Martin V. Holt
Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Sep 20, 2022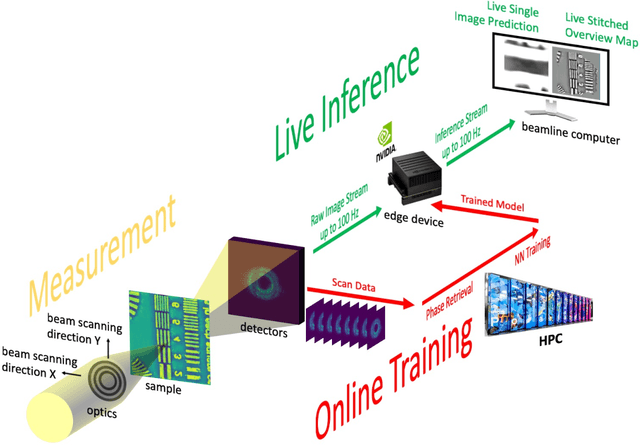
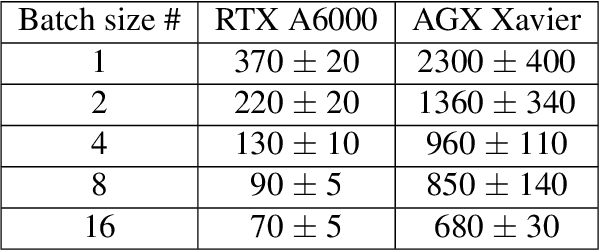
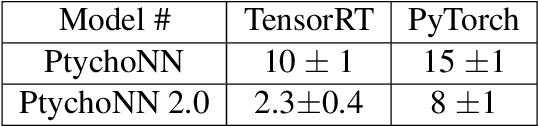
Abstract:Coherent microscopy techniques provide an unparalleled multi-scale view of materials across scientific and technological fields, from structural materials to quantum devices, from integrated circuits to biological cells. Driven by the construction of brighter sources and high-rate detectors, coherent X-ray microscopy methods like ptychography are poised to revolutionize nanoscale materials characterization. However, associated significant increases in data and compute needs mean that conventional approaches no longer suffice for recovering sample images in real-time from high-speed coherent imaging experiments. Here, we demonstrate a workflow that leverages artificial intelligence at the edge and high-performance computing to enable real-time inversion on X-ray ptychography data streamed directly from a detector at up to 2 kHz. The proposed AI-enabled workflow eliminates the sampling constraints imposed by traditional ptychography, allowing low dose imaging using orders of magnitude less data than required by traditional methods.
Real-time sparse-sampled Ptychographic imaging through deep neural networks
Apr 15, 2020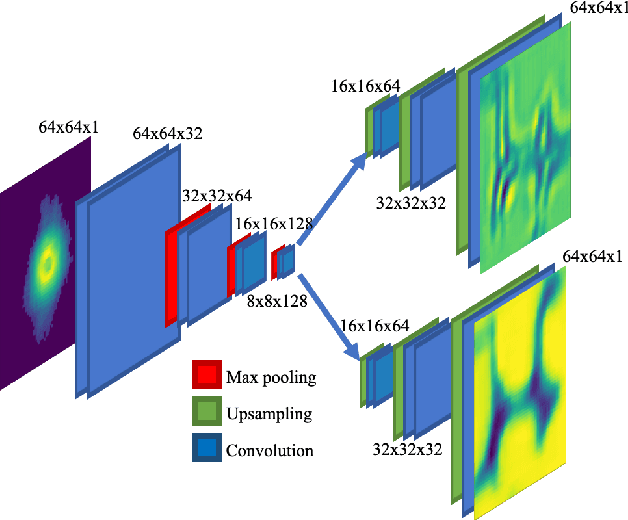
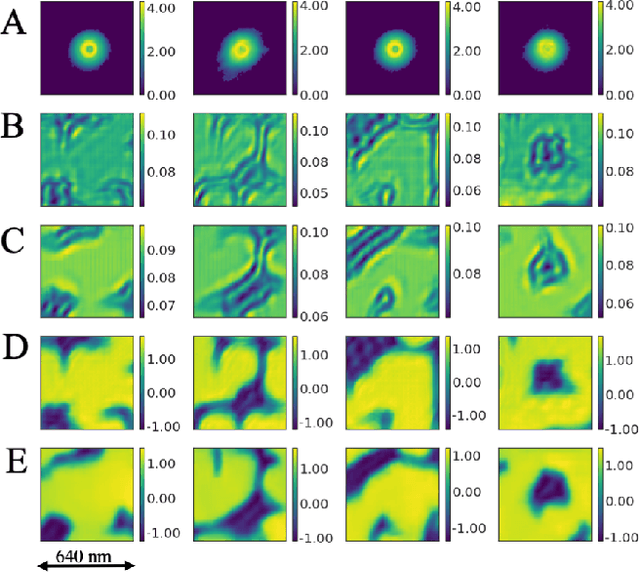
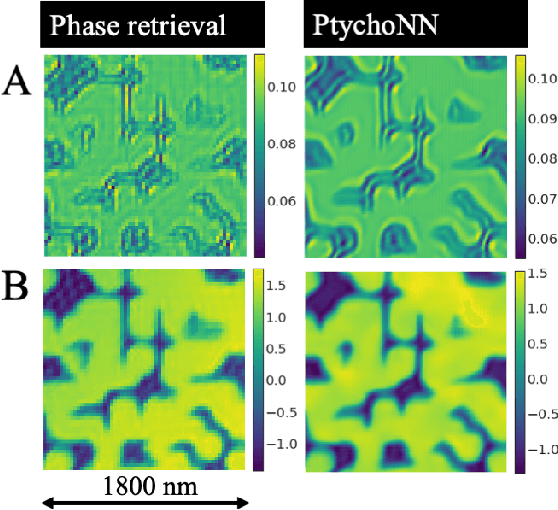
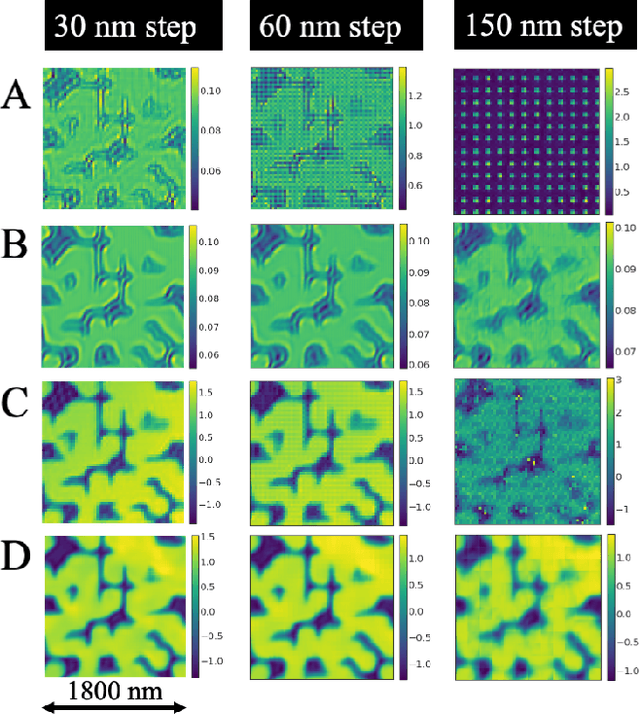
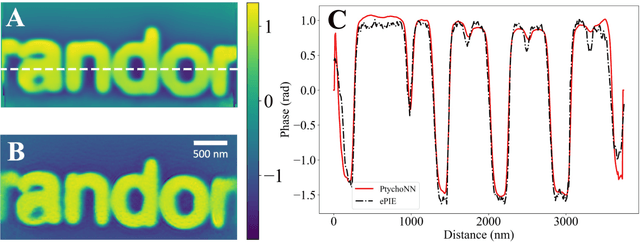
Abstract:Ptychography has rapidly grown in the fields of X-ray and electron imaging for its unprecedented ability to achieve nano or atomic scale resolution while simultaneously retrieving chemical or magnetic information from a sample. A ptychographic reconstruction is achieved by means of solving a complex inverse problem that imposes constraints both on the acquisition and on the analysis of the data, which typically precludes real-time imaging due to computational cost involved in solving this inverse problem. In this work we propose PtychoNN, a novel approach to solve the ptychography reconstruction problem based on deep convolutional neural networks. We demonstrate how the proposed method can be used to predict real-space structure and phase at each scan point solely from the corresponding far-field diffraction data. The presented results demonstrate how PtychoNN can effectively be used on experimental data, being able to generate high quality reconstructions of a sample up to hundreds of times faster than state-of-the-art ptychography reconstruction solutions once trained. By surpassing the typical constraints of iterative model-based methods, we can significantly relax the data acquisition sampling conditions and produce equally satisfactory reconstructions. Besides drastically accelerating acquisition and analysis, this capability can enable new imaging scenarios that were not possible before, in cases of dose sensitive, dynamic and extremely voluminous samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge