Marcelo Gennari do Nascimento
SliceGPT: Compress Large Language Models by Deleting Rows and Columns
Jan 26, 2024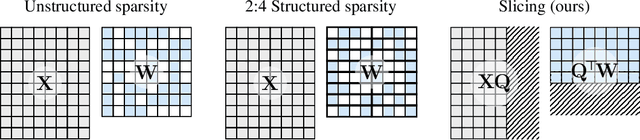
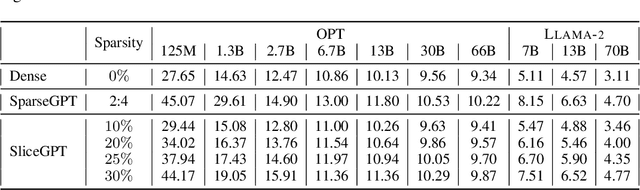

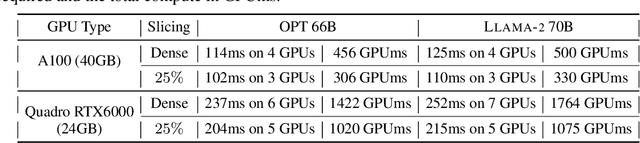
Abstract:Large language models have become the cornerstone of natural language processing, but their use comes with substantial costs in terms of compute and memory resources. Sparsification provides a solution to alleviate these resource constraints, and recent works have shown that trained models can be sparsified post-hoc. Existing sparsification techniques face challenges as they need additional data structures and offer constrained speedup with current hardware. In this paper we present SliceGPT, a new post-training sparsification scheme which replaces each weight matrix with a smaller (dense) matrix, reducing the embedding dimension of the network. Through extensive experimentation, we show that SliceGPT can remove up to 25% of the model parameters (including embeddings) for LLAMA2-70B, OPT 66B and Phi-2 models while maintaining 99%, 99% and 90% zero-shot task performance of the dense model respectively. Our sliced models run on fewer GPUs and run faster without any additional code optimization: on 24GB consumer GPUs we reduce the total compute for inference on LLAMA2-70B to 64% of that of the dense model; on 40GB A100 GPUs we reduce it to 66%. We offer a new insight, computational invariance in transformer networks, which enables SliceGPT and we hope it will inspire and enable future avenues to reduce memory and computation demands for pre-trained models. Code is available at: https://github.com/microsoft/TransformerCompression
Finding Non-Uniform Quantization Schemes using Multi-Task Gaussian Processes
Jul 20, 2020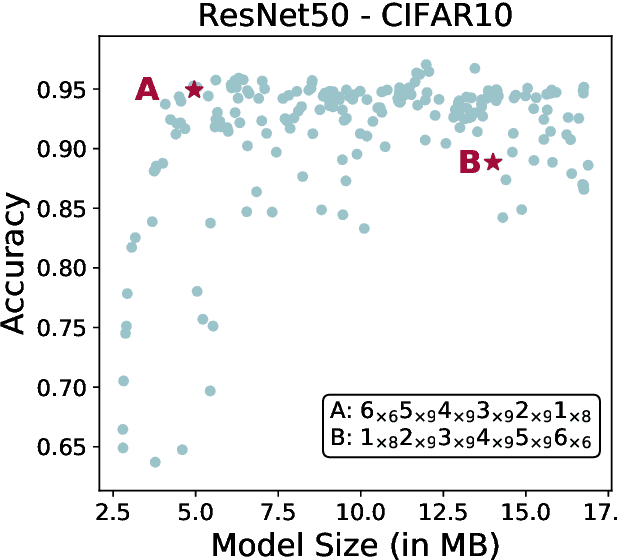
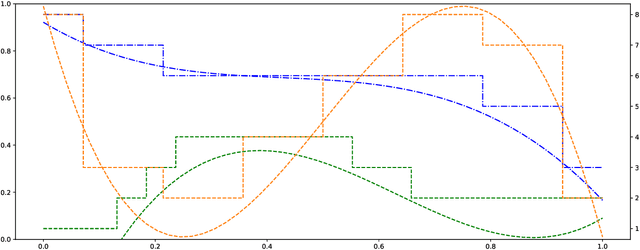
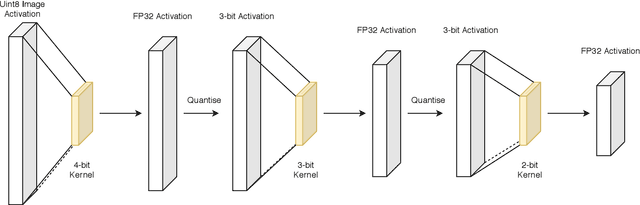
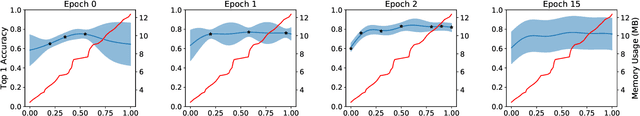
Abstract:We propose a novel method for neural network quantization that casts the neural architecture search problem as one of hyperparameter search to find non-uniform bit distributions throughout the layers of a CNN. We perform the search assuming a Multi-Task Gaussian Processes prior, which splits the problem to multiple tasks, each corresponding to different number of training epochs, and explore the space by sampling those configurations that yield maximum information. We then show that with significantly lower precision in the last layers we achieve a minimal loss of accuracy with appreciable memory savings. We test our findings on the CIFAR10 and ImageNet datasets using the VGG, ResNet and GoogLeNet architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge