Maaz Amjad
Classification of Hope in Textual Data using Transformer-Based Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a transformer-based approach for classifying hope expressions in text. We developed and compared three architectures (BERT, GPT-2, and DeBERTa) for both binary classification (Hope vs. Not Hope) and multiclass categorization (five hope-related categories). Our initial BERT implementation achieved 83.65% binary and 74.87% multiclass accuracy. In the extended comparison, BERT demonstrated superior performance (84.49% binary, 72.03% multiclass accuracy) while requiring significantly fewer computational resources (443s vs. 704s training time) than newer architectures. GPT-2 showed lowest overall accuracy (79.34% binary, 71.29% multiclass), while DeBERTa achieved moderate results (80.70% binary, 71.56% multiclass) but at substantially higher computational cost (947s for multiclass training). Error analysis revealed architecture-specific strengths in detecting nuanced hope expressions, with GPT-2 excelling at sarcasm detection (92.46% recall). This study provides a framework for computational analysis of hope, with applications in mental health and social media analysis, while demonstrating that architectural suitability may outweigh model size for specialized emotion detection tasks.
Optimism, Expectation, or Sarcasm? Multi-Class Hope Speech Detection in Spanish and English
Apr 24, 2025
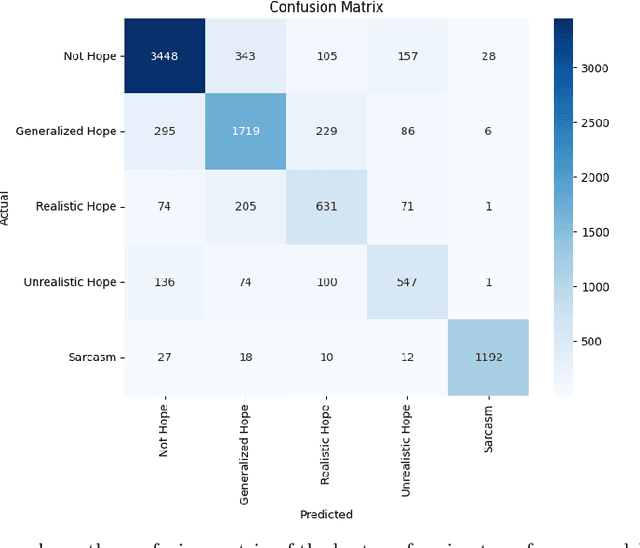
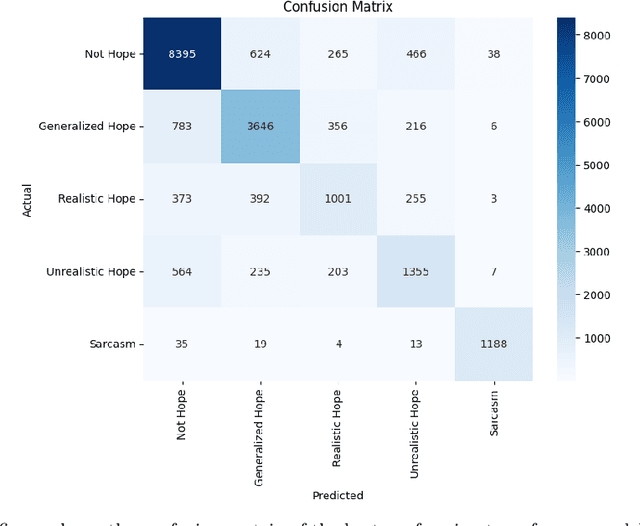
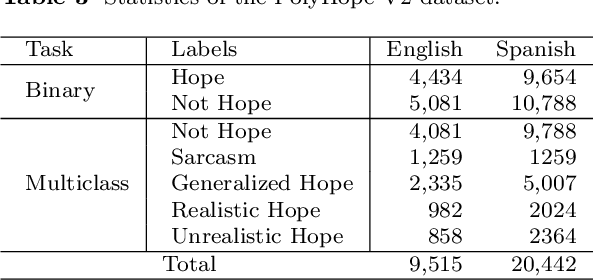
Abstract:Hope is a complex and underexplored emotional state that plays a significant role in education, mental health, and social interaction. Unlike basic emotions, hope manifests in nuanced forms ranging from grounded optimism to exaggerated wishfulness or sarcasm, making it difficult for Natural Language Processing systems to detect accurately. This study introduces PolyHope V2, a multilingual, fine-grained hope speech dataset comprising over 30,000 annotated tweets in English and Spanish. This resource distinguishes between four hope subtypes Generalized, Realistic, Unrealistic, and Sarcastic and enhances existing datasets by explicitly labeling sarcastic instances. We benchmark multiple pretrained transformer models and compare them with large language models (LLMs) such as GPT 4 and Llama 3 under zero-shot and few-shot regimes. Our findings show that fine-tuned transformers outperform prompt-based LLMs, especially in distinguishing nuanced hope categories and sarcasm. Through qualitative analysis and confusion matrices, we highlight systematic challenges in separating closely related hope subtypes. The dataset and results provide a robust foundation for future emotion recognition tasks that demand greater semantic and contextual sensitivity across languages.
GuReT: Distinguishing Guilt and Regret related Text
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:The intricate relationship between human decision-making and emotions, particularly guilt and regret, has significant implications on behavior and well-being. Yet, these emotions subtle distinctions and interplay are often overlooked in computational models. This paper introduces a dataset tailored to dissect the relationship between guilt and regret and their unique textual markers, filling a notable gap in affective computing research. Our approach treats guilt and regret recognition as a binary classification task and employs three machine learning and six transformer-based deep learning techniques to benchmark the newly created dataset. The study further implements innovative reasoning methods like chain-of-thought and tree-of-thought to assess the models interpretive logic. The results indicate a clear performance edge for transformer-based models, achieving a 90.4% macro F1 score compared to the 85.3% scored by the best machine learning classifier, demonstrating their superior capability in distinguishing complex emotional states.
UrduFake@FIRE2020: Shared Track on Fake News Identification in Urdu
Jul 25, 2022


Abstract:This paper gives the overview of the first shared task at FIRE 2020 on fake news detection in the Urdu language. This is a binary classification task in which the goal is to identify fake news using a dataset composed of 900 annotated news articles for training and 400 news articles for testing. The dataset contains news in five domains: (i) Health, (ii) Sports, (iii) Showbiz, (iv) Technology, and (v) Business. 42 teams from 6 different countries (India, China, Egypt, Germany, Pakistan, and the UK) registered for the task. 9 teams submitted their experimental results. The participants used various machine learning methods ranging from feature-based traditional machine learning to neural network techniques. The best performing system achieved an F-score value of 0.90, showing that the BERT-based approach outperforms other machine learning classifiers.
Overview of the Shared Task on Fake News Detection in Urdu at FIRE 2020
Jul 25, 2022



Abstract:This overview paper describes the first shared task on fake news detection in Urdu language. The task was posed as a binary classification task, in which the goal is to differentiate between real and fake news. We provided a dataset divided into 900 annotated news articles for training and 400 news articles for testing. The dataset contained news in five domains: (i) Health, (ii) Sports, (iii) Showbiz, (iv) Technology, and (v) Business. 42 teams from 6 different countries (India, China, Egypt, Germany, Pakistan, and the UK) registered for the task. 9 teams submitted their experimental results. The participants used various machine learning methods ranging from feature-based traditional machine learning to neural networks techniques. The best performing system achieved an F-score value of 0.90, showing that the BERT-based approach outperforms other machine learning techniques
Overview of Abusive and Threatening Language Detection in Urdu at FIRE 2021
Jul 14, 2022



Abstract:With the growth of social media platform influence, the effect of their misuse becomes more and more impactful. The importance of automatic detection of threatening and abusive language can not be overestimated. However, most of the existing studies and state-of-the-art methods focus on English as the target language, with limited work on low- and medium-resource languages. In this paper, we present two shared tasks of abusive and threatening language detection for the Urdu language which has more than 170 million speakers worldwide. Both are posed as binary classification tasks where participating systems are required to classify tweets in Urdu into two classes, namely: (i) Abusive and Non-Abusive for the first task, and (ii) Threatening and Non-Threatening for the second. We present two manually annotated datasets containing tweets labelled as (i) Abusive and Non-Abusive, and (ii) Threatening and Non-Threatening. The abusive dataset contains 2400 annotated tweets in the train part and 1100 annotated tweets in the test part. The threatening dataset contains 6000 annotated tweets in the train part and 3950 annotated tweets in the test part. We also provide logistic regression and BERT-based baseline classifiers for both tasks. In this shared task, 21 teams from six countries registered for participation (India, Pakistan, China, Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, and Taiwan), 10 teams submitted their runs for Subtask A, which is Abusive Language Detection and 9 teams submitted their runs for Subtask B, which is Threatening Language detection, and seven teams submitted their technical reports. The best performing system achieved an F1-score value of 0.880 for Subtask A and 0.545 for Subtask B. For both subtasks, m-Bert based transformer model showed the best performance.
UrduFake@FIRE2021: Shared Track on Fake News Identification in Urdu
Jul 11, 2022


Abstract:This study reports the second shared task named as UrduFake@FIRE2021 on identifying fake news detection in Urdu language. This is a binary classification problem in which the task is to classify a given news article into two classes: (i) real news, or (ii) fake news. In this shared task, 34 teams from 7 different countries (China, Egypt, Israel, India, Mexico, Pakistan, and UAE) registered to participate in the shared task, 18 teams submitted their experimental results and 11 teams submitted their technical reports. The proposed systems were based on various count-based features and used different classifiers as well as neural network architectures. The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) algorithm outperformed other classifiers and achieved 0.679 F-score.
Overview of the Shared Task on Fake News Detection in Urdu at FIRE 2021
Jul 11, 2022
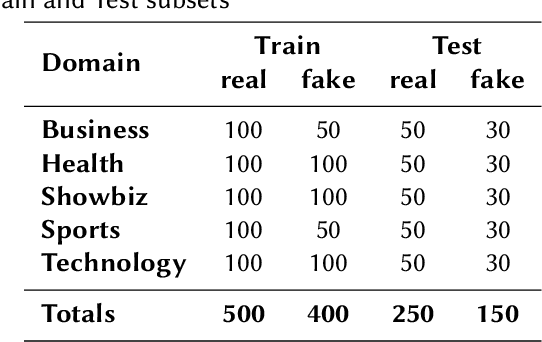


Abstract:Automatic detection of fake news is a highly important task in the contemporary world. This study reports the 2nd shared task called UrduFake@FIRE2021 on identifying fake news detection in Urdu. The goal of the shared task is to motivate the community to come up with efficient methods for solving this vital problem, particularly for the Urdu language. The task is posed as a binary classification problem to label a given news article as a real or a fake news article. The organizers provide a dataset comprising news in five domains: (i) Health, (ii) Sports, (iii) Showbiz, (iv) Technology, and (v) Business, split into training and testing sets. The training set contains 1300 annotated news articles -- 750 real news, 550 fake news, while the testing set contains 300 news articles -- 200 real, 100 fake news. 34 teams from 7 different countries (China, Egypt, Israel, India, Mexico, Pakistan, and UAE) registered to participate in the UrduFake@FIRE2021 shared task. Out of those, 18 teams submitted their experimental results, and 11 of those submitted their technical reports, which is substantially higher compared to the UrduFake shared task in 2020 when only 6 teams submitted their technical reports. The technical reports submitted by the participants demonstrated different data representation techniques ranging from count-based BoW features to word vector embeddings as well as the use of numerous machine learning algorithms ranging from traditional SVM to various neural network architectures including Transformers such as BERT and RoBERTa. In this year's competition, the best performing system obtained an F1-macro score of 0.679, which is lower than the past year's best result of 0.907 F1-macro. Admittedly, while training sets from the past and the current years overlap to a large extent, the testing set provided this year is completely different.
A distinct approach to diagnose Dengue Fever with the help of Soft Set Theory
May 24, 2018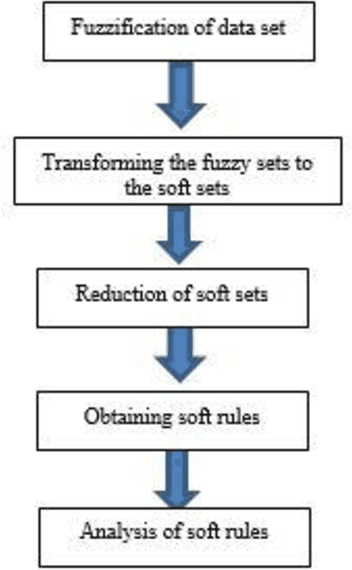
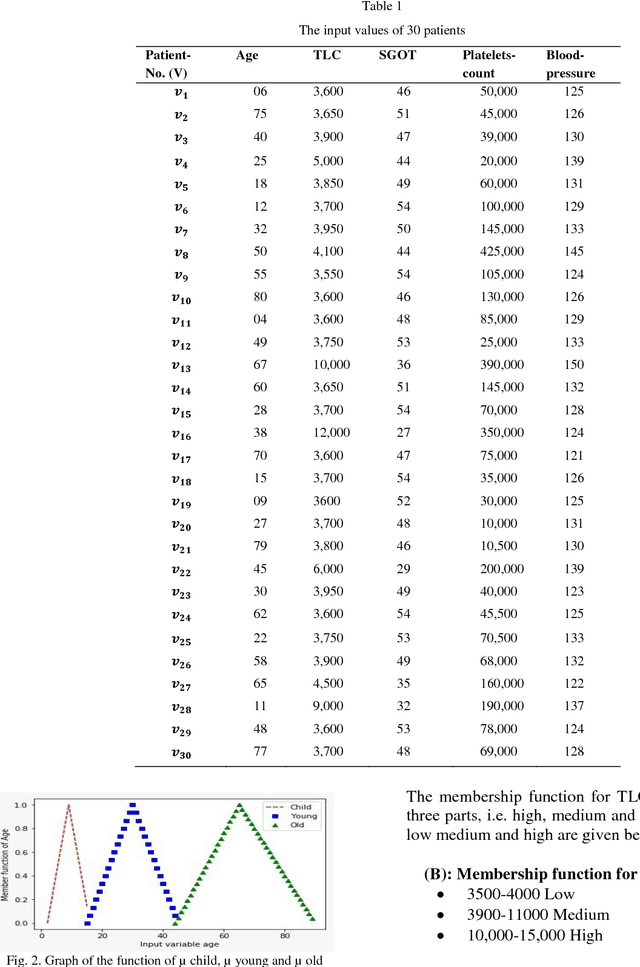
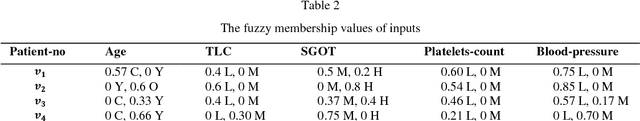
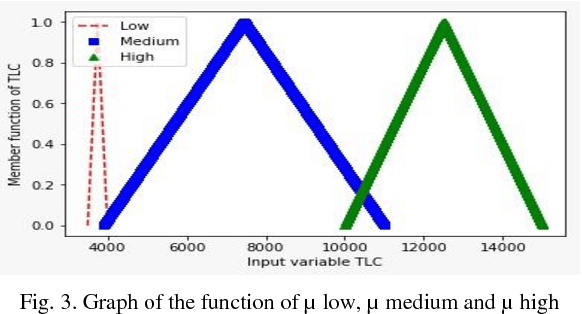
Abstract:Mathematics has played a substantial role to revolutionize the medical science. Intelligent systems based on mathematical theories have proved to be efficient in diagnosing various diseases. In this paper, we used an expert system based on soft set theory and fuzzy set theory named as a soft expert system to diagnose tropical disease dengue. The objective to use soft expert system is to predict the risk level of a patient having dengue fever by using input variables like age, TLC, SGOT, platelets count and blood pressure. The proposed method explicitly demonstrates the exact percentage of the risk level of dengue fever automatically circumventing for all possible (medical) imprecisions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge