Lilin Wang
SWE-Bench++: A Framework for the Scalable Generation of Software Engineering Benchmarks from Open-Source Repositories
Dec 19, 2025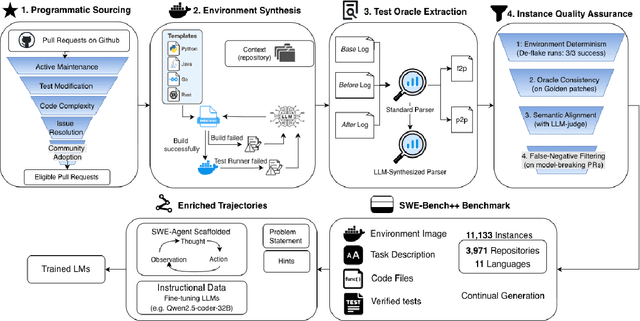


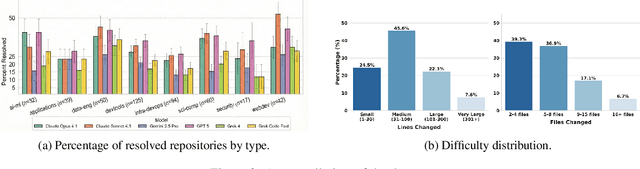
Abstract:Benchmarks like SWE-bench have standardized the evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) on repository-level software engineering tasks. However, these efforts remain limited by manual curation, static datasets, and a focus on Python-based bug fixes. We introduce SWE-Bench++, an automated framework that generates repository-level coding tasks from open-source GitHub projects. Unlike synthetic approaches, our pipeline harvests live pull requests to cover both bug fixes and feature requests across 11 languages. SWE-Bench++ turns GitHub pull requests (PRs) into reproducible, execution-based tasks via four stages: programmatic sourcing, environment synthesis, test oracle extraction, and quality assurance. A final hint-guided trajectory synthesis step converts instances that strong models fail on into training trajectories. Our initial benchmark consists of 11,133 instances from 3,971 repositories across 11 languages. On a subset of 1,782 instances of this benchmark, today's strongest models perform as follows: claude-sonnet-4.5 achieves 36.20% pass@10, gpt-5-2025-08-07 34.57%, gemini/gemini-2.5-pro 24.92%, and gpt-4o 16.89%. We further demonstrate the utility of our dataset by showing that fine-tuning on SWE-Bench++ instances yields measurable improvements on the SWE-bench Multilingual benchmark. SWE-Bench++ provides a scalable, multilingual benchmark for evaluating and improving repository-level code generation.
Guardians of Discourse: Evaluating LLMs on Multilingual Offensive Language Detection
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Identifying offensive language is essential for maintaining safety and sustainability in the social media era. Though large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated encouraging potential in social media analytics, they lack thorough evaluation when in offensive language detection, particularly in multilingual environments. We for the first time evaluate multilingual offensive language detection of LLMs in three languages: English, Spanish, and German with three LLMs, GPT-3.5, Flan-T5, and Mistral, in both monolingual and multilingual settings. We further examine the impact of different prompt languages and augmented translation data for the task in non-English contexts. Furthermore, we discuss the impact of the inherent bias in LLMs and the datasets in the mispredictions related to sensitive topics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge