Magdalena Wache
Factored space models: Towards causality between levels of abstraction
Dec 03, 2024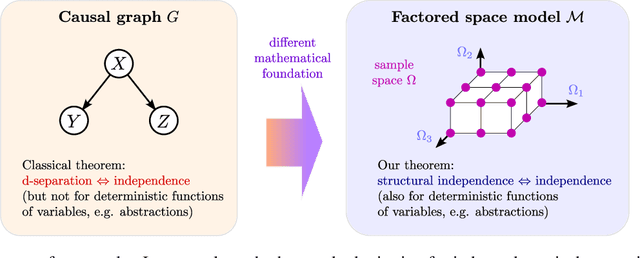


Abstract:Causality plays an important role in understanding intelligent behavior, and there is a wealth of literature on mathematical models for causality, most of which is focused on causal graphs. Causal graphs are a powerful tool for a wide range of applications, in particular when the relevant variables are known and at the same level of abstraction. However, the given variables can also be unstructured data, like pixels of an image. Meanwhile, the causal variables, such as the positions of objects in the image, can be arbitrary deterministic functions of the given variables. Moreover, the causal variables may form a hierarchy of abstractions, in which the macro-level variables are deterministic functions of the micro-level variables. Causal graphs are limited when it comes to modeling this kind of situation. In the presence of deterministic relationships there is generally no causal graph that satisfies both the Markov condition and the faithfulness condition. We introduce factored space models as an alternative to causal graphs which naturally represent both probabilistic and deterministic relationships at all levels of abstraction. Moreover, we introduce structural independence and establish that it is equivalent to statistical independence in every distribution that factorizes over the factored space. This theorem generalizes the classical soundness and completeness theorem for d-separation.
The Local Interaction Basis: Identifying Computationally-Relevant and Sparsely Interacting Features in Neural Networks
May 17, 2024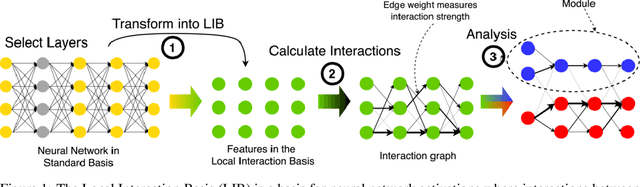
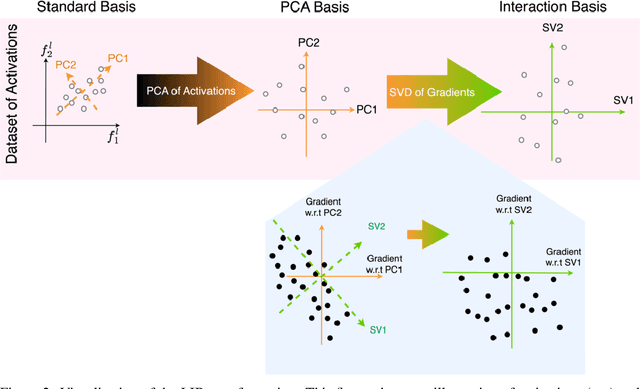
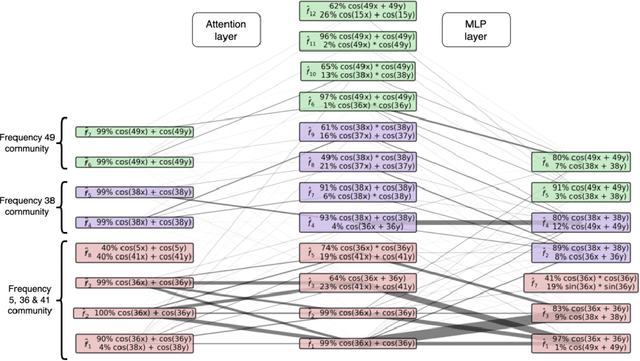
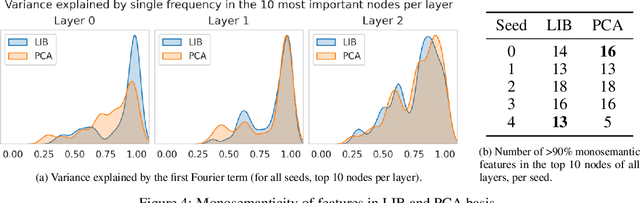
Abstract:Mechanistic interpretability aims to understand the behavior of neural networks by reverse-engineering their internal computations. However, current methods struggle to find clear interpretations of neural network activations because a decomposition of activations into computational features is missing. Individual neurons or model components do not cleanly correspond to distinct features or functions. We present a novel interpretability method that aims to overcome this limitation by transforming the activations of the network into a new basis - the Local Interaction Basis (LIB). LIB aims to identify computational features by removing irrelevant activations and interactions. Our method drops irrelevant activation directions and aligns the basis with the singular vectors of the Jacobian matrix between adjacent layers. It also scales features based on their importance for downstream computation, producing an interaction graph that shows all computationally-relevant features and interactions in a model. We evaluate the effectiveness of LIB on modular addition and CIFAR-10 models, finding that it identifies more computationally-relevant features that interact more sparsely, compared to principal component analysis. However, LIB does not yield substantial improvements in interpretability or interaction sparsity when applied to language models. We conclude that LIB is a promising theory-driven approach for analyzing neural networks, but in its current form is not applicable to large language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge