Liangkai Zhou
Distributed Dynamic Map Fusion via Federated Learning for Intelligent Networked Vehicles
Mar 05, 2021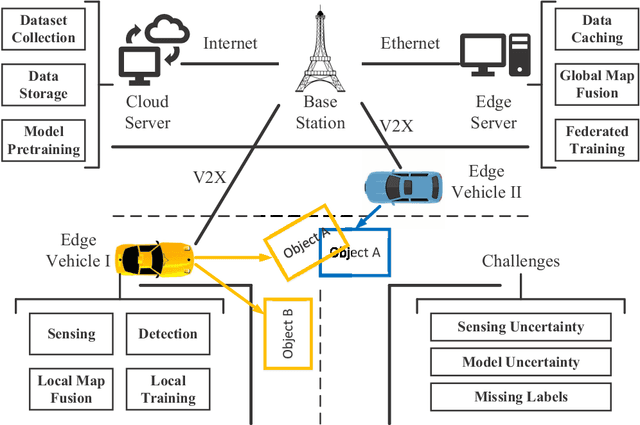



Abstract:The technology of dynamic map fusion among networked vehicles has been developed to enlarge sensing ranges and improve sensing accuracies for individual vehicles. This paper proposes a federated learning (FL) based dynamic map fusion framework to achieve high map quality despite unknown numbers of objects in fields of view (FoVs), various sensing and model uncertainties, and missing data labels for online learning. The novelty of this work is threefold: (1) developing a three-stage fusion scheme to predict the number of objects effectively and to fuse multiple local maps with fidelity scores; (2) developing an FL algorithm which fine-tunes feature models (i.e., representation learning networks for feature extraction) distributively by aggregating model parameters; (3) developing a knowledge distillation method to generate FL training labels when data labels are unavailable. The proposed framework is implemented in the Car Learning to Act (CARLA) simulation platform. Extensive experimental results are provided to verify the superior performance and robustness of the developed map fusion and FL schemes.
Learning Centric Wireless Resource Allocation for Edge Computing: Algorithm and Experiment
Oct 29, 2020
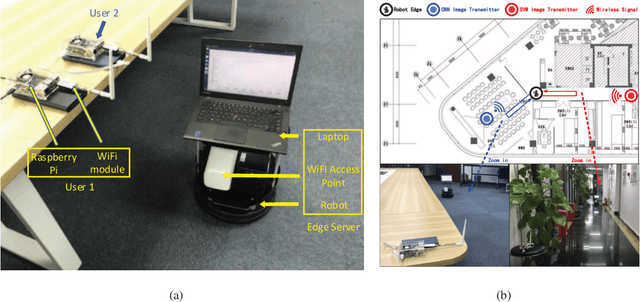


Abstract:Edge intelligence is an emerging network architecture that integrates sensing, communication, computing components, and supports various machine learning applications, where a fundamental communication question is: how to allocate the limited wireless resources (such as time, energy) to the simultaneous model training of heterogeneous learning tasks? Existing methods ignore two important facts: 1) different models have heterogeneous demands on training data; 2) there is a mismatch between the simulated environment and the real-world environment. As a result, they could lead to low learning performance in practice. This paper proposes the learning centric wireless resource allocation (LCWRA) scheme that maximizes the worst learning performance of multiple classification tasks. Analysis shows that the optimal transmission time has an inverse power relationship with respect to the classification error. Finally, both simulation and experimental results are provided to verify the performance of the proposed LCWRA scheme and its robustness in real implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge