Masaki Asada
A Video-grounded Dialogue Dataset and Metric for Event-driven Activities
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents VDAct, a dataset for a Video-grounded Dialogue on Event-driven Activities, alongside VDEval, a session-based context evaluation metric specially designed for the task. Unlike existing datasets, VDAct includes longer and more complex video sequences that depict a variety of event-driven activities that require advanced contextual understanding for accurate response generation. The dataset comprises 3,000 dialogues with over 30,000 question-and-answer pairs, derived from 1,000 videos with diverse activity scenarios. VDAct displays a notably challenging characteristic due to its broad spectrum of activity scenarios and wide range of question types. Empirical studies on state-of-the-art vision foundation models highlight their limitations in addressing certain question types on our dataset. Furthermore, VDEval, which integrates dialogue session history and video content summaries extracted from our supplementary Knowledge Graphs to evaluate individual responses, demonstrates a significantly higher correlation with human assessments on the VDAct dataset than existing evaluation metrics that rely solely on the context of single dialogue turns.
ProMQA: Question Answering Dataset for Multimodal Procedural Activity Understanding
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Multimodal systems have great potential to assist humans in procedural activities, where people follow instructions to achieve their goals. Despite diverse application scenarios, systems are typically evaluated on traditional classification tasks, e.g., action recognition or temporal action segmentation. In this paper, we present a novel evaluation dataset, ProMQA, to measure system advancements in application-oriented scenarios. ProMQA consists of 401 multimodal procedural QA pairs on user recording of procedural activities coupled with their corresponding instruction. For QA annotation, we take a cost-effective human-LLM collaborative approach, where the existing annotation is augmented with LLM-generated QA pairs that are later verified by humans. We then provide the benchmark results to set the baseline performance on ProMQA. Our experiment reveals a significant gap between human performance and that of current systems, including competitive proprietary multimodal models. We hope our dataset sheds light on new aspects of models' multimodal understanding capabilities.
Integrating Heterogeneous Domain Information into Relation Extraction: A Case Study on Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:The development of deep neural networks has improved representation learning in various domains, including textual, graph structural, and relational triple representations. This development opened the door to new relation extraction beyond the traditional text-oriented relation extraction. However, research on the effectiveness of considering multiple heterogeneous domain information simultaneously is still under exploration, and if a model can take an advantage of integrating heterogeneous information, it is expected to exhibit a significant contribution to many problems in the world. This thesis works on Drug-Drug Interactions (DDIs) from the literature as a case study and realizes relation extraction utilizing heterogeneous domain information. First, a deep neural relation extraction model is prepared and its attention mechanism is analyzed. Next, a method to combine the drug molecular structure information and drug description information to the input sentence information is proposed, and the effectiveness of utilizing drug molecular structures and drug descriptions for the relation extraction task is shown. Then, in order to further exploit the heterogeneous information, drug-related items, such as protein entries, medical terms and pathways are collected from multiple existing databases and a new data set in the form of a knowledge graph (KG) is constructed. A link prediction task on the constructed data set is conducted to obtain embedding representations of drugs that contain the heterogeneous domain information. Finally, a method that integrates the input sentence information and the heterogeneous KG information is proposed. The proposed model is trained and evaluated on a widely used data set, and as a result, it is shown that utilizing heterogeneous domain information significantly improves the performance of relation extraction from the literature.
Enhancing Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction from Texts by Molecular Structure Information
May 15, 2018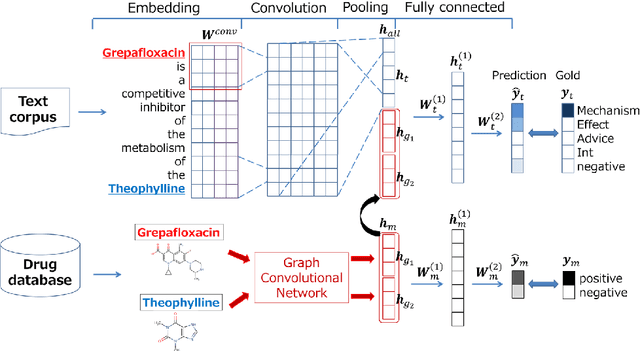
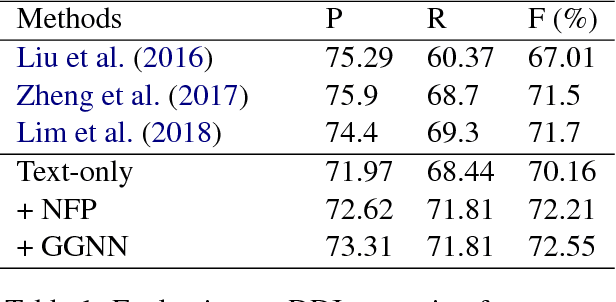
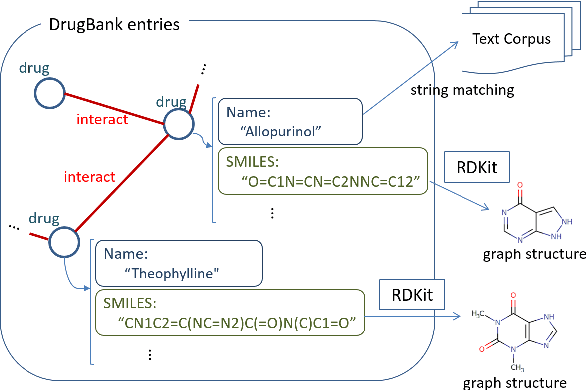

Abstract:We propose a novel neural method to extract drug-drug interactions (DDIs) from texts using external drug molecular structure information. We encode textual drug pairs with convolutional neural networks and their molecular pairs with graph convolutional networks (GCNs), and then we concatenate the outputs of these two networks. In the experiments, we show that GCNs can predict DDIs from the molecular structures of drugs in high accuracy and the molecular information can enhance text-based DDI extraction by 2.39 percent points in the F-score on the DDIExtraction 2013 shared task data set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge