Long Vuong
Fantastic Targets for Concept Erasure in Diffusion Models and Where To Find Them
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Concept erasure has emerged as a promising technique for mitigating the risk of harmful content generation in diffusion models by selectively unlearning undesirable concepts. The common principle of previous works to remove a specific concept is to map it to a fixed generic concept, such as a neutral concept or just an empty text prompt. In this paper, we demonstrate that this fixed-target strategy is suboptimal, as it fails to account for the impact of erasing one concept on the others. To address this limitation, we model the concept space as a graph and empirically analyze the effects of erasing one concept on the remaining concepts. Our analysis uncovers intriguing geometric properties of the concept space, where the influence of erasing a concept is confined to a local region. Building on this insight, we propose the Adaptive Guided Erasure (AGE) method, which \emph{dynamically} selects optimal target concepts tailored to each undesirable concept, minimizing unintended side effects. Experimental results show that AGE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art erasure methods on preserving unrelated concepts while maintaining effective erasure performance. Our code is published at {https://github.com/tuananhbui89/Adaptive-Guided-Erasure}.
Erasing Undesirable Concepts in Diffusion Models with Adversarial Preservation
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models excel at generating visually striking content from text but can inadvertently produce undesirable or harmful content when trained on unfiltered internet data. A practical solution is to selectively removing target concepts from the model, but this may impact the remaining concepts. Prior approaches have tried to balance this by introducing a loss term to preserve neutral content or a regularization term to minimize changes in the model parameters, yet resolving this trade-off remains challenging. In this work, we propose to identify and preserving concepts most affected by parameter changes, termed as \textit{adversarial concepts}. This approach ensures stable erasure with minimal impact on the other concepts. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method using the Stable Diffusion model, showing that it outperforms state-of-the-art erasure methods in eliminating unwanted content while maintaining the integrity of other unrelated elements. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/tuananhbui89/Erasing-Adversarial-Preservation}.
On Learning Domain-Invariant Representations for Transfer Learning with Multiple Sources
Nov 27, 2021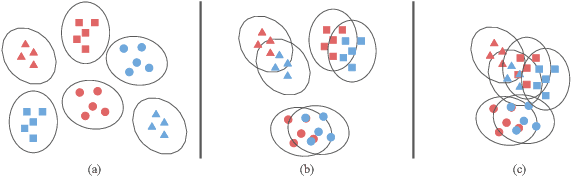
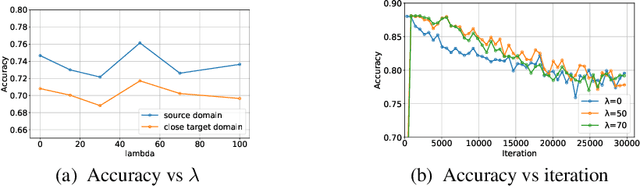
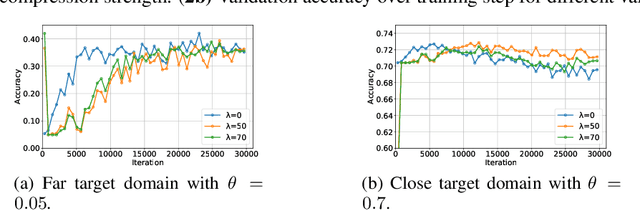
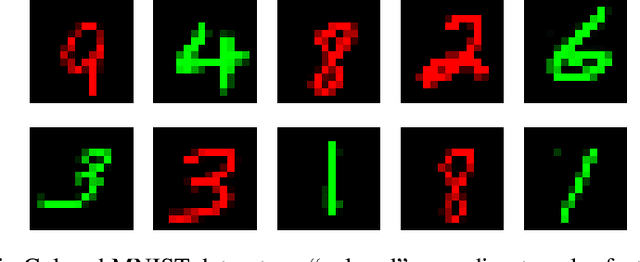
Abstract:Domain adaptation (DA) benefits from the rigorous theoretical works that study its insightful characteristics and various aspects, e.g., learning domain-invariant representations and its trade-off. However, it seems not the case for the multiple source DA and domain generalization (DG) settings which are remarkably more complicated and sophisticated due to the involvement of multiple source domains and potential unavailability of target domain during training. In this paper, we develop novel upper-bounds for the target general loss which appeal to us to define two kinds of domain-invariant representations. We further study the pros and cons as well as the trade-offs of enforcing learning each domain-invariant representation. Finally, we conduct experiments to inspect the trade-off of these representations for offering practical hints regarding how to use them in practice and explore other interesting properties of our developed theory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge