Marc-Antoine Maheux
Fast Cross-Correlation for TDoA Estimation on Small Aperture Microphone Arrays
Apr 28, 2022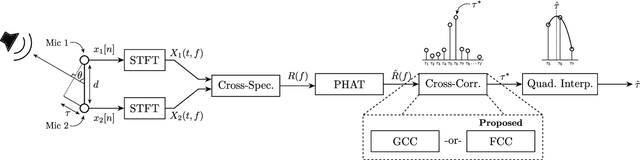
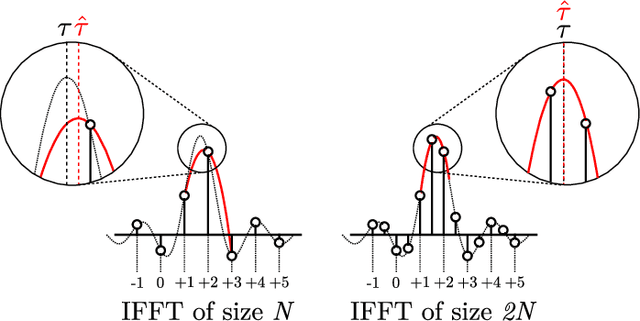
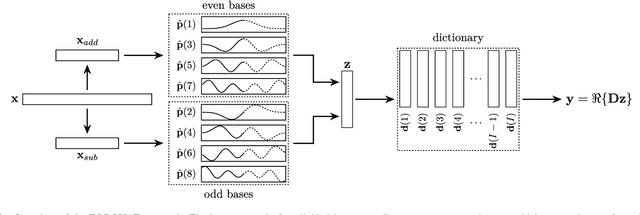
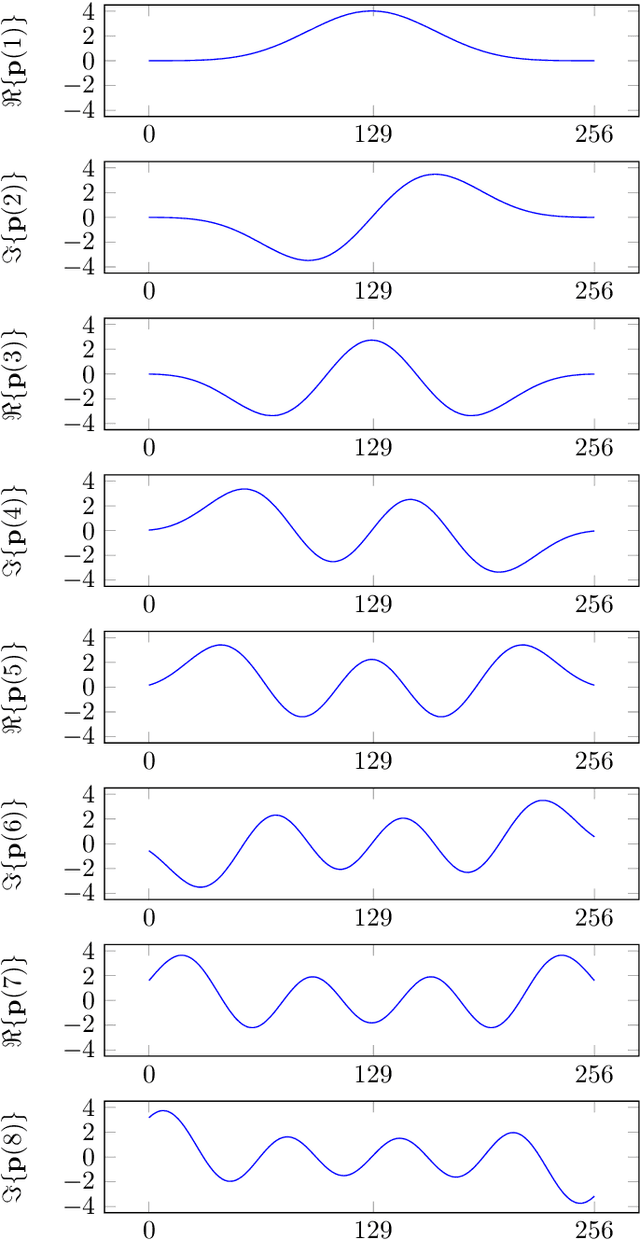
Abstract:This paper introduces the Fast Cross-Correlation (FCC) method for Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) Estimation for pairs of microphones on a small aperture microphone array. FCC relies on low-rank decomposition and exploits symmetry in even and odd bases to speed up computation while preserving TDoA accuracy. FCC reduces the number of flops by a factor of 4.5 and the execution speed by factors of 8.2, 2.6 and 2.7 on a Raspberry Pi Zero, a Raspberry Pi 4 and a Nvidia Jetson TX2 devices, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art Generalized Cross-Correlation (GCC) method that relies on the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This improvement can provide portable microphone arrays with extended battery life and allow real-time processing on low-cost hardware.
SMP-PHAT: Lightweight DoA Estimation by Merging Microphone Pairs
Mar 27, 2022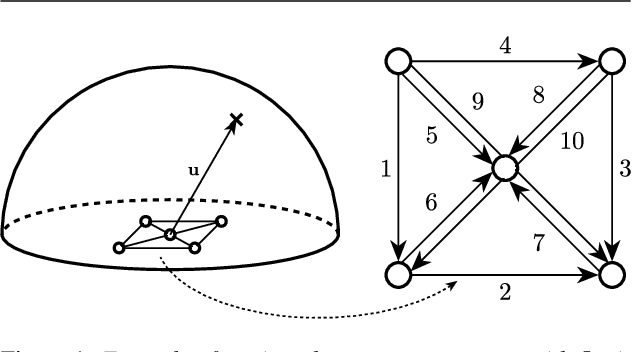
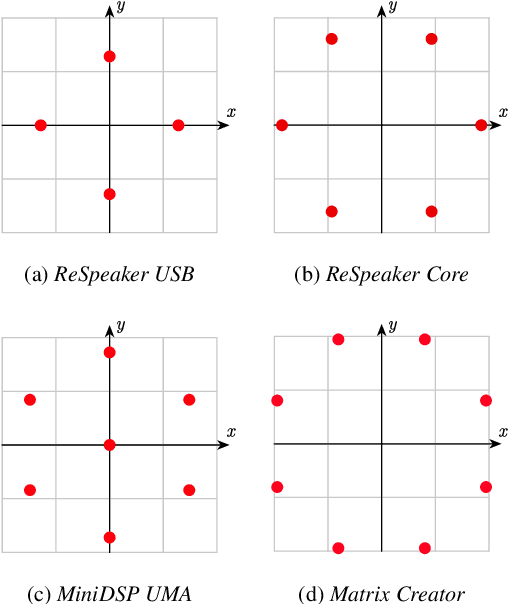
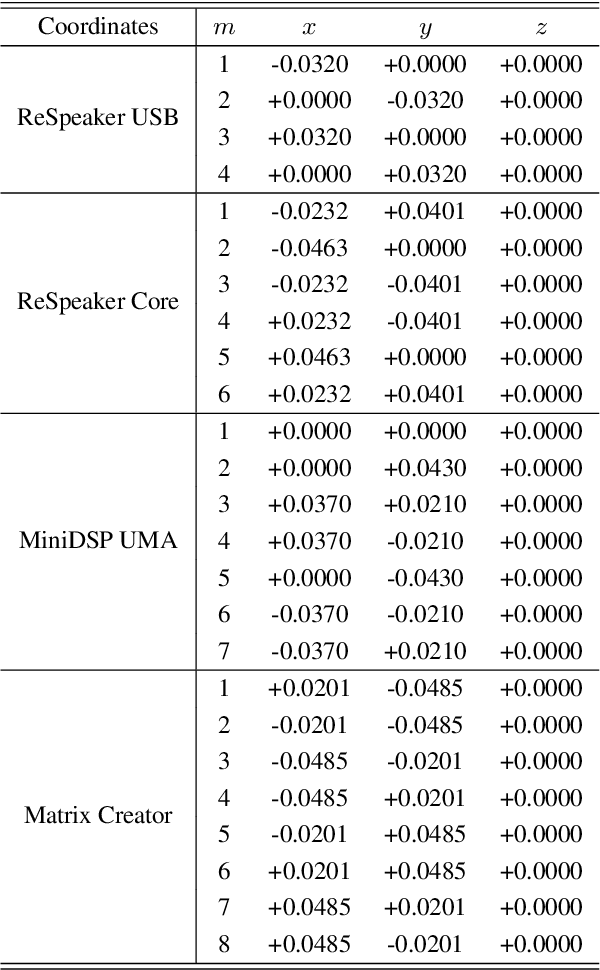
Abstract:This paper introduces SMP-PHAT, which performs direction of arrival (DoA) of sound estimation with a microphone array by merging pairs of microphones that are parallel in space. This approach reduces the number of pairwise cross-correlation computations, and brings down the number of flops and memory lookups when searching for DoA. Experiments on low-cost hardware with commonly used microphone arrays show that the proposed method provides the same accuracy as the former SRP-PHAT approach, while reducing the computational load by 39% in some cases.
OpenTera: A Microservice Architecture Solution for Rapid Prototyping of Robotic Solutions to COVID-19 Challenges in Care Facilities
Mar 10, 2021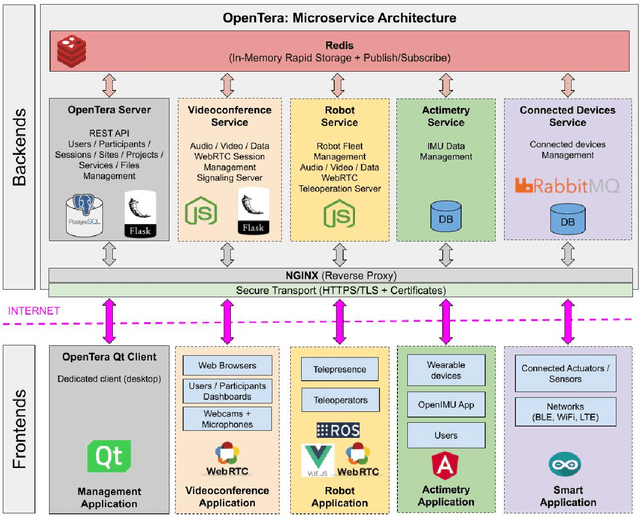
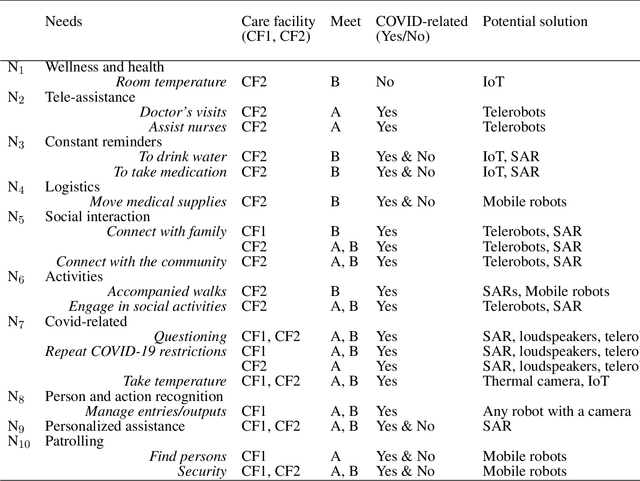
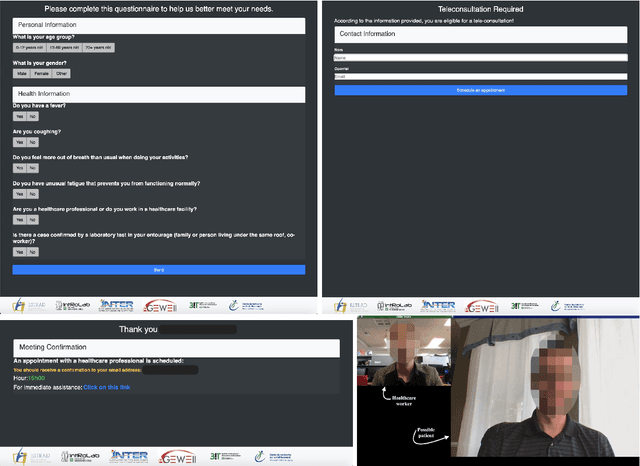
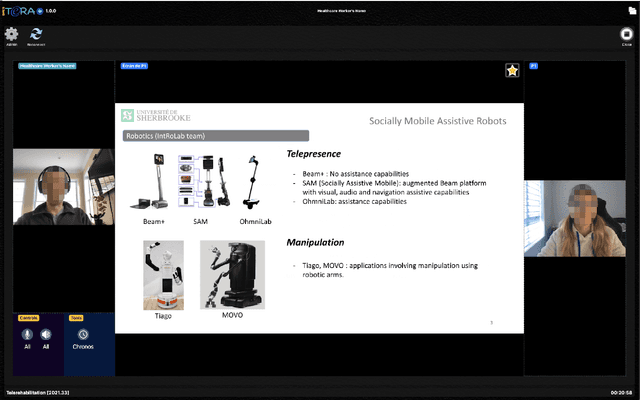
Abstract:As telecommunications technology progresses, telehealth frameworks are becoming more widely adopted in the context of long-term care (LTC) for older adults, both in care facilities and in homes. Today, robots could assist healthcare workers when they provide care to elderly patients, who constitute a particularly vulnerable population during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previous work on user-centered design of assistive technologies in LTC facilities for seniors has identified positive impacts. The need to deal with the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic emphasizes the benefits of this approach, but also highlights some new challenges for which robots could be interesting solutions to be deployed in LTC facilities. This requires customization of telecommunication and audio/video/data processing to address specific clinical requirements and needs. This paper presents OpenTera, an open source telehealth framework, aiming to facilitate prototyping of such solutions by software and robotic designers. Designed as a microservice-oriented platform, OpenTera is an end-to-end solution that employs a series of independent modules for tasks such as data and session management, telehealth, daily assistive tasks/actions, together with smart devices and environments, all connected through the framework. After explaining the framework, we illustrate how OpenTera can be used to implement robotic solutions for different applications identified in LTC facilities and homes, and we describe how we plan to validate them through field trials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge