Manuel Schottdorf
Unsupervised discovery of the shared and private geometry in multi-view data
Aug 22, 2024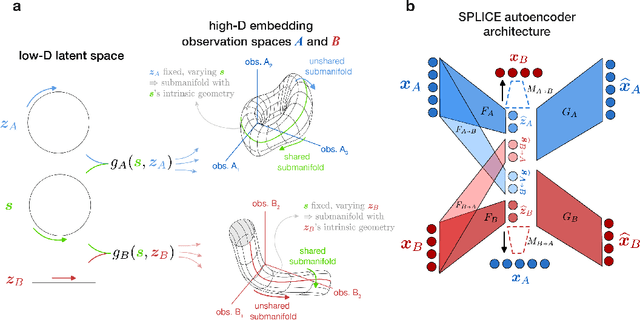
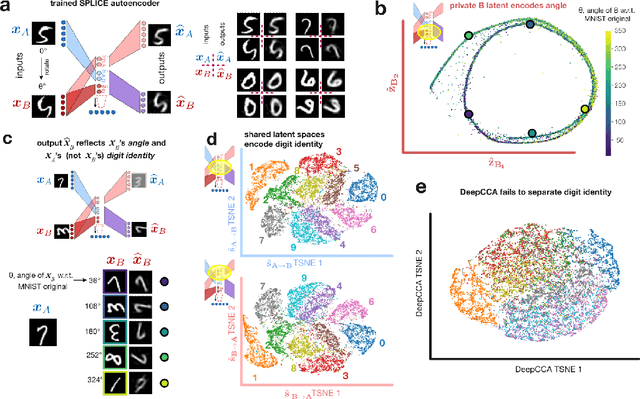
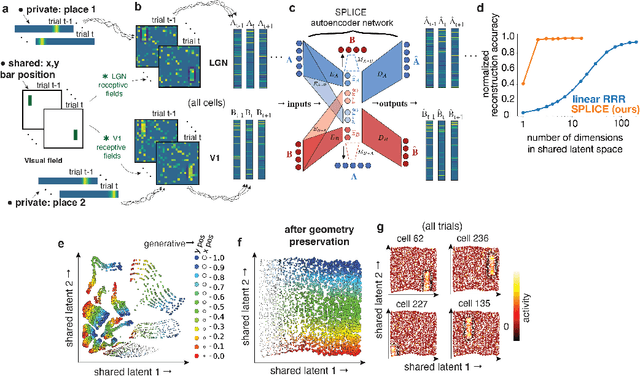
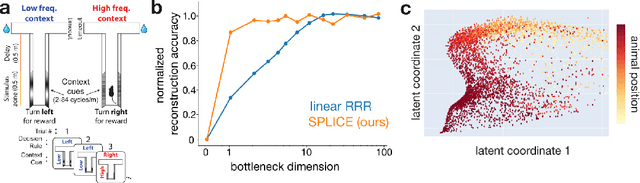
Abstract:Modern applications often leverage multiple views of a subject of study. Within neuroscience, there is growing interest in large-scale simultaneous recordings across multiple brain regions. Understanding the relationship between views (e.g., the neural activity in each region recorded) can reveal fundamental principles about the characteristics of each representation and about the system. However, existing methods to characterize such relationships either lack the expressivity required to capture complex nonlinearities, describe only sources of variance that are shared between views, or discard geometric information that is crucial to interpreting the data. Here, we develop a nonlinear neural network-based method that, given paired samples of high-dimensional views, disentangles low-dimensional shared and private latent variables underlying these views while preserving intrinsic data geometry. Across multiple simulated and real datasets, we demonstrate that our method outperforms competing methods. Using simulated populations of lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and V1 neurons we demonstrate our model's ability to discover interpretable shared and private structure across different noise conditions. On a dataset of unrotated and corresponding but randomly rotated MNIST digits, we recover private latents for the rotated view that encode rotation angle regardless of digit class, and places the angle representation on a 1-d manifold, while shared latents encode digit class but not rotation angle. Applying our method to simultaneous Neuropixels recordings of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex while mice run on a linear track, we discover a low-dimensional shared latent space that encodes the animal's position. We propose our approach as a general-purpose method for finding succinct and interpretable descriptions of paired data sets in terms of disentangled shared and private latent variables.
Machine Learning for Mechanical Ventilation Control (Extended Abstract)
Nov 23, 2021Abstract:Mechanical ventilation is one of the most widely used therapies in the ICU. However, despite broad application from anaesthesia to COVID-related life support, many injurious challenges remain. We frame these as a control problem: ventilators must let air in and out of the patient's lungs according to a prescribed trajectory of airway pressure. Industry-standard controllers, based on the PID method, are neither optimal nor robust. Our data-driven approach learns to control an invasive ventilator by training on a simulator itself trained on data collected from the ventilator. This method outperforms popular reinforcement learning algorithms and even controls the physical ventilator more accurately and robustly than PID. These results underscore how effective data-driven methodologies can be for invasive ventilation and suggest that more general forms of ventilation (e.g., non-invasive, adaptive) may also be amenable.
Machine Learning for Mechanical Ventilation Control
Feb 26, 2021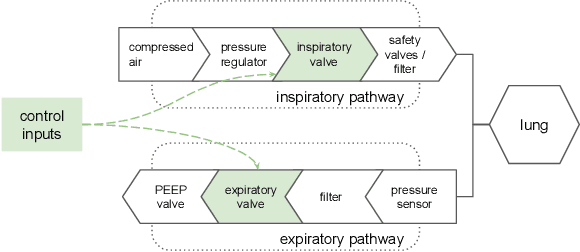
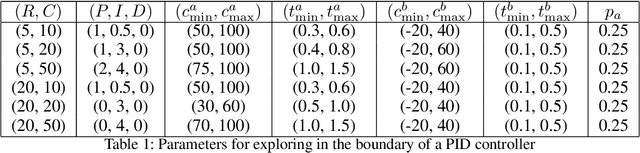
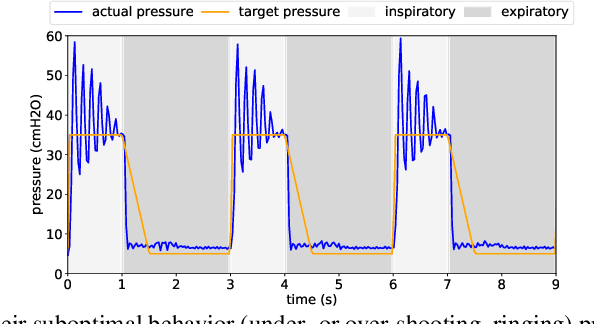
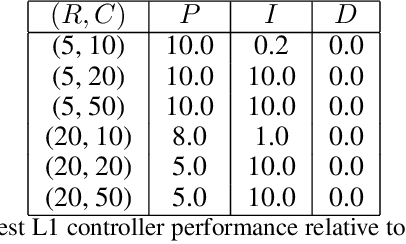
Abstract:We consider the problem of controlling an invasive mechanical ventilator for pressure-controlled ventilation: a controller must let air in and out of a sedated patient's lungs according to a trajectory of airway pressures specified by a clinician. Hand-tuned PID controllers and similar variants have comprised the industry standard for decades, yet can behave poorly by over- or under-shooting their target or oscillating rapidly. We consider a data-driven machine learning approach: First, we train a simulator based on data we collect from an artificial lung. Then, we train deep neural network controllers on these simulators.We show that our controllers are able to track target pressure waveforms significantly better than PID controllers. We further show that a learned controller generalizes across lungs with varying characteristics much more readily than PID controllers do.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge