Markus Bajones
Help, Anyone? A User Study For Modeling Robotic Behavior To Mitigate Malfunctions With The Help Of The User
Jun 08, 2016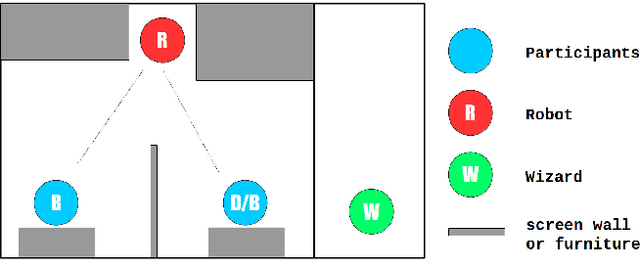
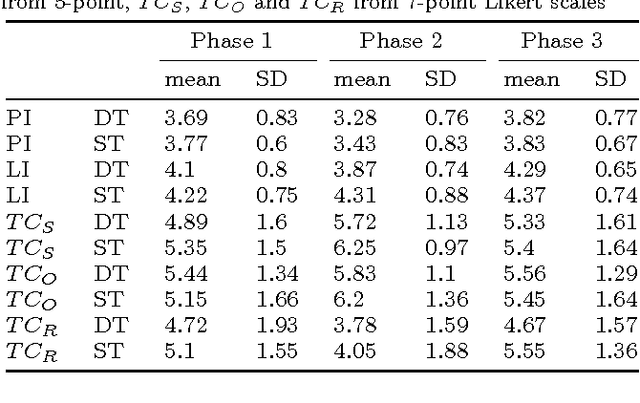
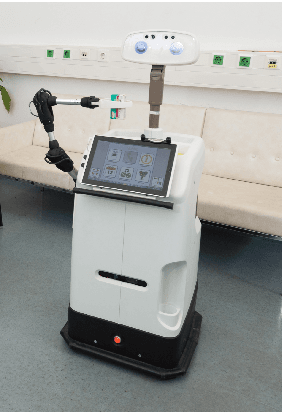
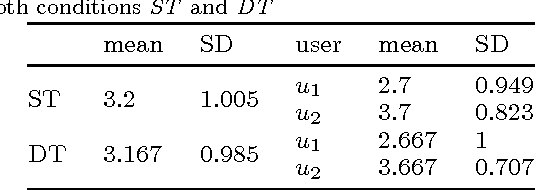
Abstract:Service robots for the domestic environment are intended to autonomously provide support for their users. However, state-of-the-art robots still often get stuck in failure situations leading to breakdowns in the interaction flow from which the robot cannot recover alone. We performed a multi-user Wizard-of-Oz experiment in which we manipulated the robot's behavior in such a way that it appeared unexpected and malfunctioning, and asked participants to help the robot in order to restore the interaction flow. We examined how participants reacted to the robot's error, its subsequent request for help and how it changed their perception of the robot with respect to perceived intelligence, likability, and task contribution. As interaction scenario we used a game of building Lego models performed by user dyads. In total 38 participants interacted with the robot and helped in malfunctioning situations. We report two major findings: (1) in user dyads, the user who gave the last command followed by the user who is closer is more likely to help (2) malfunctions that can be actively fixed by the user seem not to negatively impact perceived intelligence and likability ratings. This work offers insights in how far user support can be a strategy for domestic service robots to recover from repeating malfunctions.
Where to look first? Behaviour control for fetch-and-carry missions of service robots
Oct 06, 2015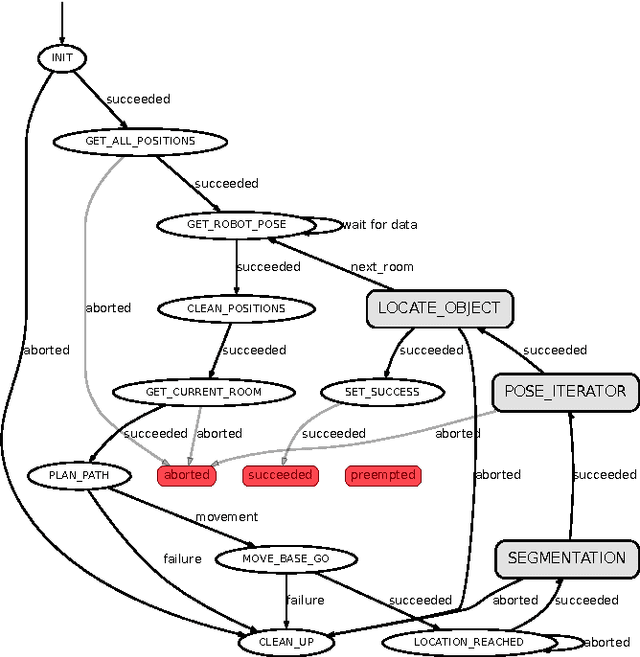
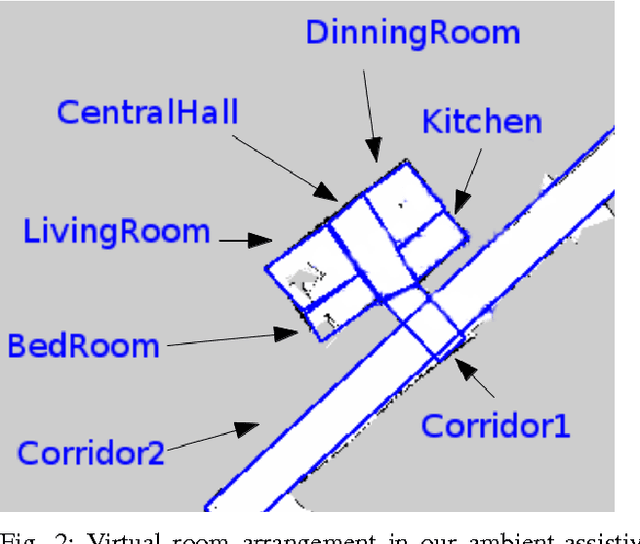


Abstract:This paper presents the behaviour control of a service robot for intelligent object search in a domestic environment. A major challenge in service robotics is to enable fetch-and-carry missions that are satisfying for the user in terms of efficiency and human-oriented perception. The proposed behaviour controller provides an informed intelligent search based on a semantic segmentation framework for indoor scenes and integrates it with object recognition and grasping. Instead of manually annotating search positions in the environment, the framework automatically suggests likely locations to search for an object based on contextual information, e.g. next to tables and shelves. In a preliminary set of experiments we demonstrate that this behaviour control is as efficient as using manually annotated locations. Moreover, we argue that our approach will reduce the intensity of labour associated with programming fetch-and-carry tasks for service robots and that it will be perceived as more human-oriented.
Find my mug: Efficient object search with a mobile robot using semantic segmentation
Apr 23, 2014
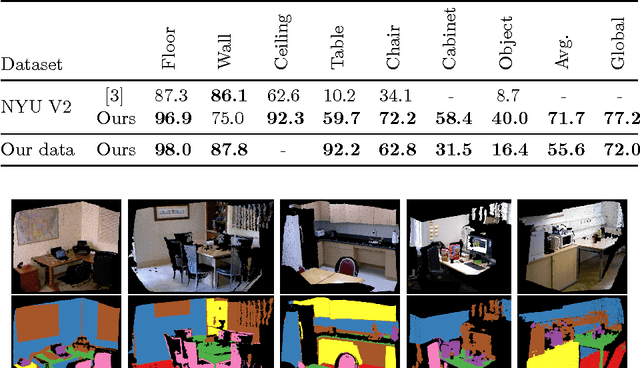
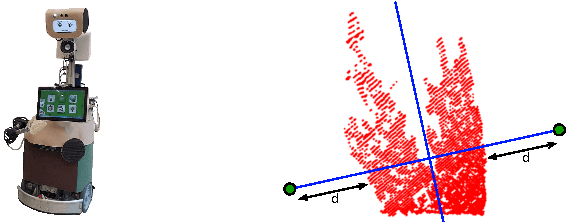
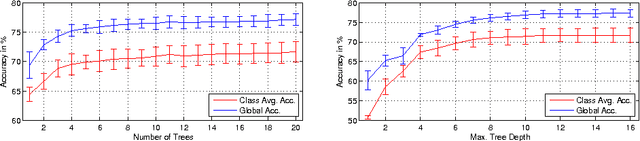
Abstract:In this paper, we propose an efficient semantic segmentation framework for indoor scenes, tailored to the application on a mobile robot. Semantic segmentation can help robots to gain a reasonable understanding of their environment, but to reach this goal, the algorithms not only need to be accurate, but also fast and robust. Therefore, we developed an optimized 3D point cloud processing framework based on a Randomized Decision Forest, achieving competitive results at sufficiently high frame rates. We evaluate the capabilities of our method on the popular NYU depth dataset and our own data and demonstrate its feasibility by deploying it on a mobile service robot, for which we could optimize an object search procedure using our results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge