Mart Ratas
RelCAT: Advancing Extraction of Clinical Inter-Entity Relationships from Unstructured Electronic Health Records
Jan 27, 2025Abstract:This study introduces RelCAT (Relation Concept Annotation Toolkit), an interactive tool, library, and workflow designed to classify relations between entities extracted from clinical narratives. Building upon the CogStack MedCAT framework, RelCAT addresses the challenge of capturing complete clinical relations dispersed within text. The toolkit implements state-of-the-art machine learning models such as BERT and Llama along with proven evaluation and training methods. We demonstrate a dataset annotation tool (built within MedCATTrainer), model training, and evaluate our methodology on both openly available gold-standard and real-world UK National Health Service (NHS) hospital clinical datasets. We perform extensive experimentation and a comparative analysis of the various publicly available models with varied approaches selected for model fine-tuning. Finally, we achieve macro F1-scores of 0.977 on the gold-standard n2c2, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art performance, and achieve performance of >=0.93 F1 on our NHS gathered datasets.
Improving Extraction of Clinical Event Contextual Properties from Electronic Health Records: A Comparative Study
Aug 30, 2024
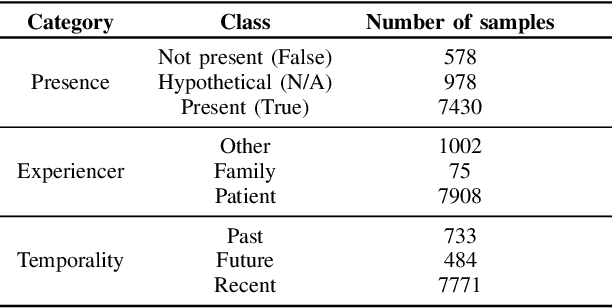
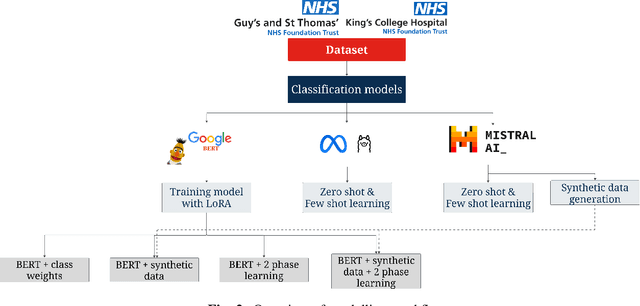
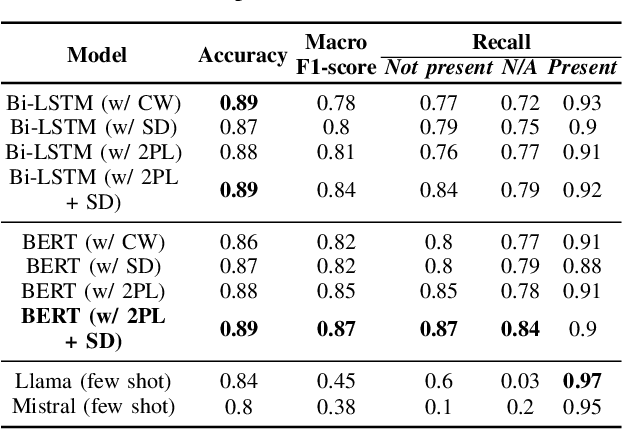
Abstract:Electronic Health Records are large repositories of valuable clinical data, with a significant portion stored in unstructured text format. This textual data includes clinical events (e.g., disorders, symptoms, findings, medications and procedures) in context that if extracted accurately at scale can unlock valuable downstream applications such as disease prediction. Using an existing Named Entity Recognition and Linking methodology, MedCAT, these identified concepts need to be further classified (contextualised) for their relevance to the patient, and their temporal and negated status for example, to be useful downstream. This study performs a comparative analysis of various natural language models for medical text classification. Extensive experimentation reveals the effectiveness of transformer-based language models, particularly BERT. When combined with class imbalance mitigation techniques, BERT outperforms Bi-LSTM models by up to 28% and the baseline BERT model by up to 16% for recall of the minority classes. The method has been implemented as part of CogStack/MedCAT framework and made available to the community for further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge