Mallikarjuna Vayugundla
GPGM-SLAM: a Robust SLAM System for Unstructured Planetary Environments with Gaussian Process Gradient Maps
Sep 14, 2021


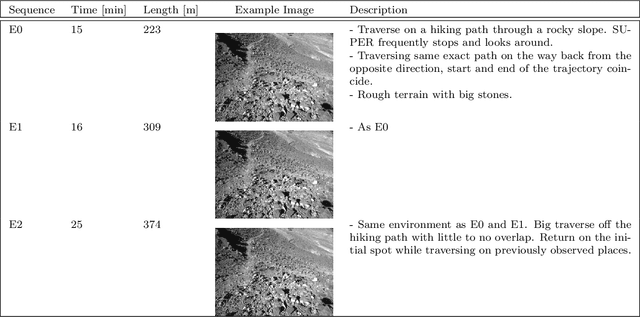
Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) techniques play a key role towards long-term autonomy of mobile robots due to the ability to correct localization errors and produce consistent maps of an environment over time. Contrarily to urban or man-made environments, where the presence of unique objects and structures offer unique cues for localization, the appearance of unstructured natural environments is often ambiguous and self-similar, hindering the performances of loop closure detection. In this paper, we present an approach to improve the robustness of place recognition in the context of a submap-based stereo SLAM based on Gaussian Process Gradient Maps (GPGMaps). GPGMaps embed a continuous representation of the gradients of the local terrain elevation by means of Gaussian Process regression and Structured Kernel Interpolation, given solely noisy elevation measurements. We leverage the image-like structure of GPGMaps to detect loop closures using traditional visual features and Bag of Words. GPGMap matching is performed as an SE(2) alignment to establish loop closure constraints within a pose graph. We evaluate the proposed pipeline on a variety of datasets recorded on Mt. Etna, Sicily and in the Morocco desert, respectively Moon- and Mars-like environments, and we compare the localization performances with state-of-the-art approaches for visual SLAM and visual loop closure detection.
Multi-Modal Loop Closing in Unstructured Planetary Environments with Visually Enriched Submaps
May 05, 2021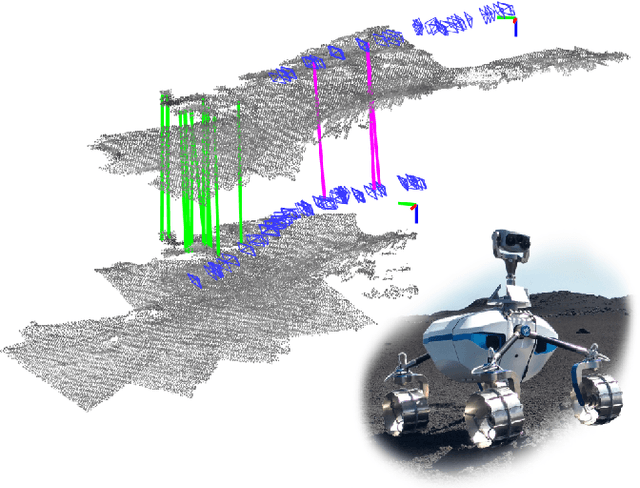

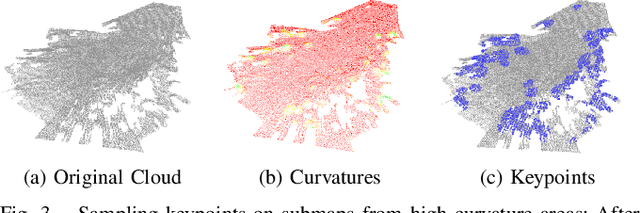
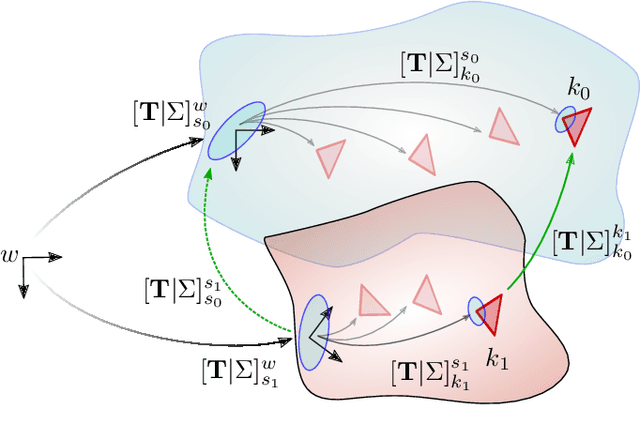
Abstract:Future planetary missions will rely on rovers that can autonomously explore and navigate in unstructured environments. An essential element is the ability to recognize places that were already visited or mapped. In this work we leverage the ability of stereo cameras to provide both visual and depth information, guiding the search and validation of loop closures from a multi-modal perspective. We propose to augment submaps that are created by aggregating stereo point clouds, with visual keyframes. Point clouds matches are found by comparing CSHOT descriptors and validated by clustering while visual matches are established by comparing keyframes using Bag-of-Words (BoW) and ORB descriptors. The relative transformations resulting from both keyframe and point cloud matches are then fused to provide pose constraints between submaps in our graph-based SLAM framework. Using the LRU rover, we performed several tests in both an indoor laboratory environment as well as a challenging planetary analog environment on Mount Etna, Italy. These environments consist of areas where either keyframes or point clouds alone fail to provide adequate matches, thus demonstrating the benefit of the proposed multi-modal approach.
Gaussian Process Gradient Maps for Loop-Closure Detection in Unstructured Planetary Environments
Sep 01, 2020

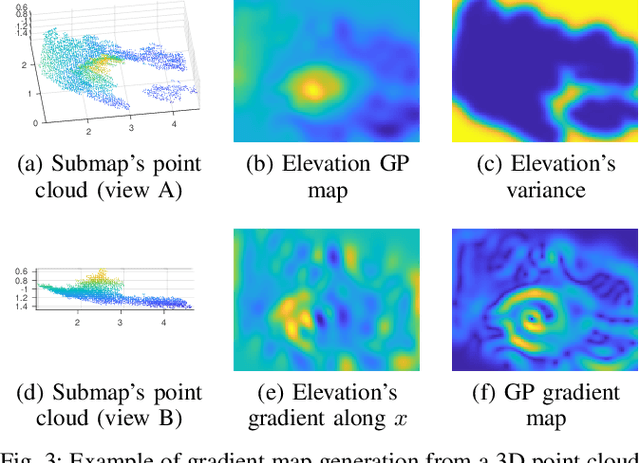

Abstract:The ability to recognize previously mapped locations is an essential feature for autonomous systems. Unstructured planetary-like environments pose a major challenge to these systems due to the similarity of the terrain. As a result, the ambiguity of the visual appearance makes state-of-the-art visual place recognition approaches less effective than in urban or man-made environments. This paper presents a method to solve the loop closure problem using only spatial information. The key idea is to use a novel continuous and probabilistic representations of terrain elevation maps. Given 3D point clouds of the environment, the proposed approach exploits Gaussian Process (GP) regression with linear operators to generate continuous gradient maps of the terrain elevation information. Traditional image registration techniques are then used to search for potential matches. Loop closures are verified by leveraging both the spatial characteristic of the elevation maps (SE(2) registration) and the probabilistic nature of the GP representation. A submap-based localization and mapping framework is used to demonstrate the validity of the proposed approach. The performance of this pipeline is evaluated and benchmarked using real data from a rover that is equipped with a stereo camera and navigates in challenging, unstructured planetary-like environments in Morocco and on Mt. Etna.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge