Lukas R. Buschle
Exploring Optical Flow Inclusion into nnU-Net Framework for Surgical Instrument Segmentation
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Surgical instrument segmentation in laparoscopy is essential for computer-assisted surgical systems. Despite the Deep Learning progress in recent years, the dynamic setting of laparoscopic surgery still presents challenges for precise segmentation. The nnU-Net framework excelled in semantic segmentation analyzing single frames without temporal information. The framework's ease of use, including its ability to be automatically configured, and its low expertise requirements, have made it a popular base framework for comparisons. Optical flow (OF) is a tool commonly used in video tasks to estimate motion and represent it in a single frame, containing temporal information. This work seeks to employ OF maps as an additional input to the nnU-Net architecture to improve its performance in the surgical instrument segmentation task, taking advantage of the fact that instruments are the main moving objects in the surgical field. With this new input, the temporal component would be indirectly added without modifying the architecture. Using CholecSeg8k dataset, three different representations of movement were estimated and used as new inputs, comparing them with a baseline model. Results showed that the use of OF maps improves the detection of classes with high movement, even when these are scarce in the dataset. To further improve performance, future work may focus on implementing other OF-preserving augmentations.
SurgT challenge: Benchmark of Soft-Tissue Trackers for Robotic Surgery
Feb 28, 2023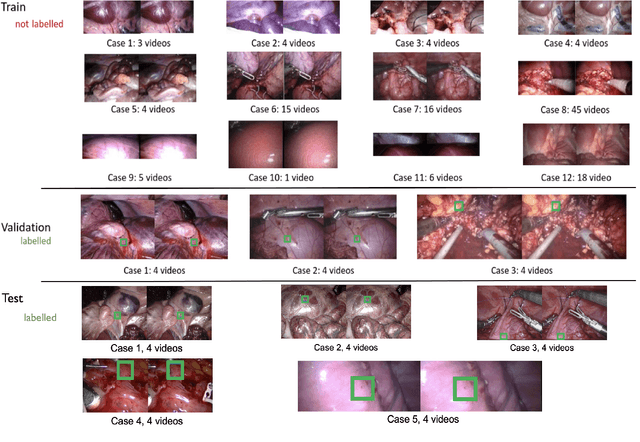
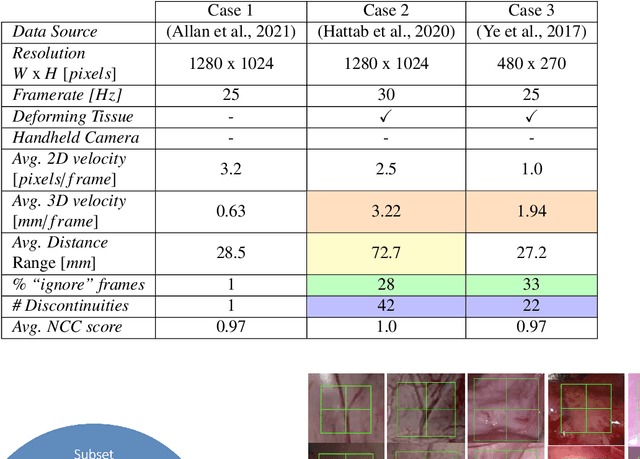
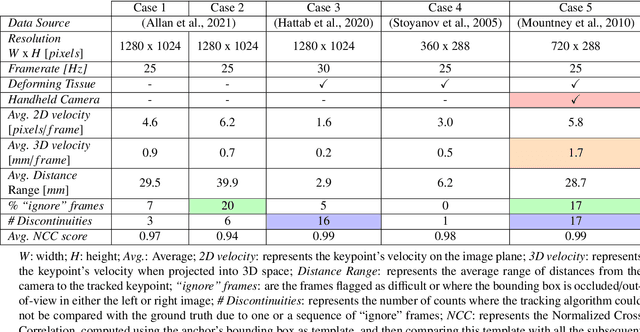
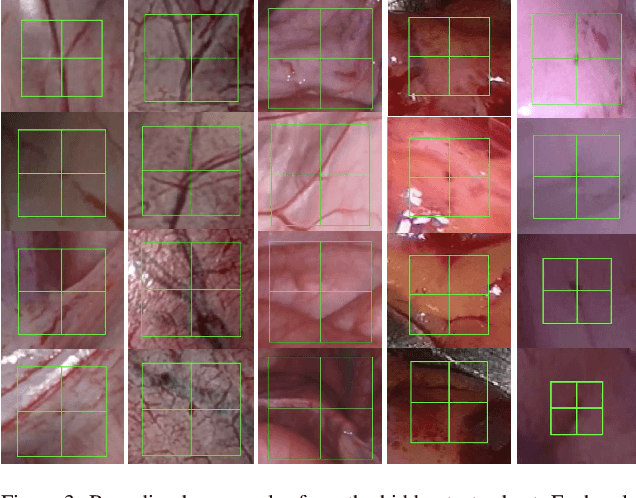
Abstract:This paper introduces the "SurgT: Surgical Tracking" challenge which was organised in conjunction with the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022). There were two purposes for the creation of this challenge: (1) the establishment of the first standardised benchmark for the research community to assess soft-tissue trackers; and (2) to encourage the development of unsupervised deep learning methods, given the lack of annotated data in surgery. A dataset of 157 stereo endoscopic videos from 20 clinical cases, along with stereo camera calibration parameters, have been provided. The participants were tasked with the development of algorithms to track a bounding box on stereo endoscopic videos. At the end of the challenge, the developed methods were assessed on a previously hidden test subset. This assessment uses benchmarking metrics that were purposely developed for this challenge and are now available online. The teams were ranked according to their Expected Average Overlap (EAO) score, which is a weighted average of the Intersection over Union (IoU) scores. The performance evaluation study verifies the efficacy of unsupervised deep learning algorithms in tracking soft-tissue. The best-performing method achieved an EAO score of 0.583 in the test subset. The dataset and benchmarking tool created for this challenge have been made publicly available. This challenge is expected to contribute to the development of autonomous robotic surgery and other digital surgical technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge