Help, Anyone? A User Study For Modeling Robotic Behavior To Mitigate Malfunctions With The Help Of The User
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2016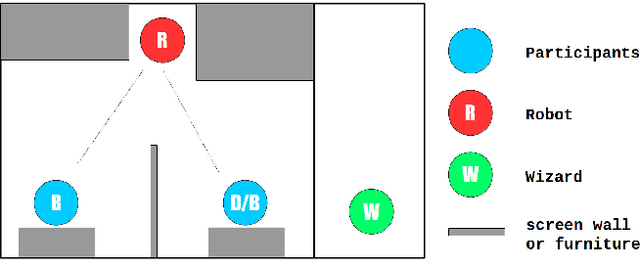
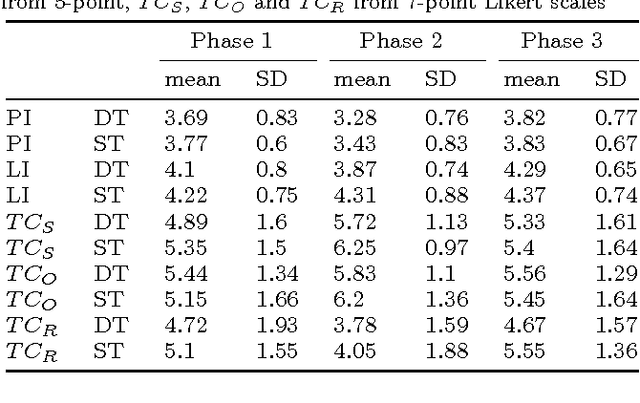
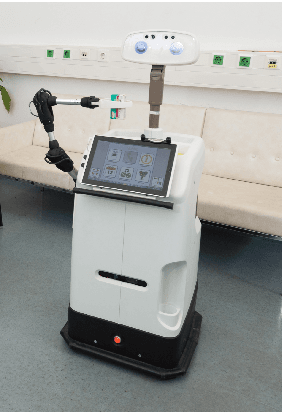
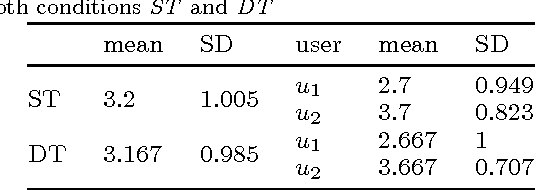
Service robots for the domestic environment are intended to autonomously provide support for their users. However, state-of-the-art robots still often get stuck in failure situations leading to breakdowns in the interaction flow from which the robot cannot recover alone. We performed a multi-user Wizard-of-Oz experiment in which we manipulated the robot's behavior in such a way that it appeared unexpected and malfunctioning, and asked participants to help the robot in order to restore the interaction flow. We examined how participants reacted to the robot's error, its subsequent request for help and how it changed their perception of the robot with respect to perceived intelligence, likability, and task contribution. As interaction scenario we used a game of building Lego models performed by user dyads. In total 38 participants interacted with the robot and helped in malfunctioning situations. We report two major findings: (1) in user dyads, the user who gave the last command followed by the user who is closer is more likely to help (2) malfunctions that can be actively fixed by the user seem not to negatively impact perceived intelligence and likability ratings. This work offers insights in how far user support can be a strategy for domestic service robots to recover from repeating malfunctions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge