Linh Bao Doan
Online pseudo labeling for polyp segmentation with momentum networks
Sep 29, 2022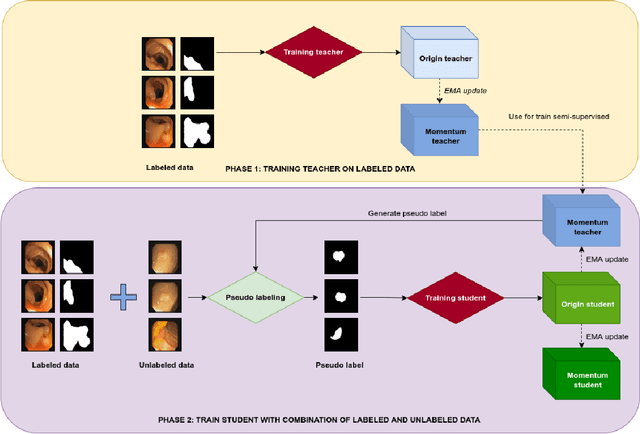

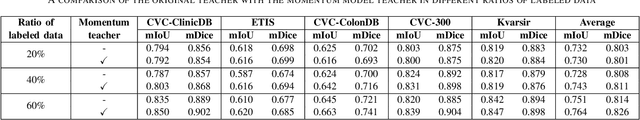
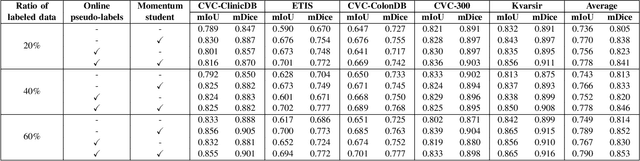
Abstract:Semantic segmentation is an essential task in developing medical image diagnosis systems. However, building an annotated medical dataset is expensive. Thus, semi-supervised methods are significant in this circumstance. In semi-supervised learning, the quality of labels plays a crucial role in model performance. In this work, we present a new pseudo labeling strategy that enhances the quality of pseudo labels used for training student networks. We follow the multi-stage semi-supervised training approach, which trains a teacher model on a labeled dataset and then uses the trained teacher to render pseudo labels for student training. By doing so, the pseudo labels will be updated and more precise as training progress. The key difference between previous and our methods is that we update the teacher model during the student training process. So the quality of pseudo labels is improved during the student training process. We also propose a simple but effective strategy to enhance the quality of pseudo labels using a momentum model -- a slow copy version of the original model during training. By applying the momentum model combined with re-rendering pseudo labels during student training, we achieved an average of 84.1% Dice Score on five datasets (i.e., Kvarsir, CVC-ClinicDB, ETIS-LaribPolypDB, CVC-ColonDB, and CVC-300) with only 20% of the dataset used as labeled data. Our results surpass common practice by 3% and even approach fully-supervised results on some datasets. Our source code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/sun-asterisk-research/online learning ssl
From Universal Language Model to Downstream Task: Improving RoBERTa-Based Vietnamese Hate Speech Detection
Feb 24, 2021Abstract:Natural language processing is a fast-growing field of artificial intelligence. Since the Transformer was introduced by Google in 2017, a large number of language models such as BERT, GPT, and ELMo have been inspired by this architecture. These models were trained on huge datasets and achieved state-of-the-art results on natural language understanding. However, fine-tuning a pre-trained language model on much smaller datasets for downstream tasks requires a carefully-designed pipeline to mitigate problems of the datasets such as lack of training data and imbalanced data. In this paper, we propose a pipeline to adapt the general-purpose RoBERTa language model to a specific text classification task: Vietnamese Hate Speech Detection. We first tune the PhoBERT on our dataset by re-training the model on the Masked Language Model task; then, we employ its encoder for text classification. In order to preserve pre-trained weights while learning new feature representations, we further utilize different training techniques: layer freezing, block-wise learning rate, and label smoothing. Our experiments proved that our proposed pipeline boosts the performance significantly, achieving a new state-of-the-art on Vietnamese Hate Speech Detection campaign with 0.7221 F1 score.
* Published in 2020 12th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE)
Interpreting the Latent Space of Generative Adversarial Networks using Supervised Learning
Feb 24, 2021
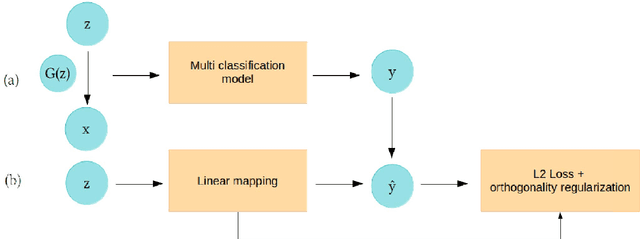


Abstract:With great progress in the development of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), in recent years, the quest for insights in understanding and manipulating the latent space of GAN has gained more and more attention due to its wide range of applications. While most of the researches on this task have focused on unsupervised learning method, which induces difficulties in training and limitation in results, our work approaches another direction, encoding human's prior knowledge to discover more about the hidden space of GAN. With this supervised manner, we produce promising results, demonstrated by accurate manipulation of generated images. Even though our model is more suitable for task-specific problems, we hope that its ease in implementation, preciseness, robustness, and the allowance of richer set of properties (compared to other approaches) for image manipulation can enhance the result of many current applications.
* Published in 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP)
Efficient Palm-Line Segmentation with U-Net Context Fusion Module
Feb 24, 2021
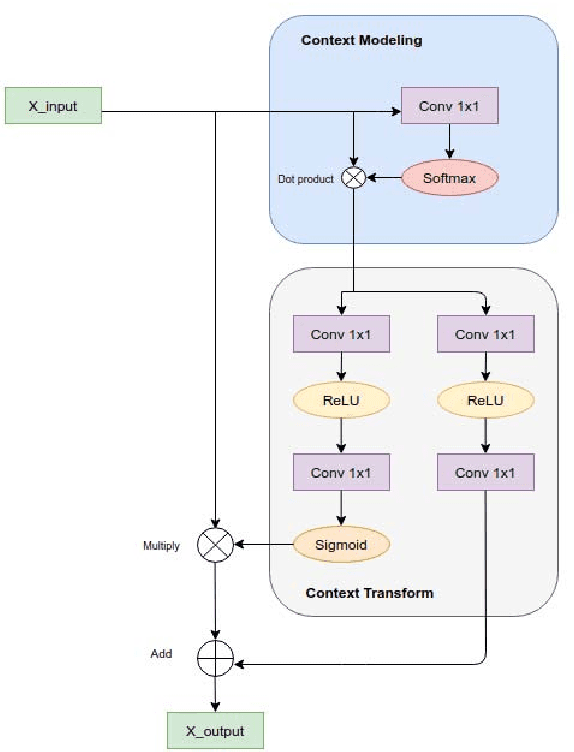
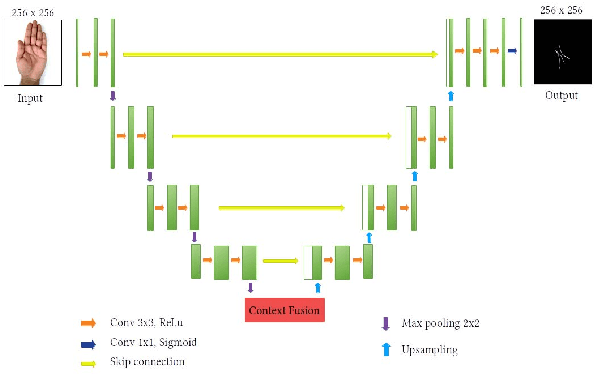

Abstract:Many cultures around the world believe that palm reading can be used to predict the future life of a person. Palmistry uses features of the hand such as palm lines, hand shape, or fingertip position. However, the research on palm-line detection is still scarce, many of them applied traditional image processing techniques. In most real-world scenarios, images usually are not in well-conditioned, causing these methods to severely under-perform. In this paper, we propose an algorithm to extract principle palm lines from an image of a person's hand. Our method applies deep learning networks (DNNs) to improve performance. Another challenge of this problem is the lack of training data. To deal with this issue, we handcrafted a dataset from scratch. From this dataset, we compare the performance of readily available methods with ours. Furthermore, based on the UNet segmentation neural network architecture and the knowledge of attention mechanism, we propose a highly efficient architecture to detect palm-lines. We proposed the Context Fusion Module to capture the most important context feature, which aims to improve segmentation accuracy. The experimental results show that it outperforms the other methods with the highest F1 Score about 99.42% and mIoU is 0.584 for the same dataset.
* Published in 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge