Longyin Zhang
Toward Real-World Chinese Psychological Support Dialogues: CPsDD Dataset and a Co-Evolving Multi-Agent System
Jul 10, 2025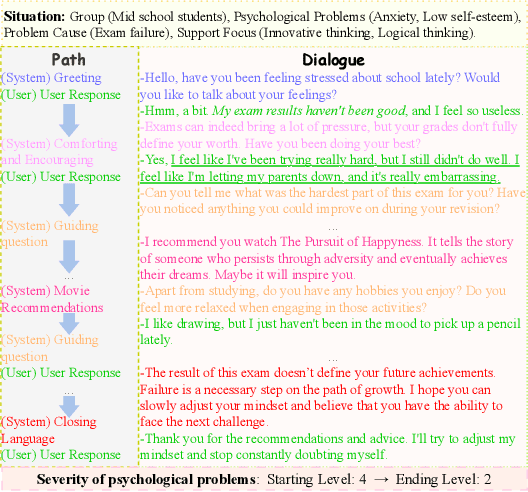
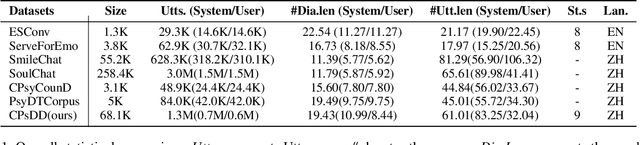
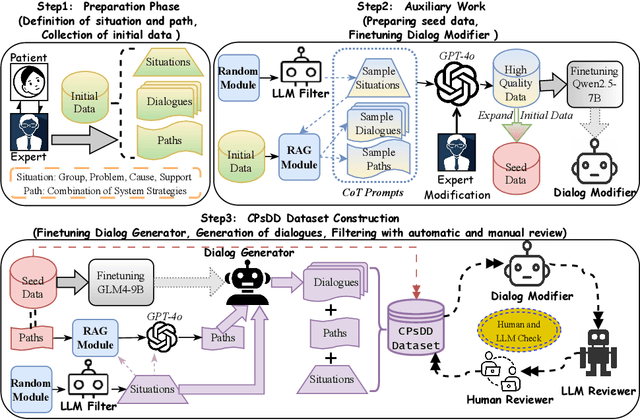
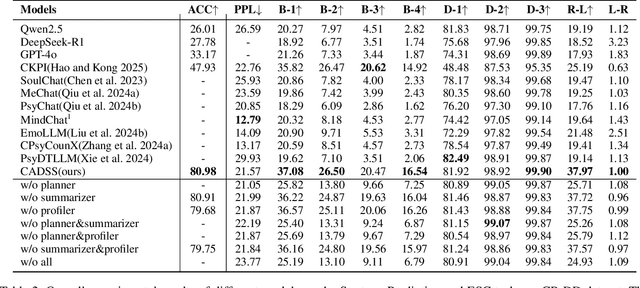
Abstract:The growing need for psychological support due to increasing pressures has exposed the scarcity of relevant datasets, particularly in non-English languages. To address this, we propose a framework that leverages limited real-world data and expert knowledge to fine-tune two large language models: Dialog Generator and Dialog Modifier. The Generator creates large-scale psychological counseling dialogues based on predefined paths, which guide system response strategies and user interactions, forming the basis for effective support. The Modifier refines these dialogues to align with real-world data quality. Through both automated and manual review, we construct the Chinese Psychological support Dialogue Dataset (CPsDD), containing 68K dialogues across 13 groups, 16 psychological problems, 13 causes, and 12 support focuses. Additionally, we introduce the Comprehensive Agent Dialogue Support System (CADSS), where a Profiler analyzes user characteristics, a Summarizer condenses dialogue history, a Planner selects strategies, and a Supporter generates empathetic responses. The experimental results of the Strategy Prediction and Emotional Support Conversation (ESC) tasks demonstrate that CADSS achieves state-of-the-art performance on both CPsDD and ESConv datasets.
Improving Multilingual Social Media Insights: Aspect-based Comment Analysis
May 29, 2025Abstract:The inherent nature of social media posts, characterized by the freedom of language use with a disjointed array of diverse opinions and topics, poses significant challenges to downstream NLP tasks such as comment clustering, comment summarization, and social media opinion analysis. To address this, we propose a granular level of identifying and generating aspect terms from individual comments to guide model attention. Specifically, we leverage multilingual large language models with supervised fine-tuning for comment aspect term generation (CAT-G), further aligning the model's predictions with human expectations through DPO. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in enhancing the comprehension of social media discourse on two NLP tasks. Moreover, this paper contributes the first multilingual CAT-G test set on English, Chinese, Malay, and Bahasa Indonesian. As LLM capabilities vary among languages, this test set allows for a comparative analysis of performance across languages with varying levels of LLM proficiency.
Multi-Hop Question Generation via Dual-Perspective Keyword Guidance
May 21, 2025Abstract:Multi-hop question generation (MQG) aims to generate questions that require synthesizing multiple information snippets from documents to derive target answers. The primary challenge lies in effectively pinpointing crucial information snippets related to question-answer (QA) pairs, typically relying on keywords. However, existing works fail to fully utilize the guiding potential of keywords and neglect to differentiate the distinct roles of question-specific and document-specific keywords. To address this, we define dual-perspective keywords (i.e., question and document keywords) and propose a Dual-Perspective Keyword-Guided (DPKG) framework, which seamlessly integrates keywords into the multi-hop question generation process. We argue that question keywords capture the questioner's intent, whereas document keywords reflect the content related to the QA pair. Functionally, question and document keywords work together to pinpoint essential information snippets in the document, with question keywords required to appear in the generated question. The DPKG framework consists of an expanded transformer encoder and two answer-aware transformer decoders for keyword and question generation, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our work, showcasing its promising performance and underscoring its significant value in the MQG task.
Discourse Cohesion Evaluation for Document-Level Neural Machine Translation
Aug 19, 2022



Abstract:It is well known that translations generated by an excellent document-level neural machine translation (NMT) model are consistent and coherent. However, existing sentence-level evaluation metrics like BLEU can hardly reflect the model's performance at the document level. To tackle this issue, we propose a Discourse Cohesion Evaluation Method (DCoEM) in this paper and contribute a new test suite that considers four cohesive manners (reference, conjunction, substitution, and lexical cohesion) to measure the cohesiveness of document translations. The evaluation results on recent document-level NMT systems show that our method is practical and essential in estimating translations at the document level.
Are Eliminated Spans Useless for Coreference Resolution? Not at all
Jan 04, 2021



Abstract:Various neural-based methods have been proposed so far for joint mention detection and coreference resolution. However, existing works on coreference resolution are mainly dependent on filtered mention representation, while other spans are largely neglected. In this paper, we aim at increasing the utilization rate of data and investigating whether those eliminated spans are totally useless, or to what extent they can improve the performance of coreference resolution. To achieve this, we propose a mention representation refining strategy where spans highly related to mentions are well leveraged using a pointer network for representation enhancing. Notably, we utilize an additional loss term in this work to encourage the diversity between entity clusters. Experimental results on the document-level CoNLL-2012 Shared Task English dataset show that eliminated spans are indeed much effective and our approach can achieve competitive results when compared with previous state-of-the-art in coreference resolution.
A Top-Down Neural Architecture towards Text-Level Parsing of Discourse Rhetorical Structure
May 21, 2020



Abstract:Due to its great importance in deep natural language understanding and various down-stream applications, text-level parsing of discourse rhetorical structure (DRS) has been drawing more and more attention in recent years. However, all the previous studies on text-level discourse parsing adopt bottom-up approaches, which much limit the DRS determination on local information and fail to well benefit from global information of the overall discourse. In this paper, we justify from both computational and perceptive points-of-view that the top-down architecture is more suitable for text-level DRS parsing. On the basis, we propose a top-down neural architecture toward text-level DRS parsing. In particular, we cast discourse parsing as a recursive split point ranking task, where a split point is classified to different levels according to its rank and the elementary discourse units (EDUs) associated with it are arranged accordingly. In this way, we can determine the complete DRS as a hierarchical tree structure via an encoder-decoder with an internal stack. Experimentation on both the English RST-DT corpus and the Chinese CDTB corpus shows the great effectiveness of our proposed top-down approach towards text-level DRS parsing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge