Yutaka Sasaki
Extracting ORR Catalyst Information for Fuel Cell from Scientific Literature
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst plays a critical role in enhancing fuel cell efficiency, making it a key focus in material science research. However, extracting structured information about ORR catalysts from vast scientific literature remains a significant challenge due to the complexity and diversity of textual data. In this study, we propose a named entity recognition (NER) and relation extraction (RE) approach using DyGIE++ with multiple pre-trained BERT variants, including MatSciBERT and PubMedBERT, to extract ORR catalyst-related information from the scientific literature, which is compiled into a fuel cell corpus for materials informatics (FC-CoMIcs). A comprehensive dataset was constructed manually by identifying 12 critical entities and two relationship types between pairs of the entities. Our methodology involves data annotation, integration, and fine-tuning of transformer-based models to enhance information extraction accuracy. We assess the impact of different BERT variants on extraction performance and investigate the effects of annotation consistency. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that the fine-tuned PubMedBERT model achieves the highest NER F1-score of 82.19% and the MatSciBERT model attains the best RE F1-score of 66.10%. Furthermore, the comparison with human annotators highlights the reliability of fine-tuned models for ORR catalyst extraction, demonstrating their potential for scalable and automated literature analysis. The results indicate that domain-specific BERT models outperform general scientific models like BlueBERT for ORR catalyst extraction.
End-to-End Trainable Soft Retriever for Low-resource Relation Extraction
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:This study addresses a crucial challenge in instance-based relation extraction using text generation models: end-to-end training in target relation extraction task is not applicable to retrievers due to the non-differentiable nature of instance selection. We propose a novel End-to-end TRAinable Soft K-nearest neighbor retriever (ETRASK) by the neural prompting method that utilizes a soft, differentiable selection of the $k$ nearest instances. This approach enables the end-to-end training of retrievers in target tasks. On the TACRED benchmark dataset with a low-resource setting where the training data was reduced to 10\%, our method achieved a state-of-the-art F1 score of 71.5\%. Moreover, ETRASK consistently improved the baseline model by adding instances for all settings. These results highlight the efficacy of our approach in enhancing relation extraction performance, especially in resource-constrained environments. Our findings offer a promising direction for future research with extraction and the broader application of text generation in natural language processing.
Physical Context and Timing Aware Sequence Generating GANs
Sep 28, 2021



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have shown remarkable successes in generating realistic images and interpolating changes between images. Existing models, however, do not take into account physical contexts behind images in generating the images, which may cause unrealistic changes. Furthermore, it is difficult to generate the changes at a specific timing and they often do not match with actual changes. This paper proposes a novel GAN, named Physical Context and Timing aware sequence generating GANs (PCTGAN), that generates an image in a sequence at a specific timing between two images with considering physical contexts behind them. Our method consists of three components: an encoder, a generator, and a discriminator. The encoder estimates latent vectors from the beginning and ending images, their timings, and a target timing. The generator generates images and the physical contexts at the beginning, ending, and target timing from the corresponding latent vectors. The discriminator discriminates whether the generated images and contexts are real or not. In the experiments, PCTGAN is applied to a data set of sequential changes of shapes in die forging processes. We show that both timing and physical contexts are effective in generating sequential images.
A Neural Edge-Editing Approach for Document-Level Relation Graph Extraction
Jun 18, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel edge-editing approach to extract relation information from a document. We treat the relations in a document as a relation graph among entities in this approach. The relation graph is iteratively constructed by editing edges of an initial graph, which might be a graph extracted by another system or an empty graph. The way to edit edges is to classify them in a close-first manner using the document and temporally-constructed graph information; each edge is represented with a document context information by a pretrained transformer model and a graph context information by a graph convolutional neural network model. We evaluate our approach on the task to extract material synthesis procedures from materials science texts. The experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach in editing the graphs initialized by our in-house rule-based system and empty graphs.
Enhancing Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction from Texts by Molecular Structure Information
May 15, 2018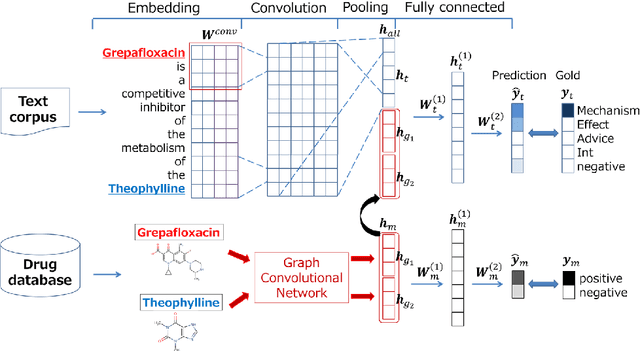
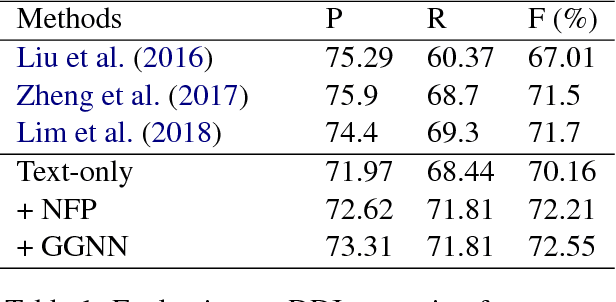
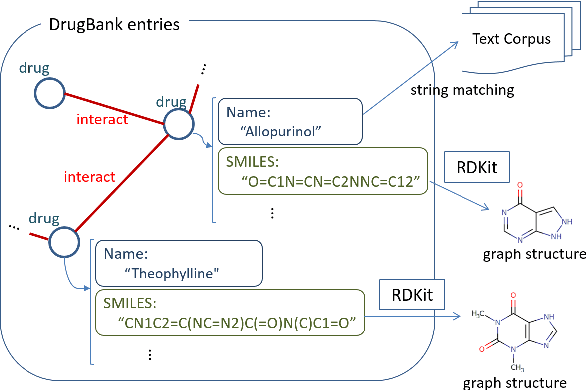

Abstract:We propose a novel neural method to extract drug-drug interactions (DDIs) from texts using external drug molecular structure information. We encode textual drug pairs with convolutional neural networks and their molecular pairs with graph convolutional networks (GCNs), and then we concatenate the outputs of these two networks. In the experiments, we show that GCNs can predict DDIs from the molecular structures of drugs in high accuracy and the molecular information can enhance text-based DDI extraction by 2.39 percent points in the F-score on the DDIExtraction 2013 shared task data set.
Bib2vec: An Embedding-based Search System for Bibliographic Information
Apr 05, 2018



Abstract:We propose a novel embedding model that represents relationships among several elements in bibliographic information with high representation ability and flexibility. Based on this model, we present a novel search system that shows the relationships among the elements in the ACL Anthology Reference Corpus. The evaluation results show that our model can achieve a high prediction ability and produce reasonable search results.
* EACL2017 extended version. The demonstration is available at http://tti-coin.jp/demo/bib2vec/
Normalized Hierarchical SVM
Mar 04, 2016



Abstract:We present improved methods of using structured SVMs in a large-scale hierarchical classification problem, that is when labels are leaves, or sets of leaves, in a tree or a DAG. We examine the need to normalize both the regularization and the margin and show how doing so significantly improves performance, including allowing achieving state-of-the-art results where unnormalized structured SVMs do not perform better than flat models. We also describe a further extension of hierarchical SVMs that highlight the connection between hierarchical SVMs and matrix factorization models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge