Mahsa Taziki
Asynchronous Byzantine Machine Learning (the case of SGD)
Jul 09, 2018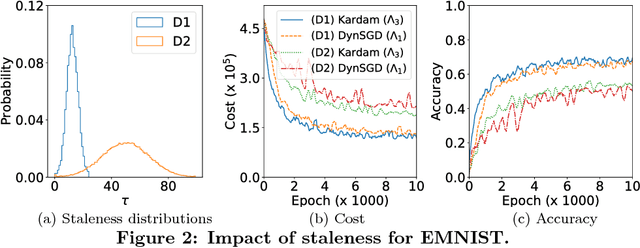
Abstract:Asynchronous distributed machine learning solutions have proven very effective so far, but always assuming perfectly functioning workers. In practice, some of the workers can however exhibit Byzantine behavior, caused by hardware failures, software bugs, corrupt data, or even malicious attacks. We introduce \emph{Kardam}, the first distributed asynchronous stochastic gradient descent (SGD) algorithm that copes with Byzantine workers. Kardam consists of two complementary components: a filtering and a dampening component. The first is scalar-based and ensures resilience against $\frac{1}{3}$ Byzantine workers. Essentially, this filter leverages the Lipschitzness of cost functions and acts as a self-stabilizer against Byzantine workers that would attempt to corrupt the progress of SGD. The dampening component bounds the convergence rate by adjusting to stale information through a generic gradient weighting scheme. We prove that Kardam guarantees almost sure convergence in the presence of asynchrony and Byzantine behavior, and we derive its convergence rate. We evaluate Kardam on the CIFAR-100 and EMNIST datasets and measure its overhead with respect to non Byzantine-resilient solutions. We empirically show that Kardam does not introduce additional noise to the learning procedure but does induce a slowdown (the cost of Byzantine resilience) that we both theoretically and empirically show to be less than $f/n$, where $f$ is the number of Byzantine failures tolerated and $n$ the total number of workers. Interestingly, we also empirically observe that the dampening component is interesting in its own right for it enables to build an SGD algorithm that outperforms alternative staleness-aware asynchronous competitors in environments with honest workers.
Personalized and Private Peer-to-Peer Machine Learning
Feb 19, 2018


Abstract:The rise of connected personal devices together with privacy concerns call for machine learning algorithms capable of leveraging the data of a large number of agents to learn personalized models under strong privacy requirements. In this paper, we introduce an efficient algorithm to address the above problem in a fully decentralized (peer-to-peer) and asynchronous fashion, with provable convergence rate. We show how to make the algorithm differentially private to protect against the disclosure of information about the personal datasets, and formally analyze the trade-off between utility and privacy. Our experiments show that our approach dramatically outperforms previous work in the non-private case, and that under privacy constraints, we can significantly improve over models learned in isolation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge