set of hand-written rules. Moreover, we demonstrate that our state-action space abstraction allows transferring of the trained models without retraining from a simulated environment with virtually no dynamics to one with significantly more realistic dynamics. Together, these results suggest that our proposed hierarchical architecture is a promising way to allow reinforcement learning to be applied to complex multi-lane cruising in the real world.
Incorporating prior knowledge in medical image segmentation: a survey
Jul 05, 2016



Abstract:Medical image segmentation, the task of partitioning an image into meaningful parts, is an important step toward automating medical image analysis and is at the crux of a variety of medical imaging applications, such as computer aided diagnosis, therapy planning and delivery, and computer aided interventions. However, the existence of noise, low contrast and objects' complexity in medical images are critical obstacles that stand in the way of achieving an ideal segmentation system. Incorporating prior knowledge into image segmentation algorithms has proven useful for obtaining more accurate and plausible results. This paper surveys the different types of prior knowledge that have been utilized in different segmentation frameworks. We focus our survey on optimization-based methods that incorporate prior information into their frameworks. We review and compare these methods in terms of the types of prior employed, the domain of formulation (continuous vs. discrete), and the optimization techniques (global vs. local). We also created an interactive online database of existing works and categorized them based on the type of prior knowledge they use. Our website is interactive so that researchers can contribute to keep the database up to date. We conclude the survey by discussing different aspects of designing an energy functional for image segmentation, open problems, and future perspectives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge