Markus Stoye
Jet Flavour Classification Using DeepJet
Aug 24, 2020
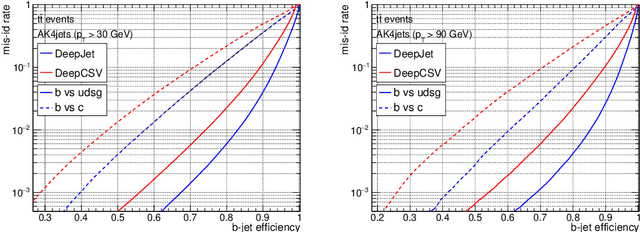
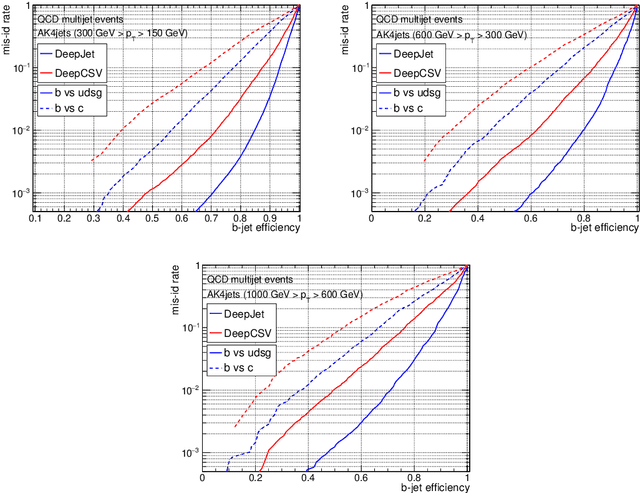
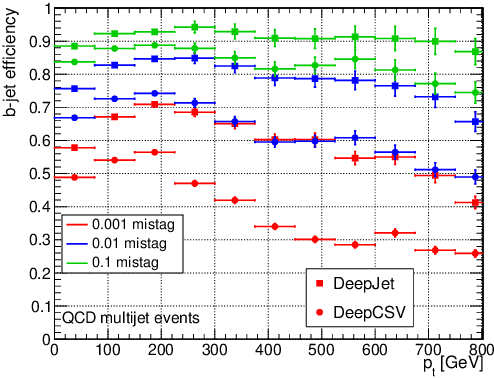
Abstract:Jet flavour classification is of paramount importance for a broad range of applications in modern-day high-energy-physics experiments, particularly at the LHC. In this paper we propose a novel architecture for this task that exploits modern deep learning techniques. This new model, called DeepJet, overcomes the limitations in input size that affected previous approaches. As a result, the classification performance improves and the number of classes to be predicted can be increased. Such, DeepJet is paving the way to an all-inclusive jet classifier.
Likelihood-free inference with an improved cross-entropy estimator
Aug 02, 2018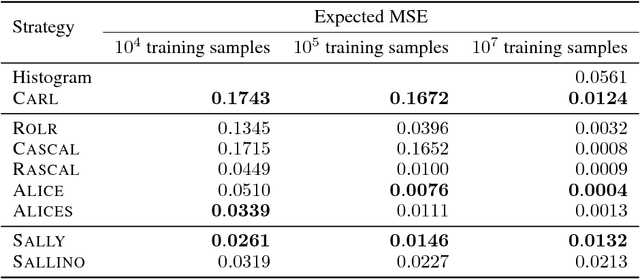
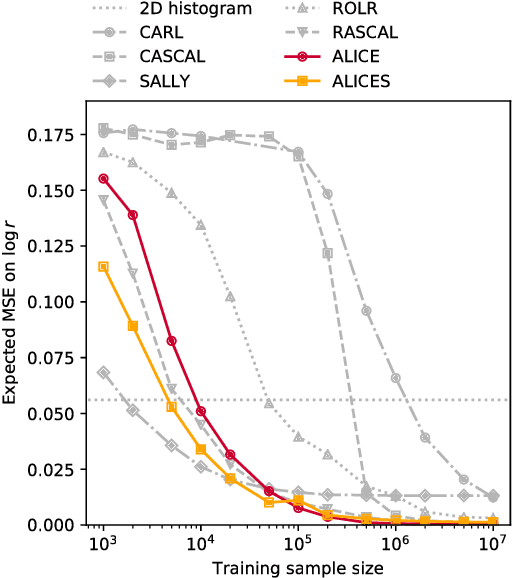
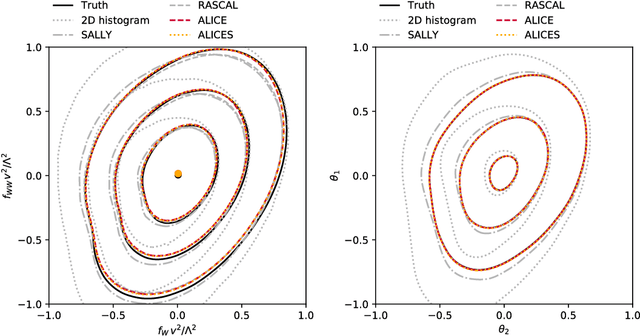
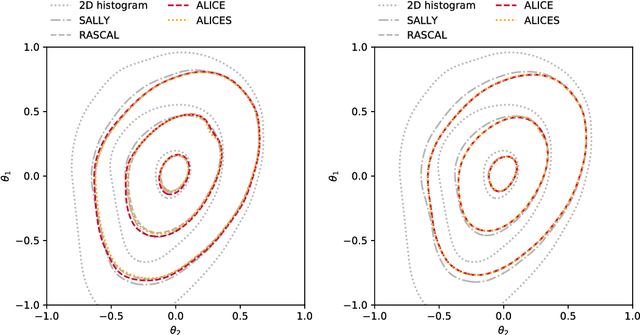
Abstract:We extend recent work (Brehmer, et. al., 2018) that use neural networks as surrogate models for likelihood-free inference. As in the previous work, we exploit the fact that the joint likelihood ratio and joint score, conditioned on both observed and latent variables, can often be extracted from an implicit generative model or simulator to augment the training data for these surrogate models. We show how this augmented training data can be used to provide a new cross-entropy estimator, which provides improved sample efficiency compared to previous loss functions exploiting this augmented training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge