Ling Tang
Interpreting Emergent Extreme Events in Multi-Agent Systems
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large language model-powered multi-agent systems have emerged as powerful tools for simulating complex human-like systems. The interactions within these systems often lead to extreme events whose origins remain obscured by the black box of emergence. Interpreting these events is critical for system safety. This paper proposes the first framework for explaining emergent extreme events in multi-agent systems, aiming to answer three fundamental questions: When does the event originate? Who drives it? And what behaviors contribute to it? Specifically, we adapt the Shapley value to faithfully attribute the occurrence of extreme events to each action taken by agents at different time steps, i.e., assigning an attribution score to the action to measure its influence on the event. We then aggregate the attribution scores along the dimensions of time, agent, and behavior to quantify the risk contribution of each dimension. Finally, we design a set of metrics based on these contribution scores to characterize the features of extreme events. Experiments across diverse multi-agent system scenarios (economic, financial, and social) demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and provide general insights into the emergence of extreme phenomena.
AgentDoG: A Diagnostic Guardrail Framework for AI Agent Safety and Security
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The rise of AI agents introduces complex safety and security challenges arising from autonomous tool use and environmental interactions. Current guardrail models lack agentic risk awareness and transparency in risk diagnosis. To introduce an agentic guardrail that covers complex and numerous risky behaviors, we first propose a unified three-dimensional taxonomy that orthogonally categorizes agentic risks by their source (where), failure mode (how), and consequence (what). Guided by this structured and hierarchical taxonomy, we introduce a new fine-grained agentic safety benchmark (ATBench) and a Diagnostic Guardrail framework for agent safety and security (AgentDoG). AgentDoG provides fine-grained and contextual monitoring across agent trajectories. More Crucially, AgentDoG can diagnose the root causes of unsafe actions and seemingly safe but unreasonable actions, offering provenance and transparency beyond binary labels to facilitate effective agent alignment. AgentDoG variants are available in three sizes (4B, 7B, and 8B parameters) across Qwen and Llama model families. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that AgentDoG achieves state-of-the-art performance in agentic safety moderation in diverse and complex interactive scenarios. All models and datasets are openly released.
The Why Behind the Action: Unveiling Internal Drivers via Agentic Attribution
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are widely used in real-world applications such as customer service, web navigation, and software engineering. As these systems become more autonomous and are deployed at scale, understanding why an agent takes a particular action becomes increasingly important for accountability and governance. However, existing research predominantly focuses on \textit{failure attribution} to localize explicit errors in unsuccessful trajectories, which is insufficient for explaining the reasoning behind agent behaviors. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel framework for \textbf{general agentic attribution}, designed to identify the internal factors driving agent actions regardless of the task outcome. Our framework operates hierarchically to manage the complexity of agent interactions. Specifically, at the \textit{component level}, we employ temporal likelihood dynamics to identify critical interaction steps; then at the \textit{sentence level}, we refine this localization using perturbation-based analysis to isolate the specific textual evidence. We validate our framework across a diverse suite of agentic scenarios, including standard tool use and subtle reliability risks like memory-induced bias. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework reliably pinpoints pivotal historical events and sentences behind the agent behavior, offering a critical step toward safer and more accountable agentic systems.
DecIF: Improving Instruction-Following through Meta-Decomposition
May 20, 2025Abstract:Instruction-following has emerged as a crucial capability for large language models (LLMs). However, existing approaches often rely on pre-existing documents or external resources to synthesize instruction-following data, which limits their flexibility and generalizability. In this paper, we introduce DecIF, a fully autonomous, meta-decomposition guided framework that generates diverse and high-quality instruction-following data using only LLMs. DecIF is grounded in the principle of decomposition. For instruction generation, we guide LLMs to iteratively produce various types of meta-information, which are then combined with response constraints to form well-structured and semantically rich instructions. We further utilize LLMs to detect and resolve potential inconsistencies within the generated instructions. Regarding response generation, we decompose each instruction into atomic-level evaluation criteria, enabling rigorous validation and the elimination of inaccurate instruction-response pairs. Extensive experiments across a wide range of scenarios and settings demonstrate DecIF's superior performance on instruction-following tasks. Further analysis highlights its strong flexibility, scalability, and generalizability in automatically synthesizing high-quality instruction data.
Towards the Resistance of Neural Network Watermarking to Fine-tuning
May 02, 2025
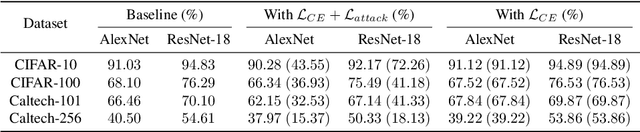

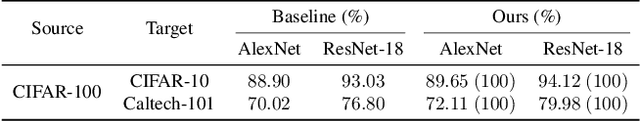
Abstract:This paper proves a new watermarking method to embed the ownership information into a deep neural network (DNN), which is robust to fine-tuning. Specifically, we prove that when the input feature of a convolutional layer only contains low-frequency components, specific frequency components of the convolutional filter will not be changed by gradient descent during the fine-tuning process, where we propose a revised Fourier transform to extract frequency components from the convolutional filter. Additionally, we also prove that these frequency components are equivariant to weight scaling and weight permutations. In this way, we design a watermark module to encode the watermark information to specific frequency components in a convolutional filter. Preliminary experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
CIMFlow: An Integrated Framework for Systematic Design and Evaluation of Digital CIM Architectures
May 02, 2025Abstract:Digital Compute-in-Memory (CIM) architectures have shown great promise in Deep Neural Network (DNN) acceleration by effectively addressing the "memory wall" bottleneck. However, the development and optimization of digital CIM accelerators are hindered by the lack of comprehensive tools that encompass both software and hardware design spaces. Moreover, existing design and evaluation frameworks often lack support for the capacity constraints inherent in digital CIM architectures. In this paper, we present CIMFlow, an integrated framework that provides an out-of-the-box workflow for implementing and evaluating DNN workloads on digital CIM architectures. CIMFlow bridges the compilation and simulation infrastructures with a flexible instruction set architecture (ISA) design, and addresses the constraints of digital CIM through advanced partitioning and parallelism strategies in the compilation flow. Our evaluation demonstrates that CIMFlow enables systematic prototyping and optimization of digital CIM architectures across diverse configurations, providing researchers and designers with an accessible platform for extensive design space exploration.
Defects of Convolutional Decoder Networks in Frequency Representation
Oct 17, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we prove representation bottlenecks of a cascaded convolutional decoder network, considering the capacity of representing different frequency components of an input sample. We conduct the discrete Fourier transform on each channel of the feature map in an intermediate layer of the decoder network. Then, we introduce the rule of the forward propagation of such intermediate-layer spectrum maps, which is equivalent to the forward propagation of feature maps through a convolutional layer. Based on this, we find that each frequency component in the spectrum map is forward propagated independently with other frequency components. Furthermore, we prove two bottlenecks in representing feature spectrums. First, we prove that the convolution operation, the zero-padding operation, and a set of other settings all make a convolutional decoder network more likely to weaken high-frequency components. Second, we prove that the upsampling operation generates a feature spectrum, in which strong signals repetitively appears at certain frequencies.
Batch Normalization Is Blind to the First and Second Derivatives of the Loss
Jun 02, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we prove the effects of the BN operation on the back-propagation of the first and second derivatives of the loss. When we do the Taylor series expansion of the loss function, we prove that the BN operation will block the influence of the first-order term and most influence of the second-order term of the loss. We also find that such a problem is caused by the standardization phase of the BN operation. Experimental results have verified our theoretical conclusions, and we have found that the BN operation significantly affects feature representations in specific tasks, where losses of different samples share similar analytic formulas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge