Marcel Sheeny
All-Weather Object Recognition Using Radar and Infrared Sensing
Oct 30, 2020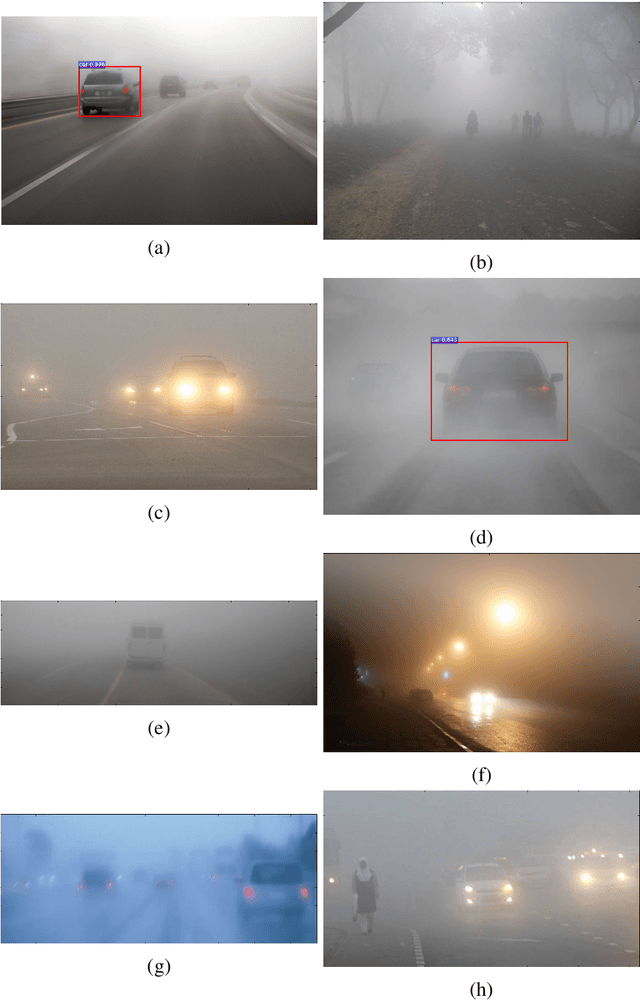



Abstract:Autonomous cars are an emergent technology which has the capacity to change human lives. The current sensor systems which are most capable of perception are based on optical sensors. For example, deep neural networks show outstanding results in recognising objects when used to process data from cameras and Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) sensors. However these sensors perform poorly under adverse weather conditions such as rain, fog, and snow due to the sensor wavelengths. This thesis explores new sensing developments based on long wave polarised infrared (IR) imagery and imaging radar to recognise objects. First, we developed a methodology based on Stokes parameters using polarised infrared data to recognise vehicles using deep neural networks. Second, we explored the potential of using only the power spectrum captured by low-THz radar sensors to perform object recognition in a controlled scenario. This latter work is based on a data-driven approach together with the development of a data augmentation method based on attenuation, range and speckle noise. Last, we created a new large-scale dataset in the "wild" with many different weather scenarios (sunny, overcast, night, fog, rain and snow) showing radar robustness to detect vehicles in adverse weather. High resolution radar and polarised IR imagery, combined with a deep learning approach, are shown as a potential alternative to current automotive sensing systems based on visible spectrum optical technology as they are more robust in severe weather and adverse light conditions.
RADIATE: A Radar Dataset for Automotive Perception
Oct 18, 2020
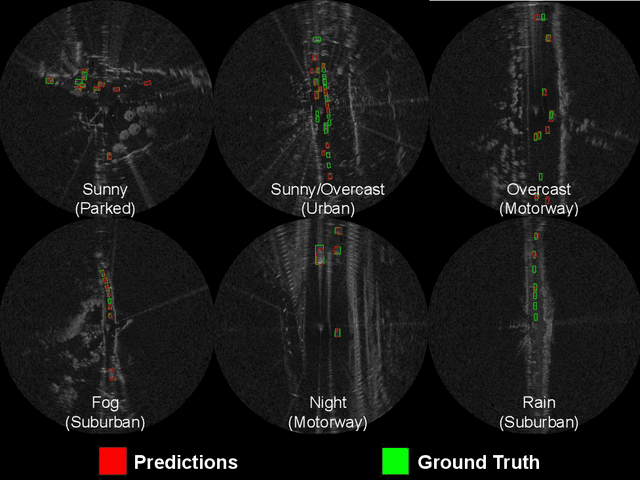
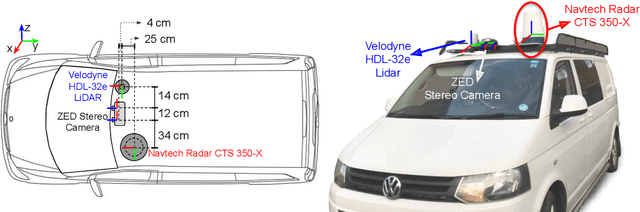

Abstract:Datasets for autonomous cars are essential for the development and benchmarking of perception systems. However, most existing datasets are captured with camera and LiDAR sensors in good weather conditions. In this paper, we present the RAdar Dataset In Adverse weaThEr (RADIATE), aiming to facilitate research on object detection, tracking and scene understanding using radar sensing for safe autonomous driving. RADIATE includes 3 hours of annotated radar images with more than 200K labelled road actors in total, on average about 4.6 instances per radar image. It covers 8 different categories of actors in a variety of weather conditions (e.g., sun, night, rain, fog and snow) and driving scenarios (e.g., parked, urban, motorway and suburban), representing different levels of challenge. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first public radar dataset which provides high-resolution radar images on public roads with a large amount of road actors labelled. The data collected in adverse weather, e.g., fog and snowfall, is unique. Some baseline results of radar based object detection and recognition are given to show that the use of radar data is promising for automotive applications in bad weather, where vision and LiDAR can fail. RADIATE also has stereo images, 32-channel LiDAR and GPS data, directed at other applications such as sensor fusion, localisation and mapping. The public dataset can be accessed at http://pro.hw.ac.uk/radiate/.
300 GHz Radar Object Recognition based on Deep Neural Networks and Transfer Learning
Dec 06, 2019



Abstract:For high resolution scene mapping and object recognition, optical technologies such as cameras and LiDAR are the sensors of choice. However, for robust future vehicle autonomy and driver assistance in adverse weather conditions, improvements in automotive radar technology, and the development of algorithms and machine learning for robust mapping and recognition are essential. In this paper, we describe a methodology based on deep neural networks to recognise objects in 300GHz radar images, investigating robustness to changes in range, orientation and different receivers in a laboratory environment. As the training data is limited, we have also investigated the effects of transfer learning. As a necessary first step before road trials, we have also considered detection and classification in multiple object scenes.
POL-LWIR Vehicle Detection: Convolutional Neural Networks Meet Polarised Infrared Sensors
Apr 07, 2018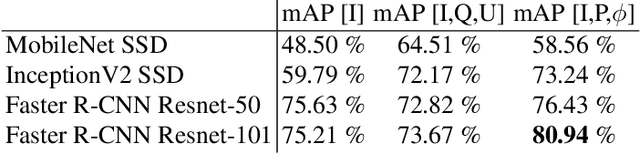

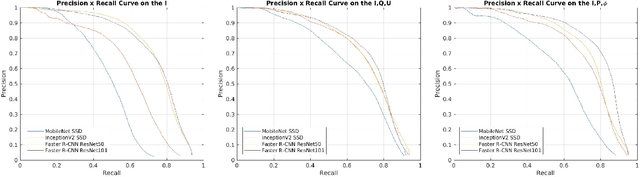
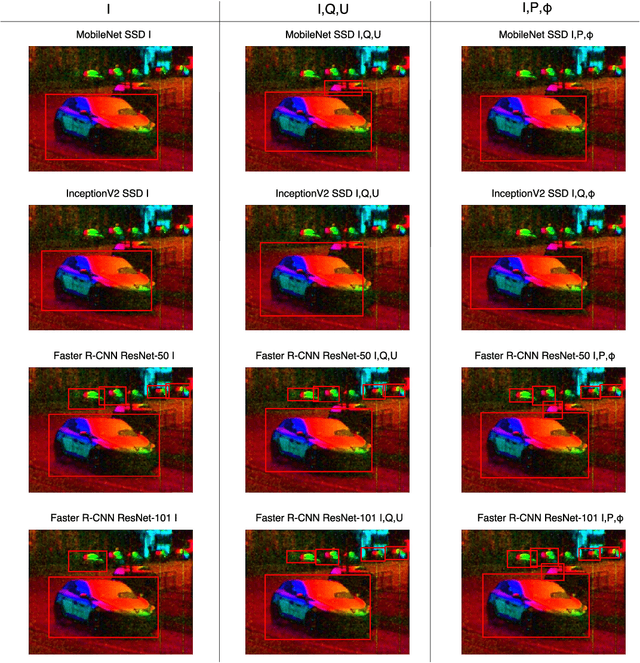
Abstract:For vehicle autonomy, driver assistance and situational awareness, it is necessary to operate at day and night, and in all weather conditions. In particular, long wave infrared (LWIR) sensors that receive predominantly emitted radiation have the capability to operate at night as well as during the day. In this work, we employ a polarised LWIR (POL-LWIR) camera to acquire data from a mobile vehicle, to compare and contrast four different convolutional neural network (CNN) configurations to detect other vehicles in video sequences. We evaluate two distinct and promising approaches, two-stage detection (Faster-RCNN) and one-stage detection (SSD), in four different configurations. We also employ two different image decompositions: the first based on the polarisation ellipse and the second on the Stokes parameters themselves. To evaluate our approach, the experimental trials were quantified by mean average precision (mAP) and processing time, showing a clear trade-off between the two factors. For example, the best mAP result of 80.94% was achieved using Faster-RCNN, but at a frame rate of 6.4 fps. In contrast, MobileNet SSD achieved only 64.51% mAP, but at 53.4 fps.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge