Mardhiyah Sanni
Kakugo: Distillation of Low-Resource Languages into Small Language Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We present Kakugo, a novel and cost-effective pipeline designed to train general-purpose Small Language Models (SLMs) for low-resource languages using only the language name as input. By using a large teacher model to generate synthetic prompts and translate instruction datasets, we produced training data and SLMs for 54 low-resource languages. Evaluations across a diverse set of general natural language processing tasks, including translation, classification, and question answering, demonstrate that our pipeline consistently improves performance over base models. With a total generation and training cost of under $50 per language, Kakugo offers an accessible method for communities to develop language-specific AI.
AfriSpeech-MultiBench: A Verticalized Multidomain Multicountry Benchmark Suite for African Accented English ASR
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in speech-enabled AI, including Google's NotebookLM and OpenAI's speech-to-speech API, are driving widespread interest in voice interfaces globally. Despite this momentum, there exists no publicly available application-specific model evaluation that caters to Africa's linguistic diversity. We present AfriSpeech-MultiBench, the first domain-specific evaluation suite for over 100 African English accents across 10+ countries and seven application domains: Finance, Legal, Medical, General dialogue, Call Center, Named Entities and Hallucination Robustness. We benchmark a diverse range of open, closed, unimodal ASR and multimodal LLM-based speech recognition systems using both spontaneous and non-spontaneous speech conversation drawn from various open African accented English speech datasets. Our empirical analysis reveals systematic variation: open-source ASR models excels in spontaneous speech contexts but degrades on noisy, non-native dialogue; multimodal LLMs are more accent-robust yet struggle with domain-specific named entities; proprietary models deliver high accuracy on clean speech but vary significantly by country and domain. Models fine-tuned on African English achieve competitive accuracy with lower latency, a practical advantage for deployment, hallucinations still remain a big problem for most SOTA models. By releasing this comprehensive benchmark, we empower practitioners and researchers to select voice technologies suited to African use-cases, fostering inclusive voice applications for underserved communities.
Afrispeech-Dialog: A Benchmark Dataset for Spontaneous English Conversations in Healthcare and Beyond
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Speech technologies are transforming interactions across various sectors, from healthcare to call centers and robots, yet their performance on African-accented conversations remains underexplored. We introduce Afrispeech-Dialog, a benchmark dataset of 50 simulated medical and non-medical African-accented English conversations, designed to evaluate automatic speech recognition (ASR) and related technologies. We assess state-of-the-art (SOTA) speaker diarization and ASR systems on long-form, accented speech, comparing their performance with native accents and discover a 10%+ performance degradation. Additionally, we explore medical conversation summarization capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to demonstrate the impact of ASR errors on downstream medical summaries, providing insights into the challenges and opportunities for speech technologies in the Global South. Our work highlights the need for more inclusive datasets to advance conversational AI in low-resource settings.
The Multicultural Medical Assistant: Can LLMs Improve Medical ASR Errors Across Borders?
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:The global adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) in healthcare shows promise to enhance clinical workflows and improve patient outcomes. However, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) errors in critical medical terms remain a significant challenge. These errors can compromise patient care and safety if not detected. This study investigates the prevalence and impact of ASR errors in medical transcription in Nigeria, the United Kingdom, and the United States. By evaluating raw and LLM-corrected transcriptions of accented English in these regions, we assess the potential and limitations of LLMs to address challenges related to accents and medical terminology in ASR. Our findings highlight significant disparities in ASR accuracy across regions and identify specific conditions under which LLM corrections are most effective.
AfriMed-QA: A Pan-African, Multi-Specialty, Medical Question-Answering Benchmark Dataset
Nov 23, 2024

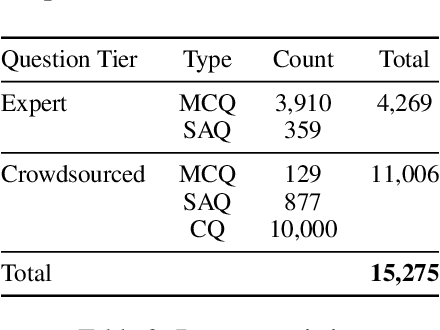

Abstract:Recent advancements in large language model(LLM) performance on medical multiple choice question (MCQ) benchmarks have stimulated interest from healthcare providers and patients globally. Particularly in low-and middle-income countries (LMICs) facing acute physician shortages and lack of specialists, LLMs offer a potentially scalable pathway to enhance healthcare access and reduce costs. However, their effectiveness in the Global South, especially across the African continent, remains to be established. In this work, we introduce AfriMed-QA, the first large scale Pan-African English multi-specialty medical Question-Answering (QA) dataset, 15,000 questions (open and closed-ended) sourced from over 60 medical schools across 16 countries, covering 32 medical specialties. We further evaluate 30 LLMs across multiple axes including correctness and demographic bias. Our findings show significant performance variation across specialties and geographies, MCQ performance clearly lags USMLE (MedQA). We find that biomedical LLMs underperform general models and smaller edge-friendly LLMs struggle to achieve a passing score. Interestingly, human evaluations show a consistent consumer preference for LLM answers and explanations when compared with clinician answers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge