Margaret Coad
Field Insights for Portable Vine Robots in Urban Search and Rescue
Nov 10, 2024
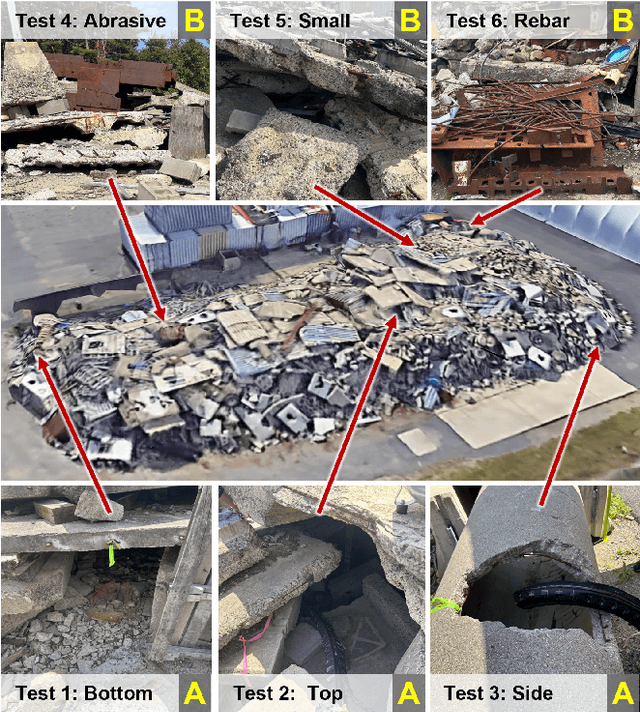


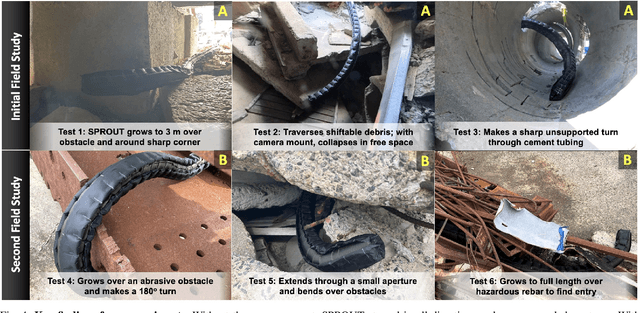
Abstract:Soft, growing vine robots are well-suited for exploring cluttered, unknown environments, and are theorized to be performant during structural collapse incidents caused by earthquakes, fires, explosions, and material flaws. These vine robots grow from the tip, enabling them to navigate rubble-filled passageways easily. State-of-the-art vine robots have been tested in archaeological and other field settings, but their translational capabilities to urban search and rescue (USAR) are not well understood. To this end, we present a set of experiments designed to test the limits of a vine robot system, the Soft Pathfinding Robotic Observation Unit (SPROUT), operating in an engineered collapsed structure. Our testing is driven by a taxonomy of difficulty derived from the challenges USAR crews face navigating void spaces and their associated hazards. Initial experiments explore the viability of the vine robot form factor, both ideal and implemented, as well as the control and sensorization of the system. A secondary set of experiments applies domain-specific design improvements to increase the portability and reliability of the system. SPROUT can grow through tight apertures, around corners, and into void spaces, but requires additional development in sensorization to improve control and situational awareness.
Estimating Infinite-Dimensional Continuum Robot States From the Tip
Nov 02, 2023Abstract:Knowing the state of a robot is critical for many problems, such as feedback control. For continuum robots, state estimation is incredibly challenging. First, the motion of a continuum robot involves many kinematic states, including poses, strains, and velocities. Second, all these states are infinite-dimensional due to the robot's flexible property. It has remained unclear whether these infinite-dimensional states are observable at all using existing sensing techniques. Recently, we presented a solution to this challenge. It was a mechanics-based dynamic state estimation algorithm, called a Cosserat theoretic boundary observer, which could recover all the infinite-dimensional robot states by only measuring the velocity twist of the tip. In this work, we generalize the algorithm to incorporate tip pose measurements for more tuning freedom. We also validate this algorithm offline using recorded experimental data of a tendon-driven continuum robot. Specifically, we feed the recorded tension of the tendon and the recorded tip measurements into a numerical solver of the Cosserat rod model based on our continuum robot. It is observed that, even with purposely deviated initialization, the state estimates by our algorithm quickly converge to the recorded ground truth states and closely follow the robot's actual motion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge